The aggregation of glandular epithelium into a definite structure for the purpose of carrying on secretion or excretion is known … Read More »
Special features of Epithelial cells
CELL POLARITY • Epithelial cells exhibit distinct polarity. They have: – Apical domain, directed towards the exterior surface. – Lateral … Read More »
Epithelial Tissue
• Epithelial tissues are formed by closely apposed cells with little or no intercellular material and occur as membranes and … Read More »
Types of Connective Tissue
Ø Loose connective tissue § Areolar tissue § Adipose tissue § Reticular tissue Ø Dense connective tissue § Dense regular … Read More »
CONNECTIVE TISSUE (GENERAL ASPECT)
Introduction ‘Connective tissue’ is the term traditionally applied to a basic type of tissue of mesodermal origin which provides structural … Read More »
Bone
Bone is a specialized connective tissue characterized by mineralized extracellular matrix. Bones are the organs of skeletal system; bone tissue … Read More »
CARTILAGE
n Is a specialised type of connective tissue. n Consists of cells and extracellular components. n Does not contain vessels … Read More »
FETAL MEMBRANES IN TWINS and PRETERM BIRTH
n Dizygotic/Fraternal twins (womb- mates) – 7-11 / 1000 births – By fertilization of two oocytes shed simultaneously – Hereditary … Read More »
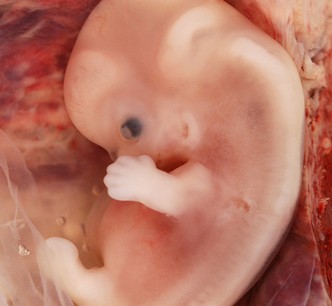
Amnion, Umblical Cord and Amniotic Fluid
1) The amnio-ectodermal junction is the primitive umbilical ring. 2) Following structures pass through the ring at the … Read More »
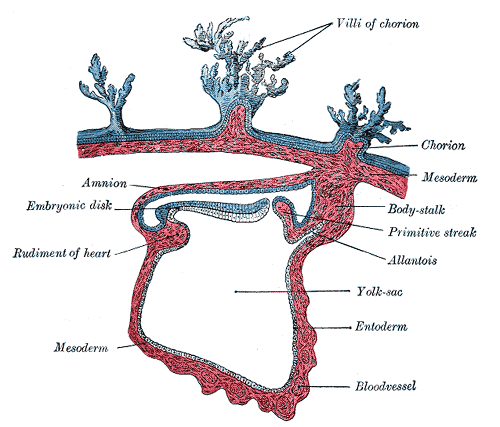
PLACENTA
INTRODUCTION In vertebrate embryo, only part of egg forms the actual embryo while other part is known as the extra … Read More »
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself