•Initially cells of mesodermal germ layer forms a thin sheet of loosely woven tissue on each side of midline.
- Paraxial mesoderm
- Intermediate mesoderm
- Lateral plate mesoderm
PARAXIAL MESODERM
•Begins to organize into segments – SOMITOMERES (Cephalocaudally) •Mesodermal cells are arranged in concentric whorls around a small cavity. •Form in association with neuromeres in the head region.
•SOMITES (from occipital region caudally)
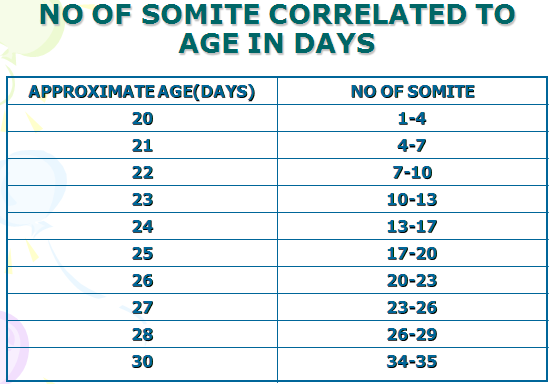
•First pair appear at about 20th day
–in craniocaudal sequence @ 3 pairs per day
–Estimation of age
–at the end of 5th week 42 – 44 pairs
- 4 occipital
- 8 cervical
- 12 thoracic
- 5 lumbar
- 5 sacral
- 8- 10 coccygeal
•By the beginning of the 4th week, cells forming the ventral and medial walls of the somite, loose their compact organization and become polymorphous, shift and surround the notochord.
These cells are collectively known as sclerotome and form a loosely woven tissue, the mesenchyme.
•Some of these cells form tendons where as the remainder surround the spinal cord and notochord to form vertebral column.
•Cells at the dorsolateral portion of the somite migrate as precursors of the limb and body wall musculature.
•Cells at the dorsomedial portion of the somite proliferate and migrate down the ventral side to form a new layer, the myotome.
•The remaining dorsal epithelium forms the dermatome and together these layers constitute the dermamyotome.
SOMITES
Each somite forms its own:
•Sclerotome – tendon, cartilage & bone component
•Myotome– providing the segmental muscle component (muscles of back) •Dermatome– segmental skin component (dermis & subcutaneous tissue of skin)
•Nerve component
THE INTERMEDIATE MESODERM
The intermediate mesoderm forms:
- Nephrotomes cranially
- Nephrogenic cord caudally
both developing into the excretory units of kidneys, gonads, ducts and accessory glands.
LATERAL PLATE MESODERM
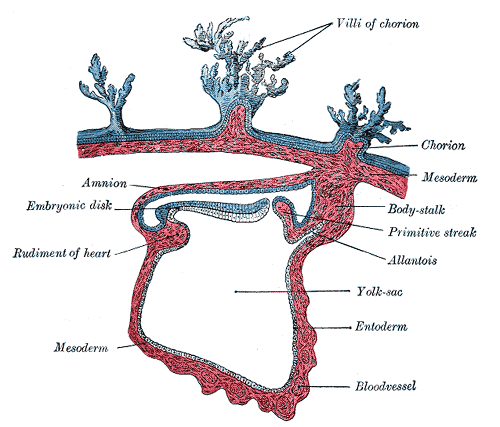
1.A layer continuous with mesoderm covering the amnion (somatic/parietal mesodermal layer)
2. A layer continuous with mesoderm covering the yolk sac (Splanchnic/visceral mesodermal layer)
•Together these layers line a newly formed cavity the intraembryonic coelom
•PARIETAL & VISCERAL LAYERS
–Parietal mesoderm with ectoderm
– lateral & ventral body wall –Visceral mesoderm & endoderm – wall of gut
•Mesoderm cells of the parietal layer surrounding the intraembryonic cavity will form mesothelial membranes or serous membranes which will line the peritoneal, pleural and pericardial cavities and secrete serous fluid. •Mesoderm cells of the visceral layer will form a thin serous membrane around each organ.
BLOOD AND BLOOD VESSELS
Blood vessels form in two ways:
•Vasculogenesis –Blood vessels arise from blood islands
•Angiogenesis –Blood vessels form by sprouting from existing vessels.
•During 3rd week of development islands appear first in the mesoderm surrounding the yolk sac and later in the lateral plate mesoderm.
•Hemangioblast is the common precursors for vessel and blood formation) induced by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) secreted by surrounding mesoderm.
•Hemangioblasts in the centre of blood island form hematopoeitic stem cells (precursors of all blood cells) whereas peripheral hemangioblasts differentiate into angioblasts (precursor to blood vessel).
•Once the process of vasculogenesis establishes a primary bed, additional vasculature is added by angiogenesis.
SITES OF HAEMOPOESIS:
•Blood islands of yolk sac
• Aorta-Gonad-Mesonephros region (AGM)
• Liver
• Bone marrow
MESODERM – DERIVATIVES
- SUPPORTING TISSUE- CONNECTIVE TISSUE,CARTILAGE & BONE
- STRIATED & SMOOTH MUSCULATURE
- BLOOD & LYMPH CELLS, WALLS OF HEART, BLOOD & LYMPH VESSELS
- KIDNEYS, GONADS & THEIR CORRESPONDING DUCTS
- CORTICAL PORTION OF ADRENAL GLAND
- SPLEEN
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself


Nice effort.realy i appreciate it.thanx