Bacteroides and Prevotella are gram negative rods, non- spore forming, encapsulated, anaerobic and non-motile bacteria.
Route of entry
Part of normal flora, colonize human colon and vagina.
Pathogenesis
• Infections are endogenous, following a break in the mucosal surface, organism causes infections.
• Local abscesses are formed at the site of mucosal breaks.
• Metastatic abscesses form by hematogenous spread to other organs.
• Lung abscesses occur by aspiration of oral flora.
• Facultative anaerobic conditions are required.
• Endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide) produces sepsis and septic shock
• Enzymes causes tissue damage:
- Hyaluronidese
- Collagenose
- Phospholipase
• Polysaccharide capsule is antiphagocytic
Virulence Factors
• Capsule
• Endotoxin-LPS
• Hyaluronidase
• Collagenase.
• Phospholipase
• B- lactamase
Predisposing Factors
• Surgery
• Trauma
• Chronic disease
• Local tissue necrosis
• Impaired blood supply
• Growth of facultative anaerobes at the site
Clinical Symptoms
• Intra-abdominal infections
• Pelvic abscesses
• Necrotizing bacteremia
Bacillus Fragilis causes disease below the diaphragm and B. melaninogenicus causes disease above the diaphragm.
Lab Diagnosis
Specimen
• Pus
• Exudates
• Inflected tissue
• Blood
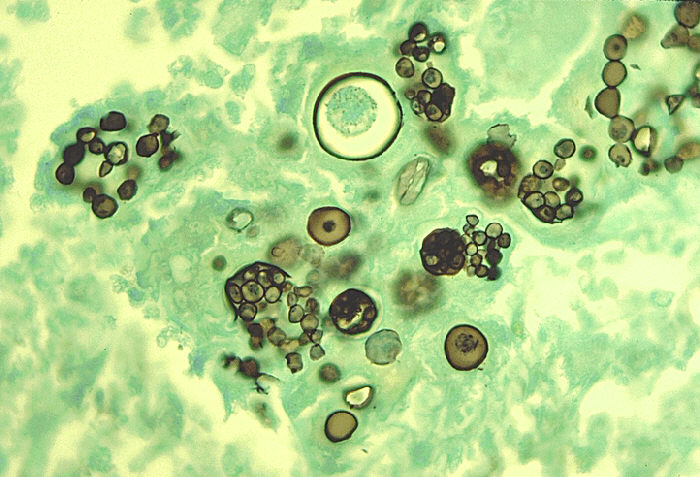
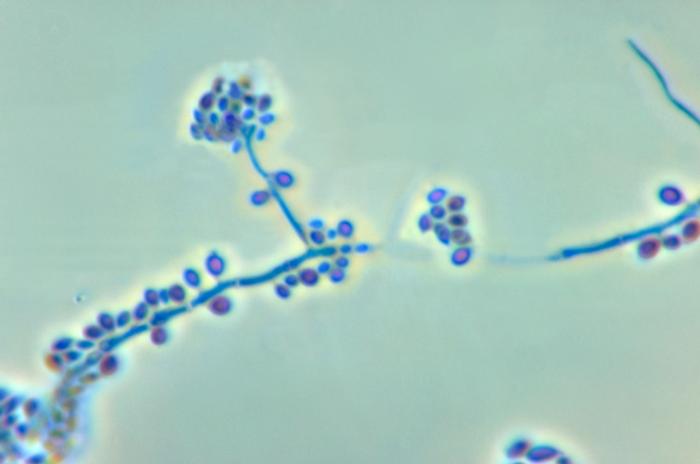
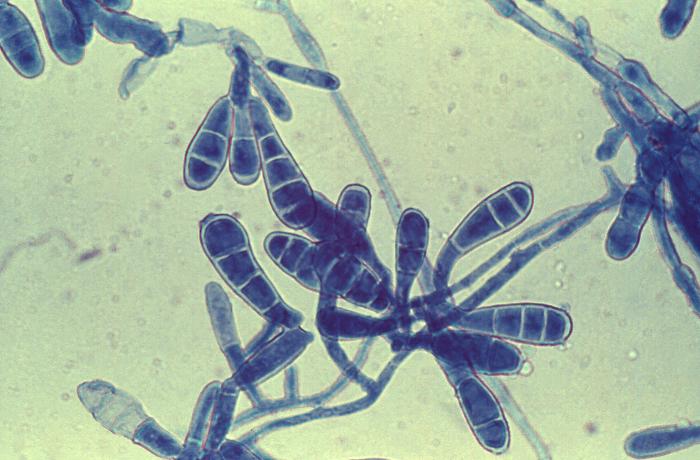
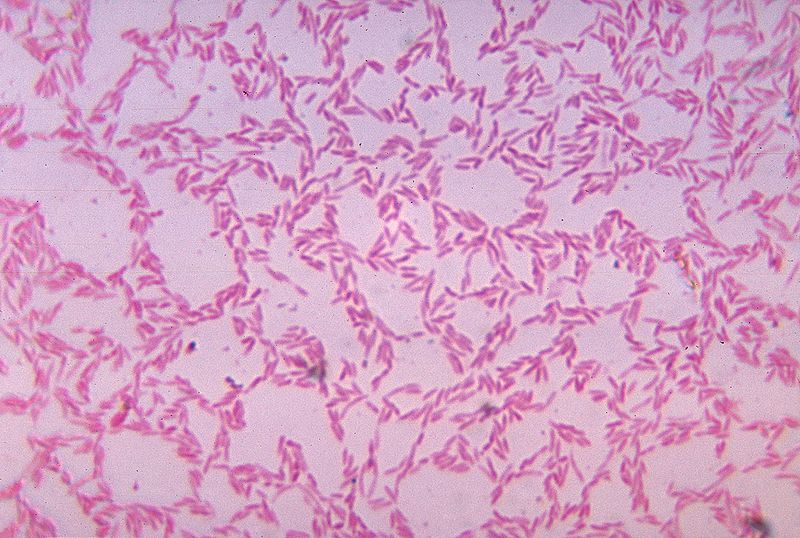
Microscopy
Important features observed under microscope include:
• Gram- negative rods
• Non- spore forming
• Capsulate
• Anaerobic
• Non- Motile
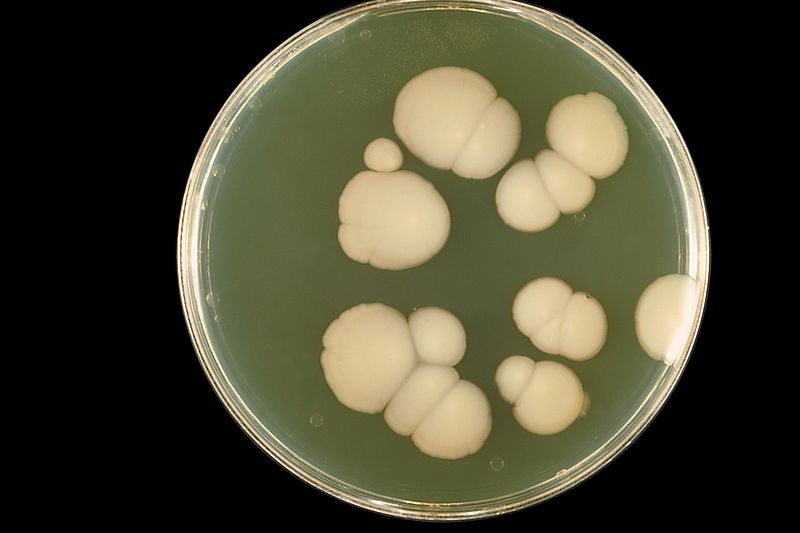
Culture
Blood agar plus vancomycin
Grey, glistening colonies are formed which are non- haemolytic
Biochemical Tests
• Sugar fermentation
• Organic acid production detected by gas chromatography
Serological Tests
• PCR
Treatment
• Penicillin resistant because of B- lactamose
• Metronidazole with clindamycin is given
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself