INTRODUCTION
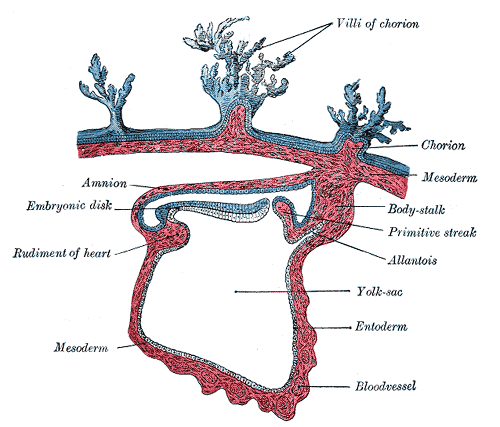
In vertebrate embryo, only part of egg forms the actual embryo while other part is known as the extra embryonic and forms fetal membranes.Fetal membranes consist of:
– Yolk Sac
– Amnion
– Chorion
– Allantois
– Placenta
IMPLANTATION
Occurs mostly on the anterior or posterior wall of uterus
Start of third week:
Primary villi formation, cellular columns of cytotrophoblast lined by syncytiotrophoblast covering.
End of third week:
Secondary and tertiary villi formation, cytotrophoblastic shell formation
When heart begins to beat in the 4th week, villous system is ready.
Intervillous spaces lined with syncytiotrophoblast
Trophoblast at the Beginning of 2nd Month of Development:
Radial appearance due to increased number of Secondary & Tertiary villi
Chorion Frondosum
Chorion Laeve
Endovascular invasion & hybrid vessels
Structure of Decidua (Gravid Endometrium)
Decidua (that which falls off) is the functional layer of endometrium which is shed during parturition.
1) Decidua basalis (deep to the conceptus).
2) Decidua capsularis (overlying the conceptus).
3) Decidua parietalis
- With growth of chorionic vesicle, D.Cap. is stretched & degenerates
- Chorion leave then comes in contact with uterine wall (the Decidua Parietalis) and two fuse and obliterates the uterine lumen.
- Fusion of amnion and chorion together form amniochorionic membrane which ruptures during labour
STRUCTURE OF PLACENTA
Placenta consists of two components.
– Fetal portion (Chorion Frondosum)
– Maternal portion (Decidua basalis)
Fetal side placenta is bordered by chorionic plate
Maternal side is bordered by decidua basalis.
Junctional zone: Trophoblast & maternal cells intermingle
Intervillous space: between decidual plate & chorionic plate
During 4th to 5th month decidual septa project into intervillous spaces but do not reach chorionic plate.
Septa have a core of maternal tissue but surface is covered by syncytial cells which separates the maternal blood from fetal tissue of villi.
Placenta is divided into cotyledons by septa however contact between them is maintained.
Placenta enlarge with advancement of pregnancy and may occupy 15 to 30% of uterine space.
FULL TERM PLACENTA
Discoid in shape
Diameter 15-25cm
3cm thick
Weight 500-600g
Expulsion about 30 minutes after child birth
No. of cotyledons 15-20 visible on maternal side after child birth.
Cotyledons are covered by thin layer of decidua basalis.
Fetal surface of placenta is covered by chorionic plate; Chorionic vessels converge towards umbilical cord
Amnion
Attachment of umbilical cord is eccentric
CIRCULATION OF THE PLACENTA
Cotyledons receive their blood through 80-100 spiral arteries
Intervillous spaces of a mature placenta contain approx 150 ml of blood which is replenished 3-4 times / min
This blood moves along chorionic villi which have a surface area of 4-14 meter square
CLINICAL CORRELATES
- Erythroblastosis fetalis
- Synthetic progestins masculanize female fetuses
- Diethylstilbestrol can cause CA of vagina
- Fetal immunity is provided against diphtheria, small pox and measles but not against pertussis, and varicella (chicken pox)
Types of placenta
One classification scheme for placentas is based on which maternal layers are retained in the placenta or which maternal tissue is in contact with chorionic epithelium of the fetus.
n Placenta Accreta: An invasion of the myometrium which does not penetrate the entire thickness of the muscle.
n Placenta Increta: Occurs when the placenta further extends into the myometrium.
n Placenta Percreta: The worst form of the condition is when the placenta penetrates the entire myometrium to the uterine serosa (invades through entire uterine wall). This variant can lead to the placenta attaching to other organs such as the rectum or bladder
n Placenta previa: Blastocyct implants close to or overlying the internal os of uterus.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself


You mention such a great things here and it is always pleasure to read. Hope to hear more and learn from you.