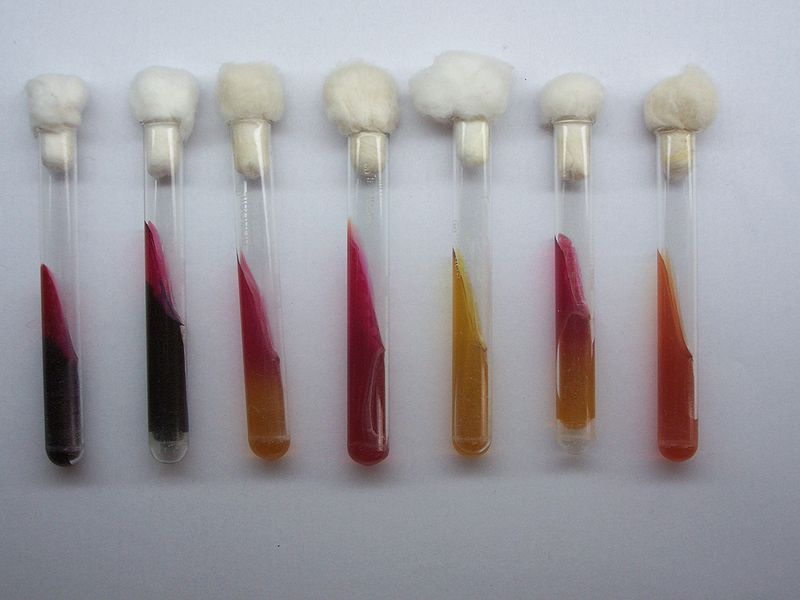
Sugar set comprises of certain biochemical tests which are used in the identification of enterobacteriaceae.
Composition
Carbohydrates comprising standard sugar sets are lactose, sucrose, glucose and maltose. Following are the main tests included in sugar set:
- Urease test
- Citrate test
- Indole test
- Triple sugar iron (TSI) test
Urease Test
Principle
Organisms producing urease enzyme split urea into ammonia and carbon dioxide. Ammonia changes pH of medium to alkaline, as a result pink color is seen.
Procedure
Inoculate the test organism into urease agar slope and incubate for 24 hours at 37 C. appearance of pink color indicates a positive test, showing the organism is urease positive. Bacteria that produce urease are Proteus, Klebsiella and Helicobacter species.
Citrate Utilization Test
Principle
This is based on the ability of certain bacteria to utilize citrate as the only source of carbon and ammonium as the only source of nitrogen. The medium contains sodium citrate, ammonium salt and bromothymol blue indicator.
Procedure
Inoculate the test organism in citrate medium and incubate at 37 C for 24 hours. The appearance of blue color indicates a positive reaction and shows that the test organism has a capability to utilize citrate. The bacteria which are citrate positive are Klebsiella species and those which are citrate negative are E. coli.
Indole Test
Principle
This test demonstrates the ability of certain organisms to breakdown the amino acid, tryptophan, into indole and the production of indole is detected by incorporation of Kovac’s reagent.
Procedure
Take peptone water tube containing tryptophan, inoculate the organism of interest and incubate at 37 C for 24 hours. After 24 hours, add Kovac’s reagent, and shake gently to see appearance of red ring at upper layer of peptone water tube. This shows that the organism is indole positive.
E. coli is indole positive while Klebsiella pneumonia is indole negative.
Triple Sugar Iron Test
Principle
The test is based on the capability of bacteria to utilize different sugars.
Composition
Important components are:
a. Ferrous sulphate
b. Glucose
c. Lactose
d. Sucrose
e. Phenol red indicator
The medium in tube is poured so that it makes a solid, poorly oxygenated area on the bottom called ‘butt’, and an angled well oxygenated area called the ‘slant’ at the top. Organism is inoculated into butt and across the surface of the slant. The tube is then incubated at 37 C for 24 hours.
Interpretation of Test
The interpretations of this test are:
a. If the lactose or sucrose are fermented, a large amount of acid is produced which turns the phenol red indicator to yellow in both the butt and the slant. Some organisms generate gases which produce bubbles in the butt.
b. If the lactose is not fermented, but small amount of glucose is, the oxygen deficient butt will be yellow but on the slant acid will be oxidized to carbon dioxide and water by the microorganisms, so the slant will appear red.
c. If neither the glucose, lactose or sucrose is fermented, both butt and slant will be red, owing to the production of ammonia from the oxidative deamination of amino acids.
d. If hydrogen sulphide is produced, black color of ferrous sulphide is produced.
Voges Proskkauer Test (VP test)
Principle
This test is used in differentiation of enterobacteriaceae like Klebsiella pneumonia, Vibrio cholera and some strains of enterobacter. These bacteria utilize glucose with the production of acetoin, which can be detected by the oxidation to diacetyl compound, which forms a pink compound with an indicator.
Procedure
Inoculate the test organism into VP medium and incubate at 37 C for 24 hours. Add VP reagent and wait for 5 to 30 minutes. Positive test is shown by a pink red color as in Klebsiella pneumonia and Enterobacter species. The negative test is shown by the absence of pink red color as in the case of E. coli.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself