Folic acid is composed of 3 subunits
- Pteridine
- Para aminobenzoic acid
- Glutamic acid residues –attached to pteryl portion forming monoglutamate, triglutamate, polyglutamate
Pharmacokinetics
50-200 micrograms are absorbed from dietary folic acid (i.e. 500-700 micrograms/day)
5-20 mg folates are stored in liver and other tissues.
Absorption
In diet it occurs in polyglutamate form, and has to be converted to monoglutamate form for absorption (hydrolyzed by a-L-glutamyl transferrase).
In our diet, it is obtained from meat, eggs, liver and green leafy vegetables like spinach.
This is why overcooking of food usually destroys folic acid. It is also synthesized by our gut flora, but that is largely unavailable for absorption.
Folic acid is absorbed in proximal portion of small intestine and transported in plasma as methyl tetrahydrofolate form both by active and passive transport. It is widely distributed. Once it enters the cells, it is converted to tetrahydrofolic acid by demethylation that requires vit B12.
Transport
Bound to plasma proteins.
Catabolism & Excretion
The catabolism and elimination of vitamin B9 is more than vitamin B12, and hepatic stores are sufficient for 1-3 months. (B12 up to 5 years)
Hepatic stores
In cells it is stored in polyglutamate form and total body folate stores are about 5-10 mg. this folic acid is essential for synthesis of amino acids, purines and DNA.
Pharmacodynamics:
Reduced forms are required for the synthesis of:
- Amino acids
- Purines
- DNA
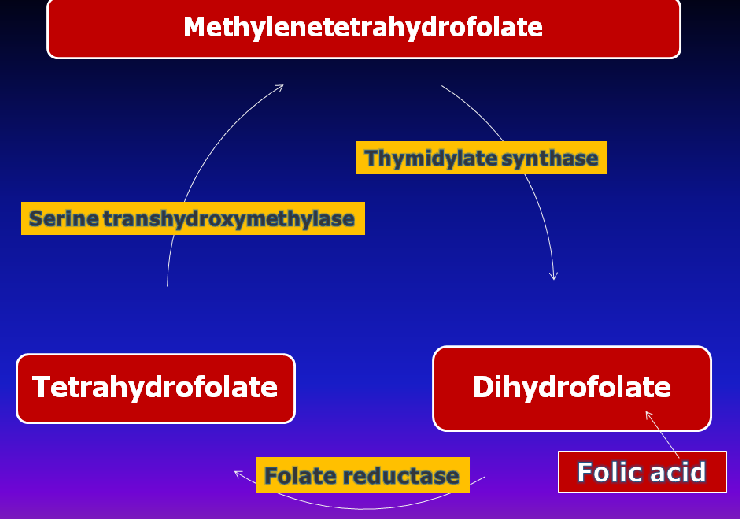
In presence of folate reductase, methyl cobalamine is converted into tetrahydrofolate, otherwise it is known as methylcolbalamine trap.
Methyl tetrahydrofolate is required for synthesis of purines. Serine is converted to glycine by conversion of tetrahydrofolate to methylenetetrahydrofolate.
During conversion of methylenetetrahydrofolate to dihydrofolate, deoxy uridine monophosphate (dUMP) is converted into deoxy thymidine monophosphate (dTMP), leading to DNA synthesis.
The combined catalytic activity of the above mentioned three enzymes is known as dTMP synthesis cycle.
2 important anti-cancer drugs act at this cycle:
- Methotrexate inhibits folate reductase
- 5-fluorouracil inhibits thymidylate synthase
As cancer cells are rapidly dividing, DNA synthesis is impaired.
When DNA synthesis is impaired, in blood RBC synthesis is impaired, giving megaloblastic picture (megakaryocytes).
Deficiency of Folic Acid
Deficiency causes megaloblastic anemia that is indistinguishable from that caused by vitamin B12 deficiency (not associated neurological disorders)
Diagnosis
Diagnosed by measuring:
- Serum folic acid levels –do not reflect tissue levels
- RBCs folic acid levels (greater diagnostic value)
Folic acid deficiency is seen in:
- Inadequate dietary intake of folates
- Prolong cooking
- In alcoholics
- Liver diseases
- Pregnancy
- Hemolytic Anemias
- Malabsorption Syndrome
- Occasionally associated with cancers, Leukemias
- Skin disorders
- Renal failure
- Drugs interfering with folate absorption or metabolism e.g. Phenytion, carbamazapines, Trimethoprim, Methotrexate, pyrimethamine.
Manifestations of deficiency
- Megaloblastic anemia
- Signs and symptoms of epithelial damage
- Glossitis
- Anthritis
- Diarrhea
- Neural Tube defect
- If deficiency occurs during pregnancy –spina bifida
General manifestations of weight loss and weakness.
Treatment of Folic Acid Deficiency
Parenteral administration is rarely needed.
Oral therapy Dose
1mg/day – continued until underlying cause is corrected or removed.
Adverse effects
Very rare. Only a few allergic manifestations have been reported.
Uses
- Treatment of megaloblastic anemia
- Prophylaxis of megaloblastic anemia
- Also given in methotrexate toxicity. Toxicity is in form of encephalopathy. Folic acid is not given, rather reduced form of folic acid 5-formyl tetrahydrofolate, also known as Leucovorin/citrovorum, but has to be given within an hour of toxicity. This should not be delayed.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself