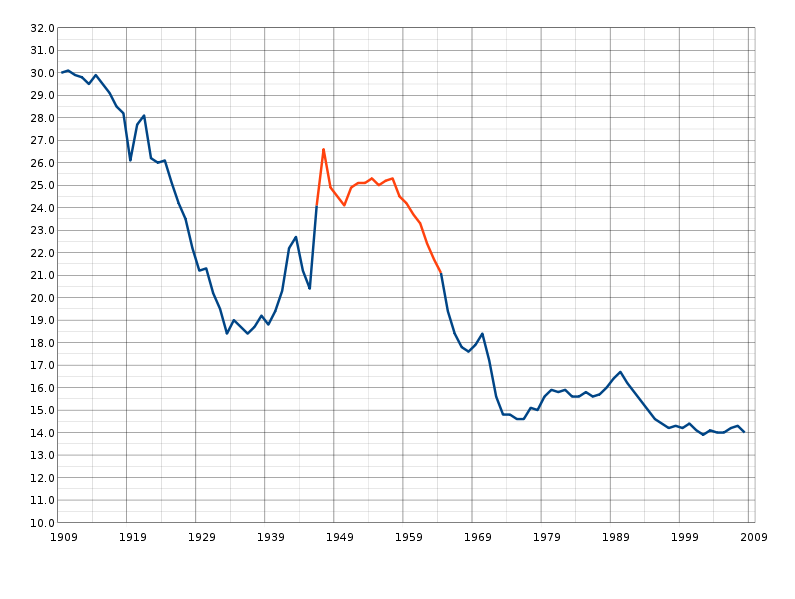
Trial is from the French ‘trier’ (to try). Trial may be:
• Clinical trial –in which we apply therapeutic interventions to sick individuals (e.g., chemotherapy trial)
• Field trial – in which we apply preventive interventions to healthy individuals (e.g., vaccine trial)
• Community trial – in which we apply interventions to aggregate units (e.g., fluoridation of public water)
Need for Non Randomized Trials
• When randomized controlled trial is not possible on ethical or administrative grounds
• When preventive measures can be applied on community basis
• When disease frequency is low and natural history is long
• When cost and logistic is limited
Types
1. Un controlled Trials
Trials with no comparison group. Experience of earlier untreated patients affected by the same disease is taken into account.
2. Natural Experiments
Natural division into two groups e.g. smoker & nonsmoker, migrants & natives, religious and social groups.
3. Before & after Comparison Studies
Without Control: Comparing the incidence of disease before and after introduction of a preventive measure
With Control: Preventive program is to be applied on entire community, another community is selected as control.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself