Epidemic is the unusual occurrence in a community or region of disease, specific health-related behavior (e.g. smoking) or other health related events clearly in excess of expected occurrence.
Epidemic Classification
A. Common Source Epidemics
i. Point Source epidemic
ii. Continuous or multiple source epidemic
B. Propagated (Progressive ) Epidemics
C. Slow (Modern) Epidemics
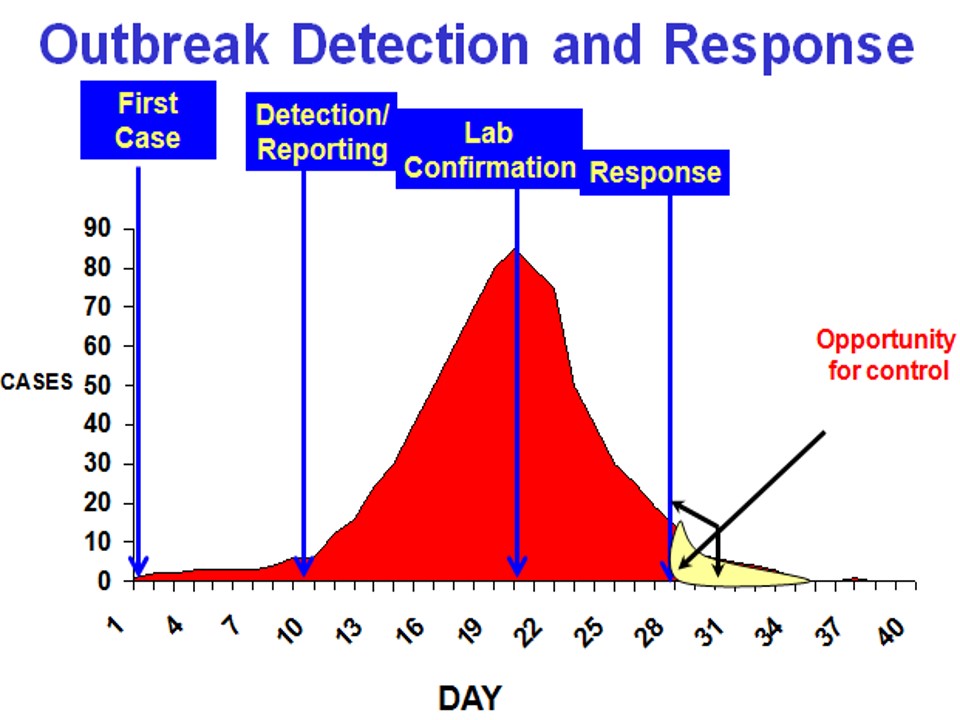
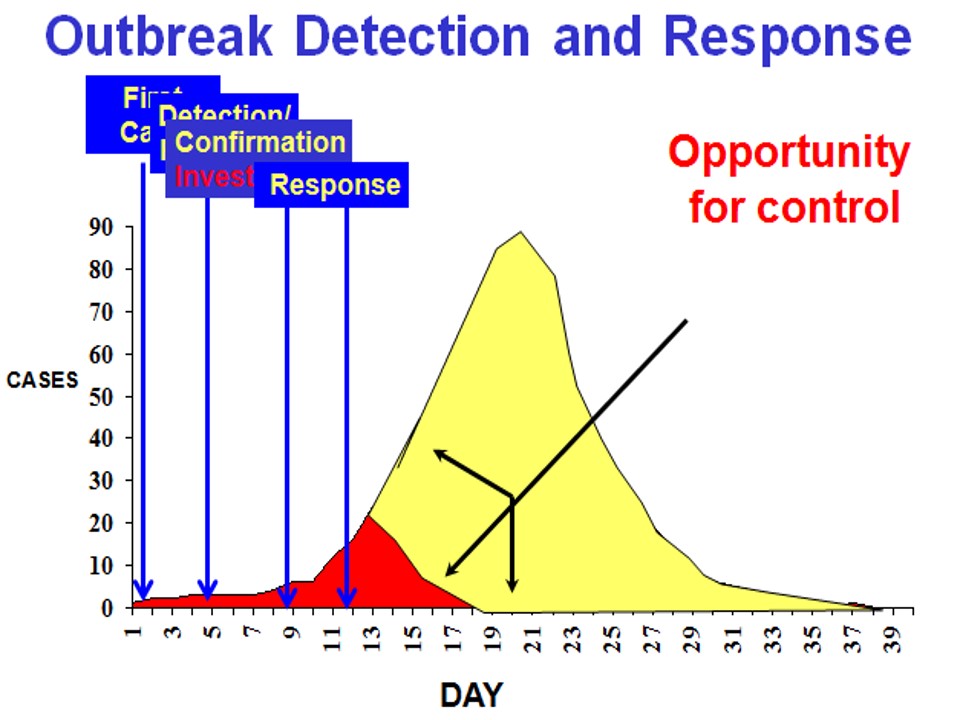
If an Epidemic occurs, how much is the opportunity to control it?
The objectives of an epidemic investigation are:
1. To define the magnitude of the epidemic and involvement in terms of time, place and person.
2. To determine the particular conditions and factors responsible for the occurrence
3. To identify the cause, source(s) of infection, and modes of transmission to determine control
4. To make recommendations to prevent recurrence
Investigation of Epidemic
Investigation of epidemic involves the following steps:
1. Verification of diagnosis
2. Confirmation of the existence of an epidemic
3. Defining the population at risk
4. Rapid search for all cases and their characteristics
5. Data analysis
6. Formulation of hypotheses
7. Testing of hypotheses
8. Evaluation of ecological factors
9. Further investigation of population at risk
10. Writing the report
Verification of Diagnosis
Verification of diagnosis is done by clinical examination of samples of cases and laboratory investigations.
Confirmation of Existence of an Epidemic
Compare the present disease frequencies with the frequencies of the previous year during same period.
Defining the Population at Risk
Population at risk may be defined by obtaining the map of the area and counting the population. This is because for calculating the crude attack rate, we need the denominator ‘Population at Risk’.
Rapid Search for all cases and their characteristics
Cases may be identified by:
a) Medical Survey
By taking history, questionnaire, etc.
b) Epidemiological case sheet
Case interview form
c) Searching for more cases
Data Analysis
Data is analyzed by using classical epidemiological parameters i.e.
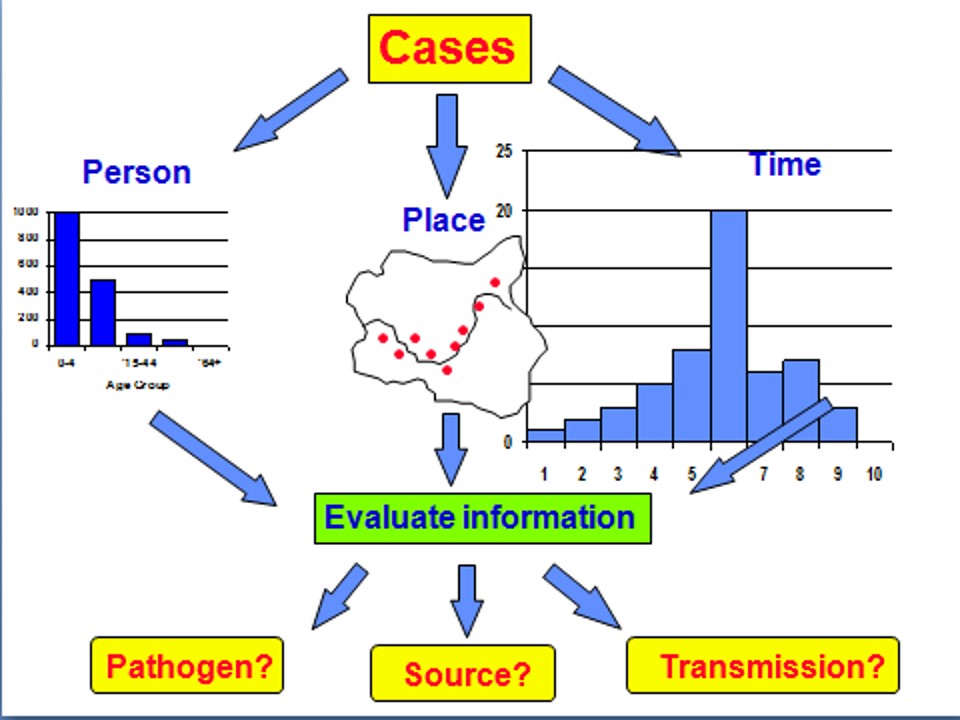
- Time -Epidemic curve, time relationship with exposure, seasonal or cyclic pattern
- Place -Prepare ‘spot map’ of cases i.e geographical distribution
- Person -Age, sex, occupation etc
Determine attack rate and case fatality rate
The purpose of data analysis is to determine;
- Common event or experience OR
- To outline the group involved in common experience.
Formulation of Hypothesis
Explain factors which enabled epidemic to occur in terms of:
Possible Source
Causative Agent
Possible mode of Spread
Environmental Factor
Testing of Hypothesis
Reasonable hypothesis need to be considered and weighted by comparing the attack rates in various groups for those exposed and those not exposed to each suspected factor.
Relative Risk = Incidence among exposed/Incidence among non exposed
Evaluation of Ecological Factors
Relate the disease to environmental factors to know the:
Source of Infection
Reservoir
Modes of Transmission
E.g. breakdown in water supply, eating habits, sanitary measures, atmospheric changes, etc.
Further Identification of Population at Risk
To obtain additional information from population at risk, following points shall be considered:
Medical Examination
Screening test
Examination of suspected food, feces, blood, etc,
Biochemical Studies
Assessment of immunity status, etc.
Writing the Report
Report shall be convincing and complete. It shall include following points:
1. Background
2. Historical Data
3. Methodology of Investigation
4. Analysis of Data
5. Control Measures
Background
Background includes geographical Location, climate conditions, demographic status, socio-economic status, organization of health service, surveillance & early warning System and normal disease prevalence
Historical Data
Historical data should include previous occurrence of epidemics, Occurrence of related diseases and discovery of first case of present epidemic.
Methodology of Investigation
Methodology should include case definition, questionnaire used in epidemic identification, survey teams, type of survey, laboratory techniques, etc.
Analysis of Data
Analysis of data involves clinical data, epidemiological data, mode of transmission, laboratory data and interpretation of data
Control Measures
- Control measures including definition of strategies, methodology of implementation, constraints & results
- Evaluation including significance of results and cost effectiveness
- Preventive Measures
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself