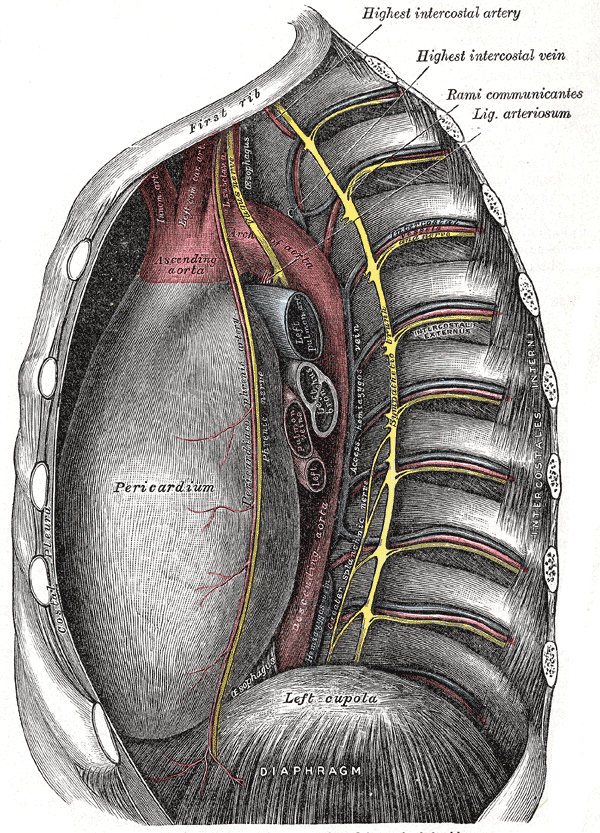
The anterior rami of the first eleven thoracic spinal nerves are known as the intercostal nerves, while that of the twelfth thoracic nerve is known as the subcostal nerve and runs forward in the abdominal wall.
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
Course of Intercostal Nerves:
The intercostal nerves enter into the intercostal spaces lying between the parietal pleura and the posterior intercostal membrane. They, then run forward, lying beneath the intercostal arteries and veins in the subcostal groove. Here they lie between the innermost intercostal and the internal intercostal muscles.
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
The first six intercostal nerves supply their own intercostal spaces.
The seventh to ninth intercostal nerves enter the anterior abdominal wall by passing deep to the costal cartilages.
The tenth and eleventh intercostal nerves pass directly into the abdomen because the corresponding ribs are floating ribs.
Branches:
1. Collateral branch:
Collateral branch runs on the upper border of the rib below lying inferior to the main nerve.
2. Rami communicantes:
Rami communicantes form a link between the intercostal nerves and the sympathetic trunk.
3. Anterior cutaneous branch:
Anterior cutaneous branch reaches the skin near the midline and divides into medial and lateral branches. It is the terminal portion of the main trunk.
4. Lateral cutaneous branch:
The lateral cutaneous branch reaches the lateral side of the chest. It also divides into an anterior and a posterior branch.
5. Muscular branches:
Muscular branches supply the intercostal muscles.
6. Pleural sensory branches:
Pleural sensory branches supply the parietal pleura.
7. Peritoneal sensory branches:
Peritoneal sensory branches supply the parietal peritoneum. These nerves arise from the seventh to eleventh intercostal nerves.
The branches of first and second intercostal nerves are special and are explained below:
First Intercostal Nerve:
A branch of brachial plexus, equivalent to the lateral cutaneous branch, joins the first intercostal nerve. There is no anterior cutaneous branch and the remainder of the first intercostal nerve is small.
Second Intercostal Nerve:
The medial cutaneous nerve of the arm joins the second intercostal nerve by a branch known as the intercostobrachial nerve, equivalent to the lateral cutaneous nerves of the the other intercostal nerves. The skin of the arm pit and the upper medial side of the arm is, therefore, supplied by the second intercostal nerve. This is the reason as to why the pain in the coronary artery disease is referred along the nerve to the medial side of the arm.
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
Apart from these, the skin, parietal pleura, covering the outer and inner aspects of each intercostal spaces, intercostal muscles, levatores costarum and the serratus posterior muscles are supplied by the first six intercostal nerves.
The skin, parietal peritoneum covering the outer and inner aspects of the abdominal wall, the anterior abdominal muscles ( external oblique, internal oblique, transversus abdominis and rectus abdominis) are supplied by the seventh to eleventh intercostal nerves.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself