n Part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch
n PRINCIPAL FEATURES are:
n The parotid gland & its related structures
n The masseter muscle
PAROTID GLAND
n Largest of the major salivary glands
n Mainly serous with few mucous acini
n Large, irregular, lobulated
n Extending from zygomatic arch to upper part of neck where it overlaps posterior belly of digastric and anterior border of sternocleidomastoid
n Anteriorly overlaps masseter muscle
n Extends below external acoustic meatus posteriorly onto mastoid process
n Occupies gap between ramus & mastoid and styloid processes of temporal bone and reach close to lateral wall of oropharynx
SHAPE
n As seen from superficial surface, its roughly wedge shaped with base above and apex behind angle of mandible
n If cut across- also wedge shaped with base in lateral position and apex against pharyngeal wall
n Facial nerve and its branches pass forward within the gland and divide it into superficial & deep parts or lobes
n GLENOID PROCESS: the superior margin of the gland extends upward behind TMJ into posterior part of mandibular fossa.
n FACIAL PROCESS: anterior margin of gland extends forward, superficial to masseter to form facial process
n A small part of facial process may be separate from the main gland & is called accessory part of gland.
n PTERYGOID PROCESS: Deep part of the gland may extend forward between medial pterygoid and ramus of mandible
CAPSULES OF THE GLAND
n Lobulated mass surrounded by C.T capsule
n In addition, it is enclosed in a dense fibrous capsule derived from investing layer of deep cervical fascia
PAROTID DUCT
n Of Stensen
n About 2 inches (5cm) long.
n Passes forward over lateral surface of masseter, one finger breadth below zygomatic arch
n Lies on middle 3rd of a line b/w intertragic notch of auricle and midpoint of philtrum-palpable on clenched masseter
n At ant border of masseter, it turns sharply medially & pierces buccal pad of fat and buccinator
n Then it passes forward for short distance b/w buccinator & mucous membrane and finally opens into vestibule, opposite upper 2nd molar tooth
n Oblique passage prevents inflation of duct system during violent blowing
n Accessory part of gland is drained by a small duct that opens into the upper border of the parotid duct
Parotid duct, being superficial, may be damaged in injuries to face or during surgical operations on face
STRUCTURES WITHIN PAROTID GLAND
n FROM LATERAL TO MEDIAL:
n Facial nerve
n Retromandibular vein &
n External carotid artery
Some members of parotid lymph nodes also present within the gland
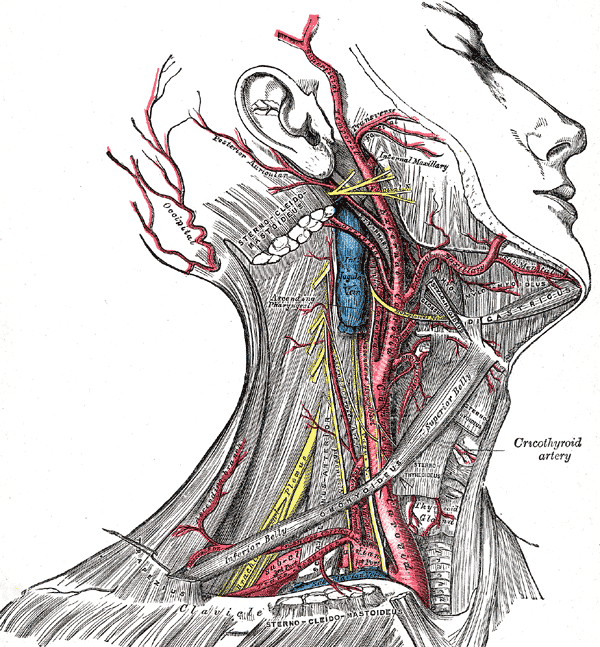
FACIAL NERVE
n Emerges from stylomastoid foramen & enters parotid gland
n Passes forward superficial to retromandibular vein and ECA, and divides into its five terminal branches
n Branches of nerve leave the gland at anteromedial surface
BRANCHES OF FACIAL N BEFORE ENTERING PAROTID:
n Muscular branch – for posterior belly of digastric & stylohyoid
n Posterior auricular nerve – ascends behind ear and supplies the posterior and superior auricular muscles and occipital belly of occipitofrontalis
RETROMANDIBULAR VEIN
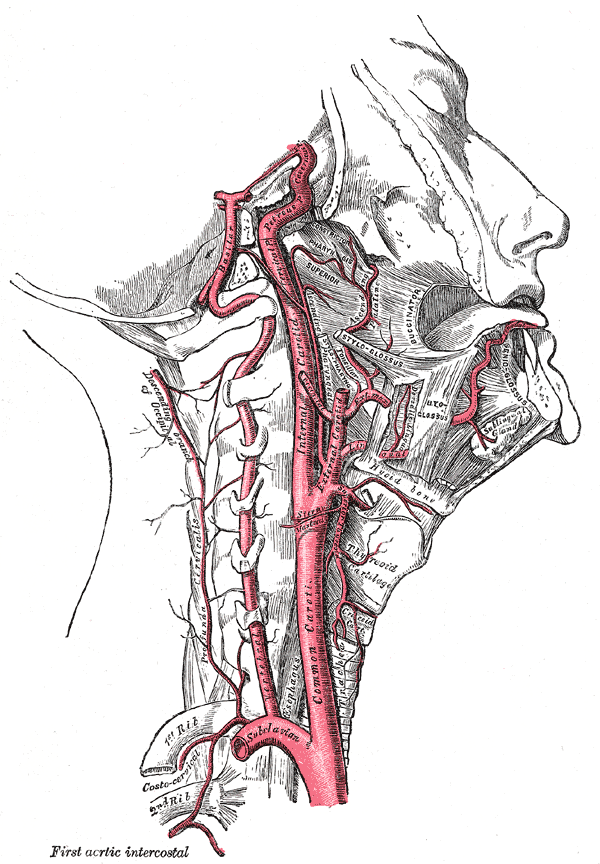
n Formed within parotid gland by the union of superficial temporal and maxillary veins
n Divides into anterior and posterior divisions which leave lower border of gland
n Anterior division joins facial vein, to IJV
n Posterior division joins post. Auricular vein to form external jugular vein
EXTERNAL CAROTID ARTERY
n Leaves carotid triangle by passing deep to posterior belly of digastric, ascends to enter parotid
n At the level of neck of mandible, divides into superficial temporal and maxillary artery
PAROTID LYMPH NODES
n Situated on or within parotid
n Receives lymph from scalp above parotid, lateral surface of auricle, ant wall of ext auditory meatus, lateral parts of eyelids
n Deeply placed nodes also receive lymph from middle ear
n Efferents to deep cervical lymph nodes
RELATIONS OF PAROTID GLAND
n PAROTID BED: structures intimately related to deep surface of parotid
n SUPERFICIAL RELATIONS:
n Parotid lymph nodes, fascia, great auricular nerve and skin
n SUPERIOR RELATIONS:
n External auditory meatus and posterior surface of TMJ
n POSTEROMEDIAL RELATIONS:
n Mastoid process, sternocleidomastoid, posterior belly of digastric, styloid process and attached muscles, carotid sheath with internal carotid artery, IJV, vagus, glossopharyngeal, accessory, hypoglossal, facial nerves
n ANTEROMEDIAL RELATIONS
n Post border of ramus,TMJ, masseter, medial pterygoid.
At the junction of anteromedial and posteromedial surfaces, the gland lies in contact with pharyngeal wall
BLOOD SUPPLY
n ECA & its terminal branches
n Veins drain into retromandibular vein
LYMPH DRAINAGE
n Into parotid and deep cervical lymph nodes
NERVE SUPPLY
n Parasympathetic secretomotor fibres:
n From inferior salivary nucleus of 9th CN
n Nerve fibres pass to otic ganglion via tympanic branch of 9th CN and lesser petrosal nerve.
n Postganglionic fibres reach parotid gland via auriculotemporal nerve, which lies in contact with deep surface of the gland
n Postganglionic sympathetic fibres:
n Reach gland as a plexus of nerves around external carotid artery
CLINICAL POINTS
n PAROTID BENIGN TUMOUR– rarely causes facial palsy
n MALIGNANT TUMOUR– highly invasive, unilateral facial paralysis
n PAROTID GLAND INFECTIONS
n Retrograde bact inf thru duct, from mouth
n Via blood stream as in mumps
n Gland swellingà causes pain because fascial capsule from investing layer limits swelling
n In acute parotitis, swollen glenoid process which extends medially behind TMJ, leads to pain while eating.
n FREY ‘S SYNDROME:
n Develops after penetrating injury to parotid
n When patient eats, beads of perspiration on skin covering parotid
n Due to damage to auriculotemporal & great auricular nerves.
n During healing, parasympathetic secretomotr fibres in auriculotemporal nerve grow out and join distal end of great auricular nerve; eventually these fibres reach sweat glands in facial skin. The stimulus intended for saliva production produces sweat secretion instead.
MASSETER
n ORIGIN:
n Lower border & medial surface of zygomatic arch
n INSERTION
n Downwards & backwards to be attached to lateral aspect of ramus of mandible
n NERVE SUPPLY
n Mandibular div of trigeminal N
n ACTION
Raises mandible to occlude teeth in mastication
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself

Hi there. I precisely did some net surfing and located this webpage website. I proceeded to go as a result of this web web site present and it’s truly outstanding.I truly really benefit from your internet site.Completely, the piece of writing is in assurance the fairly greatest on this certainly worth though subject. I added it and i?m hunting forward for your approaching website articles or blog posts or web site posts. I also observed that your internet internet site has some incredibly excellent linking finished to it. I will right apart take maintain of the rss feed to remain knowledgeable of any changes. Remarkable information you obtained right right here.Make sure you preserve up-date in your exceptional post.Thank you a ton.