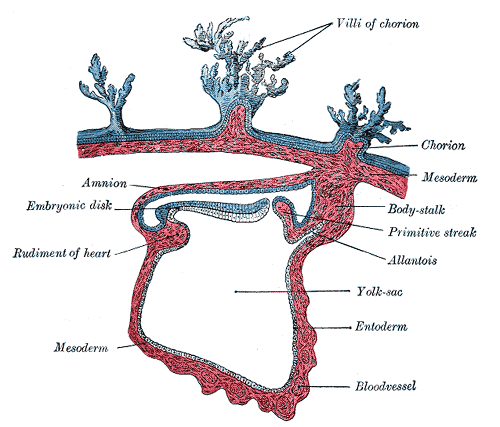
The endoderm germ layer covers the ventral surface of the embryo forming the roof of the yolk sac. The GIT is the main organ system derived from the endodermal germ layer.
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
Folding of the embryo consists of two parts:
1. Cephalocaudal folding, occuring in the median plane caused by rapid longitudinal growth of central nervous system.
2. Lateral folding, occuring in the horizontal plane caused by rapidly growing somites.
Cephalocaudal Folding:
When the brain vesicles are developed, the embryonic disc begins to bulge into the amniotic cavity and begins to fold cephalocaudally. As a result, head fold and tail fold appears.
Head fold:
The cranial region of the embryonic disc, from caudal to cranial contains:
a. The buccopharyngeal membrane
b. The cardiogenic area
c. Septum transversum
The cranial rim of the disc folds under the cephalic neural plate, wedging the septum transversum between the heart region and the yolk sac. Thus placing the cardiogenic area and the buccopharyngeal membrane in the future thoracic and mouth regions, respectively.
Tail fold:
In the 4th week buccopharyngeal membrane ruptures and an open communication is established between amniotic cavity and the primitive gut. Cloacal membrane breaks down in the 7th week to create the opening for the anus. The mid gut remains in communication with the yolk sac though vitelline duct.
Lateral Folding:
Initial flat embryonic disc also folds laterally and embryo obtains round appearance As a result of this folding:
1. The ventral body wall is established except where yolk sac duct and connecting stalk are attached
2. When vitelline duct is obliterated, only then does the midgut looses its connection with original endoderm lined cavity and obtain its free position in abdominal cavity.
3. Partial incorporation of allantois into body of embryo takes place where it forms cloaca while its distal portion remains in connecting stalk.
4. By 5th week yolk sac duct, allantois, and umblical vessels are restricted to the region of umblical ring.
Derivatives of Endodermal Germ Layer:
The derivatives of the endodermal germ layer include:
1. Epithelial lining of:
a. Primitive gut
b. Allantois & vitelline duct
c. Respiratory tract
e. Tympanic cavity & auditory tube
2. Parenchyma of thyroid, parathyroids, liver & pancreas
3. Reticular stroma of tonsils & thymus
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself


I M THE FIRST ONE COMMITING HERE …..TOMORROW IS MY PAPER AND I GOT THESE DERIVATIVES FOR MY PAPER PREPARATION:)