Classification of Mites
Phylum : Arthropoda
Class : Arachnida
Order : Astigmata
Family : Sarcopidae
Specie : Saecopets scabiei
Medical Importance:
Scabies mites are not vectors of any disease but cause the condition known in man as scabies, acariasis and itching.
General Characters of Mites
The scabies mites is visible with naked eyes, about 0.4 mm in size and white in color. The body shape is rounded like a tortoise. Dorsally the mite is covered with bristles. Adults have four pairs of short legs divided into five segments. The front legs end in long tubular processes, known as suckers and the hind legs end in long bristles. The male has suckers on all the legs except the 3rd pair.
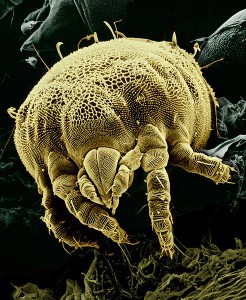 Life Cycle of Scabies Mite
Life Cycle of Scabies Mite
Metamorphosis is incomplete.
Eggs: The female scabies mites select place on the body where the skin is thin such as between the fingers and wrists, etc. The female burrows into the superficial layer of the skin and makes tunnels in which she lays about 30 eggs at the rate of 2-3 per day.
Larva: After 3-4 days the eggs hatch into larva. The larva are six legged. These larvae crawl out from the burrows. They come to the surface and bore into the hair follicles where vesicle form. After about 3 days the larvae mature into nymph.
Nymph: The nymph develop into adults in 6-8 days.
Adult: The life cycle from egg-egg takes about 14-31 days. The female mites may live about 1-2 months on man. Away from man they may survive for about 7-10 days under ideal conditions.
Mode of Spread
Close contact:
Scabies is usually transmitted by close contact with an infected person like sleeping in the same bed or children playing with each other.
Contaminated clothes:
The disease may also be transmitted by contaminated clothes.
Diagnosis of scabies
The patients complains of itching which is worse at night.
Examination reveals follicular lesions at the affected sites.
The diagnosis is probable if the other members of the house are also affected.
Confirmation of the diagnosis may be made by searching the parasites in the skin debris under microscope.
Control of scabies
Benzyl Banzoate: 25% banzyle benzoate is effective against sarcopidae. It should be applied with a brush from the neck downwards and after allowing some 5-10 minutes to dry. The application should be repeated after 12 hours.
Mitigal: It is yellowish sulfur ointment, which is painted undiluted over the body from the neck downward. A single treatment is 100% effective. In epidemic conditions, it is important to treat all members of a family living in close association.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself