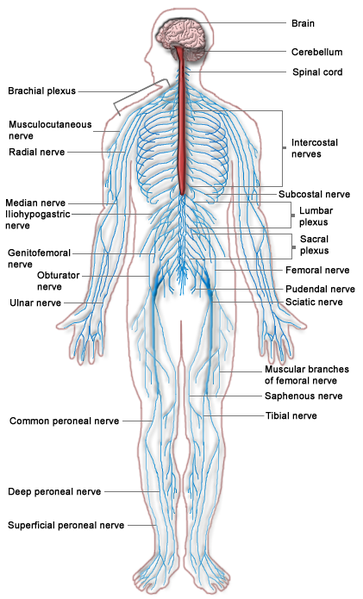
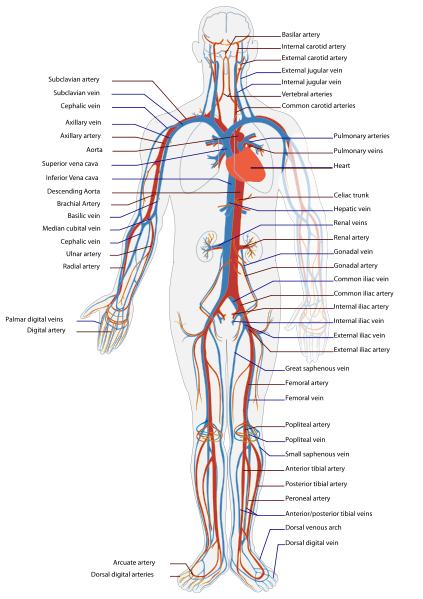
 Neurological examination should include the following:
Neurological examination should include the following:
Examination of Cranial Nerves:
1. CN I:
• History (Can you smell or any alteration in taste?)
• Anterior rhinoscopy to see any polyps, DNS, or other mass or lesion causing obstruction.
• Each nostril is tested separately with different smells with the eyes of the patient closed.
2. CN II:
• Visual acuity
i. Near
ii. Far
• Color vision
• Visual field
i. Finger confrontation
ii. Red pin confrontation
• Fundoscopy
3. CN III, IV, VI:
• ‘H’ pattern: Patient is told to report any double vision, strain or disappearance of the image
• Smooth pursuit movements: ‘+’ pattern moving 300 from the centre on each side and holding it to check for nystagmus
• Voluntary saccades: Patient is told to look up, down, left and right
• Reflex saccades: Patient is asked to look at examiners fingers held to the left and right in front of the patient.
• Pupils:
i. Size
ii. Reaction:
1. Pupillary reflex
2. Accomodation reflex
4. CN V:
• Motor:
i. Clench teeth and palpate masseter and temporalis
ii. Sideways movements (chewing etc)
iii. Forceful jaw opening against resistance
iv. Jaw jerk
• Sensory:
i. Pinprick
ii. Light touch
iii. Temperature in each division and comparing both sides
• Corneal reflex
5. CN VII:
• Motor:
i. Look at roof
ii. Shut eye and don’t let me open it (Bell’s phenonmenon)
iii. Purse the lips shut
iv. Show teeth
• Sensory:
i. Taste
ii. Hyperacusis (stapedial reflex impaired)
6. CN VIII:
• Hearing:
i. Whisper test
ii. Tuning fork tests
• Vestibular tests:
i. Nystagmus
ii. Romberg (positive if the patient can not maintain gait when eyes closed while standing with arms at sides)
iii. Unterberger test (Progressive deviation on jumping with eyes closed)
iv. Dix-Hallpike maneuver (theory)
v. Calorie test etc (theory)
7. CN IX, X:
• Gag reflex.
• Open mouth and say ‘aah’ note movement of palate and uvula
• Taste posterior tongue
• IDL for laryngeal branch of X (usually not done)
8. CN XI:
• Shrug shoulder under resistance
• Move the head to opposite side under resistance (ipsilateral innervations)
9. CN XII:
• Open mount, protrude tongue (note fasciculation, tremor, wasting, deviation)
• Touch the inside of the mouth with tongue on left and then on the right
Examination of the upper limb:
1. Inspection:
a. Muscle wasting (especially thenar and hypothenar eminences)
b. Fasciculation
c. Limb shortening
d. Color
e. Hair loss
f. Shining
g. Ulcers
h. Scar
2. Posture:
Ask the patient to stretch his arms with the wrist facing upwards. In UMNL the arm will try to pronate which is called pronator’s drift (pyramidal drift)
3. Palpation:
a. Tenderness
b. Temperature
c. Wasting (measured from 10 cm below the olecranon or any other bony landmarks, the distance should be same on both sides)
4. Percussion:
a. Fasciculation
Next TPR:
5. Tone at each joint
6. Power of the muscles: Biceps, triceps and deltoids.
7. Reflexes: Biceps, triceps and brachioradialis
8. Testing of the nerves:
a. Median: LOAF
i. Abductor pollicis brevis Pen test Ask the patient to move the pen head above the thenar eminence on supinated hand
ii. Flexor pollicis brevis: Patient is asked to flex his thumb at the interphalangeal joint while examiner tries to resist by applying his finger to distal phalanx.
iii. Opponens pollicis: ask the patient to make a ring with thumb and little finger and don’t allow the examiner to break it.
iv. Long flexor of digits (superficialis and profundus): Grasp test, if impaired digit will not bend. (Lumbricals 1st and 2nd)
b. Ulnar:
i. Abductor digiti minimi: Ask to touch pen held near the little finger
ii. Put a paper on the index fingers of both hands held vertically with radial side up, and ask the patient to touch the paper with his thumbs and don’t allow the examiner to pull out the paper. Adductor pollicis brevis
iii. Writing
c. Radial:
i. Ask the patient to try to form a fist and try to extend it while the examiner resists the movement.
ii. Ask the patient to outstretch his hands and try to move his wrist towards himself while the examiner resists this movement by placing his hand behind the wrist.
9. Coordination:
a. Finger nose
b. Finger nose finger (Past pointing and intention tremor in case of cerebellar disease)
c. Diadokinesis
Secrets are stored in grey or white matter?
Grey, white conduct
1. Sensory system:
a. Fine touch (like pin prick but with cotton)
b. Vibration
c. Position
d. Two point discrimination
All the above due to dorsal column
Spinothalamic:
Pinprick in the dermatomes:
• C5: lateral upper arm
• C6: Lateral forearm (pad of thumb)
• C7: Pad of the index finger
• C8: Pad of little finger
• T1: medial arm
• T2: Axilla
Examination of the lower Limbs:
1. Inspection:
• Same as above
2. Palpation:
• Same as above
• Muscle wasting is recorded as measurement of the bulk of muscle by measuring tape 15cm below the tibial tuberosity
3. Tone:
• Each joint i.e ankles, knee and hips
4. Power:
• Ankle:
i. Plantar flexion
ii. Dorsiflexion
iii. Eversion
iv. Inversion
• Knee:
i. Flexion
ii. Extension
• Hip:
i. Flexion
ii. Extension
iii. Medial rotation
iv. Lateral rotation
v. Circumduction
5. Reflexes:
• Plantar
• Knee jerk
• Ankle jerk
6. Coordination:
• Heel shin toe test
• Hand (examiner) heel shin toe test
• Make a circle in air with each foot separately.
• Ataxia (checked as gait)
7. Gait
Sensory:
Pain, touch and two point discrimination are checked at following places:
- L1: Over the inguinal ligament
- L2: Lateral side of the thigh
- L3: Lower medial side of the thigh
- L4: Medial side of the great toe (I)
- L5: Medial side of digit II
- S1: Little toe (V)
- S2: Back of the thigh
- S3: Skin over the gluteal fold (not usually done)
- S4: Perineum (not usually done)
Position sense is checked on the big toe.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself