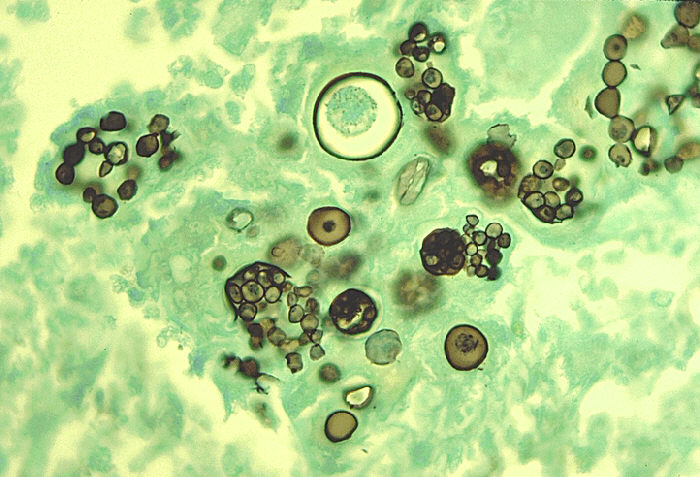
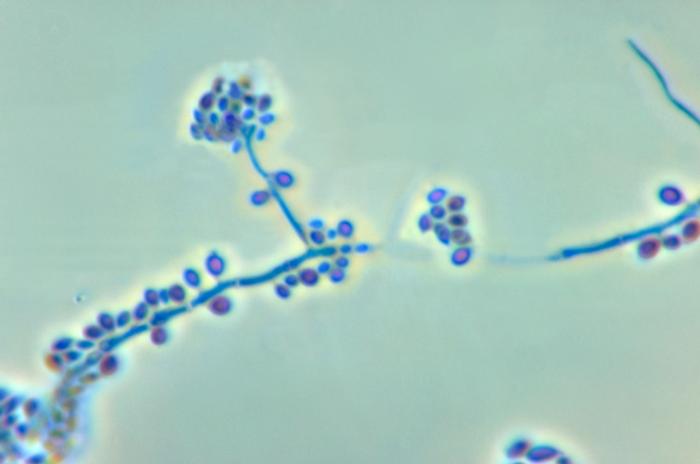
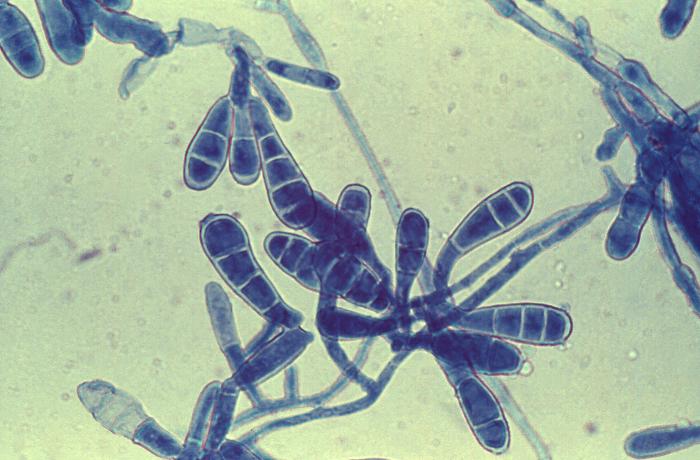
Haemophilus influenzae is a gram negative coccobacillus (short rod), which is non-motile, capsular and ong thread-like and pleomorphic in CSF specimen.
Pathogenesis
Route of Entry
H. influenzae infects humans only. It enters through the upper respiratory tract.
After entry of the organism, there are two fates:
• Asymptomatic colonization
• Infection
The organism produces IgA protease, which breaks down secretory IgA, therefore facilitating attachment to the respiratory mucosa.
Encapsulated variety enters blood stream and spreads to meninges. Non- encapsulated variety causes local infections.
The capsule of most lethal varieties is composed of polyribitol phosphate and is antiphagocytic. Endotoxin is lipopolysaccharide.
Virulence factors
• Capsule
• Endotoxin
• IgA protease
Predisposing factors
• Immunocompromised
• Childrens 6 months to 6 years of age
Clinical symptoms
Symptoms of invasive infections include:
- Meningitis
- Fever
- Headache
- Stiff neck
- Sepsis
- Epiglottitis
Symptoms of local infections include:
• Sinusitis
• Otitis media
• Conjunctivitis
• Pneumonia
Lab- Diagnosis
Specimen
• CSF
• Nasopharyngeal specimen
• Pus
• Blood
Microscopy
Features observed under microscope include:
• Gram negative coccobacillus
• Non-motile
• Capsular
• Long thread-like and pleomorphic in CSF specimen
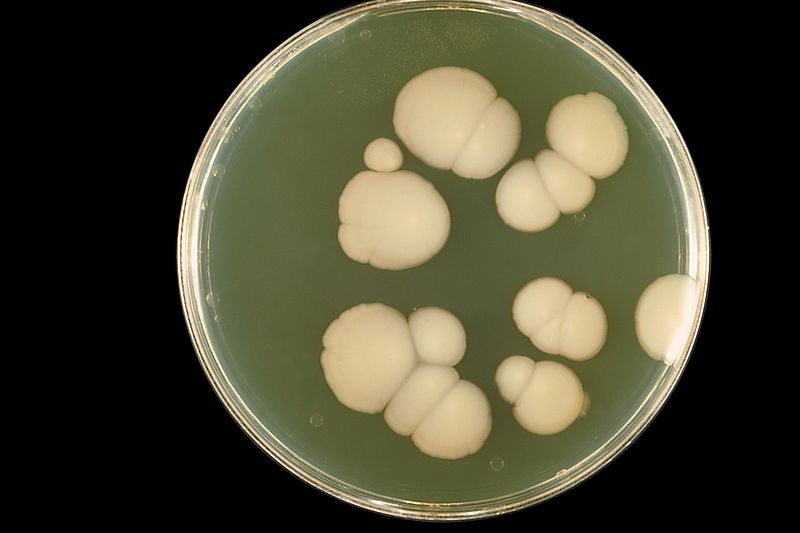
Culture
Chocolate agar plus factor X (heme compound) plus factor V (NAD)
Mucoid colonies are formed. Factor X is required to produce essential enzymes e.g cyctochromes, catalases, peroxidases. Factor V is an electron carrier.
Biochemical tests
Biochemical tests are not usually done. B-biotypes are differentiated by indole, urease and ornithine decarboxylase tests.
Serological tests
• Quelling reaction
• Fluorescent- antibody staining
• Counter-immunoelectrophoresis
• Latex agglutination test.
• PCR
Treatment
- Ceftriaxone
- In case of local infection –amoxicillin– clavulanate is given.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself