First week of development
CLEAVAGE
Cleavage is the series of mitotic cell divisions of the zygote, resulting in the formation of early embryonic cells blastomeres. size of the cleaving zygote remains unchanged while blastomeres become smaller.
Until the 8-cell stage, they form a loosely arranged clump.
SITE OF CLEAVAGE
- Division of zygote into blastomeres begins approximately 30 hours after fertilization.
- Cleavage normally occurs as the zygote passes along the uterine tube toward the uterus.
- During cleavage, zygote lies within the thick zona pellucida.
COMPACTION
After the third cleavage, blastomeres maximize their contact with each other, forming a compact ball of cells held together by tight junctions.
This process, compaction, segregates inner cells, which communicate extensively by gap junctions, from outer cells.
MORULA
- L., morus, mulberry
- Approximately, 3 days after fertilization, cells of the compacted embryo divide again to form a 16-cell morula (mulberry).
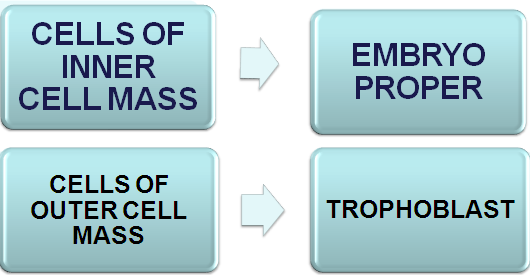
- Inner cells of the morula constitute the inner cell mass, & surrounding cells compose the outer cell mass.
BLASTOCYST FORMATION
About the time the morula enters the uterine cavity, fluids begin to penetrate through the zona pellucida into the intercellular spaces of the inner cell mass.
Gradually, the intercellular spaces become confluent, and finally, a single cavity, the blastocole forms.
At this time ZP disappears allowing implantation to occur.
Second week of development
Day 8:
Trophoblast differentiates into:
- Inner layer of mononucleated cells, the cytotrophoblast
- Outer multinucleated zone without boundaries, the syncytioblast
Embryoblast differentiates into
- Layer of cuboidal cells, the hypobast layer
- Layer of high columnar cells, the epiblast layer
Amniotic cavity apperars
Day 9:
Lacunae formed by the fusion of vacuoles which appear at the embryonic pole so called lacunar stage.
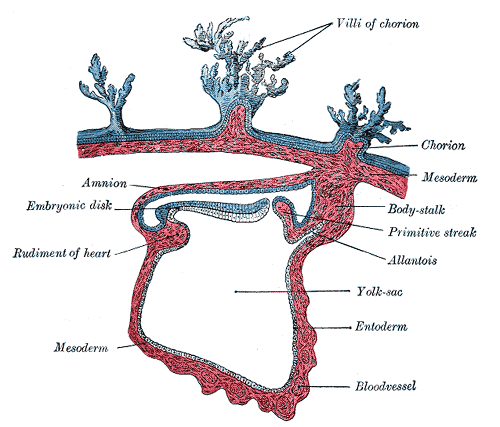
Exocoelomic membrane formed at the abembryonic pole, this membrane together with hypoblast forms primitive yolk sac (exocoelomic cavity)
Days 11 and 12
- Blastocyst completely embedded in endometrium and produces slight protusion.
- Sinusoids formed by the penetration of syncytioblast into stroma eroding endothelial lining of maternal capillaries.
- Uteroplacental circulation established.
- Extraembryonic mesoderm formed by the cells derived from yolk sac cells.
- Chorionic cavity developed by confluence of large cavities in the extraembryonic mesoderm.
- Extraembryonic somatopleuric mesoderm and extraembryonic splanchopleuric mesoderm established.
Day 13
- Surface defect in endometrium heals (bleeding might occur due to greater blood flow into lacunar spaces-may be confused with normal menstrual bleeding)
- Primary villi formed by proliferation and penetration of cytotrophic cells into syncytioblast.
- Secondary yolk sac (definitive yolk sac) established.
- Exocoelomic cysts are found in the chorionic cavity.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself


Well organized but very much short!