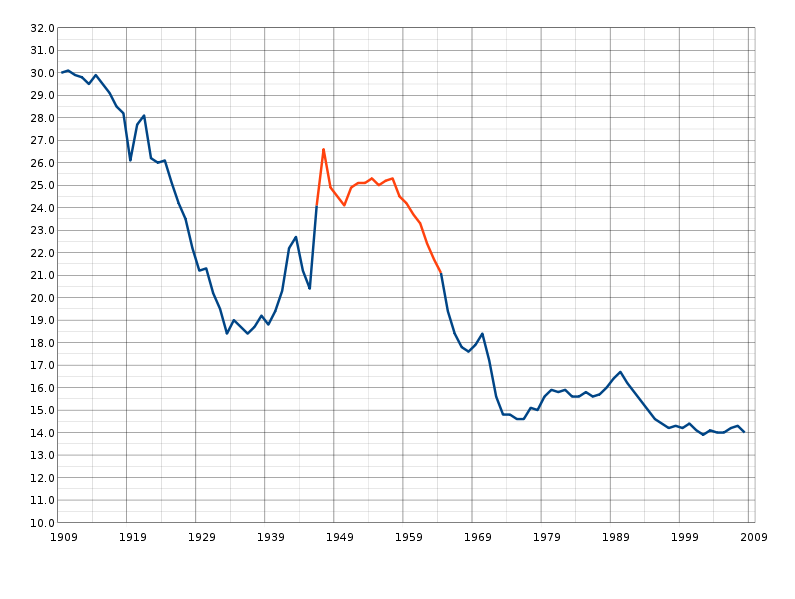
Scenario No. 1
Out of the 75 persons who attended the picnic, 46 subsequently developed gastroenteritis.
Tasks:
- Calculate the attack rate?
- Draw an appropriate epidemic curve.
- Is this a primary or a secondary attack rate?
- Is this an incidence of prevalence rate?
Scenario no. 2:
7 cases of hepatitis A occurred among 70 children attending a child day care center. Each infected child came from a different family. The total number of persons in the 7 affected families was 32. One incubation period later, 5 family member of the 7 infected children also developed hepatitis.
Tasks:
- Calculate the attack rate.
- Draw the epidemic curve.
- Is this primary of secondary attack rate?
Scenario no. 3:
The results of a study of the incidence of pulmonary tuberculosis in a village in India and given in the table below. All the persons in the village are examined during the surveys made 2 years apart, and the number of new cases was used to determine the incidence rate.
| Category of Households at first survey | Number of persons | Number of new cases |
| With culture positive case | 500 | 10 |
| Without culture positive case | 10,000 | 10 |
Task:
What is the incidence of new cases per 1000 person years in households had a culture positive case during the first survey?
Objectives:
By the end of the session, the students will be able to:
- Differentiate between Rate, Ratio and Proportion.
- Differentiate between Incidence and Prevalence of a disease.
- Appreciate various factors affecting Incidence and Prevalence rates.
- Identify different types of Incidence and Prevalence rates.
- Draw different epidemic curves.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself