Classification of louse
Phylum : Arthropoda
Class : Insecta
Order : Anoplura
Family : Pediculidae
Species: 1. Body louse (pediculus humanus
2. Head louse (pediculus capitis)
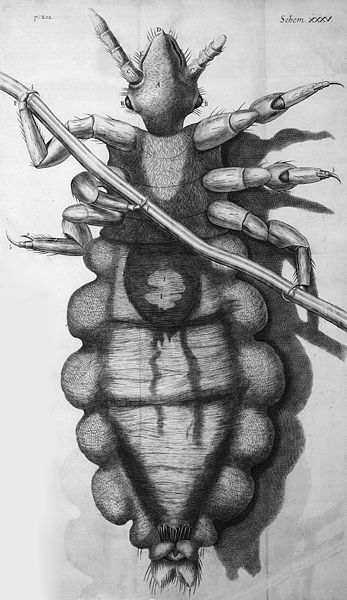 Habit of Louse
Habit of Louse
Distribution: Louse occur in all parts of the world especially colder climate regions are more affected.
Bites:Both the sexes suck the blood from mammals and birds. They bite severely and are annoying pest.
Feeding: Louse is permanently active parasite found in hairs, cloths and on the body of the host.
Dispersal: Louse is wingless insect and disperses by close contact, overcrowding. Louse may also be acquired from clothing, bedding and using comb of infested person.
Life period: Under favorable environmental conditions adult louse live from 30-50 days.
Medical importance: louse are vectors of epidemic typhus, relapsing fever, pediculosis, trench fever and dermatitis.
General characters of louse
Louse is a small, wingless insects of mammals and birds. The head and body lice differ very little in structure except in their habitat.
Head: The head bears a 5 segmented antenna. The mouth parts are adapted for sucking blood.
Thorax: Three pairs of legs are attached ventrally to the thorax. The legs are strongly developed and are provided with claws which help the insect to cling to their hairs and clothing.
Abdomen: The abdomen consist of 9 segments. The last abdominal segment is pointed in case of male and bilobed in case of female.
Life cycle of louse
There are three stages in the life cycle of louse. Metamorphosis is incomplete.
Eggs: The eggs are laid singly or in groups. They are firmly attached to the hairs or seams of clothing by cemented substance. Eggs are small, pointed at one end and white in color. The female lays up to 300 eggs at the rate of 4-9 a day. Under favorable environmental conditions of temperature, the eggs will hatch in 6-9 days. The eggs will not hatch if the temperature is below 22 c.
Nymph: The nymph looks like the adult except for its smaller size. It feeds on host and develops into adult. The nymph stage may take 10-15 days.
Adult : The entire life cycle from egg to adult takes about 15-17 days under favorable conditions. Adult louse lives from 30 -60 days. If unfed lice are kept away from their host they will die within 2-5 days. Blood fed louse may survive up to 10 days. Heavily infested person have 400-500 louse on their head and clothes.
Dissemination of Lice
- Direct Contact: Lice are disseminated by close contact with lousy or infested persons. Overcrowding provides an excellent opportunity for the direct transference of lice from one person to another. Children get easily infested at school when their heads come together at work or play.
- Indirect Contact: Lice may also be acquired from clothing, bedding, combs or brushes used by lousy persons. Lice have been seen to leave the host whose temperature rises above or falls below the normal.
Control measures
Insecticidal control: The present recommended treatment is of lotion containing o.5% malathian . The lotion should be left for 24 hours, then the hair can be washed. It will kill the louse. Dust containing carbaryle is also effective as louse powder. The powder is applied on the inner surface of the clothing as well as socks and the body of the person.
Mechanical Control: Hand picking of louse from infested person.
Personal hygiene:
a. Daily bath with soap and water.
b. Clothing, sheets and towels should be washed with hot water and soap and pressed with hot iron.
c. Woman with long hair should wash and clean their hair frequently.
d. By Improving living standard we can easily control the louse.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself