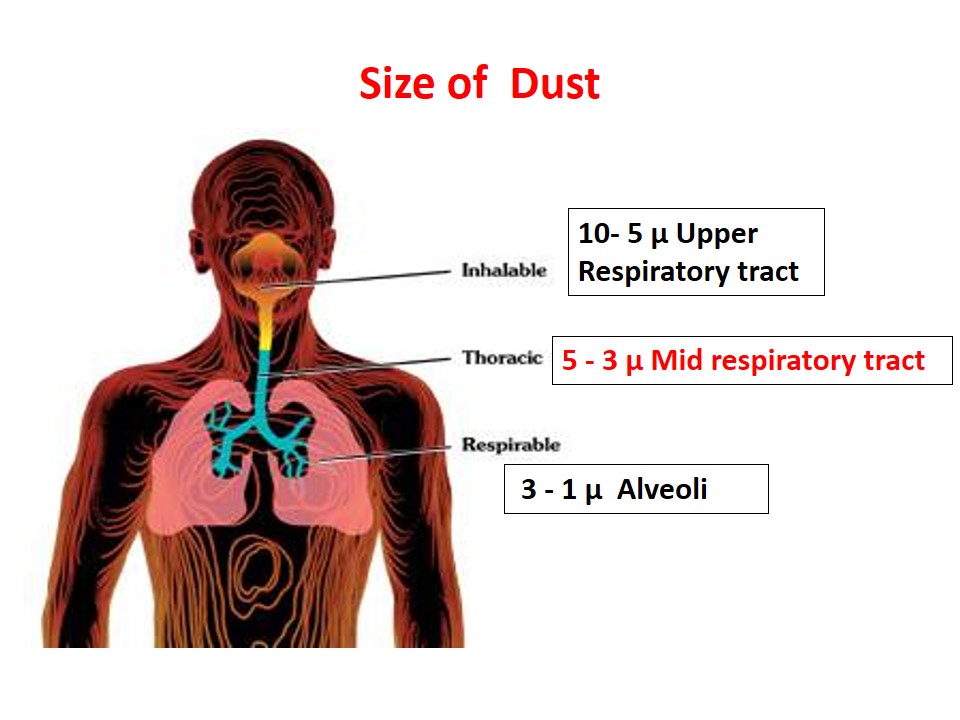
Occupational hazard may be defined as a source or situation with a potential for harm in terms of injury or ill health, damage to property, damage to the workplace environment, or a combination of these.
Types of Occupational Health Hazards
a) Physical
b) Chemical
c) Biological
d) Mechanical
e) Psychosocial
a. Diseases due to Physical Agents
1. Heat – Exhaustion, Syncope, Cramps, burns, Prickly
2. Cold – Frost bite
3. Light – Occupational Cataract, Illumination
4. Atmospheric-pressure – Caisson disease, explosion
5. Noise – Occupational deafness
6. Radiation – Cancer, Leukemia, Aplastic anemia
7. Electricity – Burns, Shocks
Heat Illness
Predisposing factors for heat illness include:
– Physical activity
– Extremes of age, poor physical condition, fatigue
– Excessive clothing
– Dehydration
– Cardiovascular disease
– Skin disorders
– Obesity
– Drugs -Phenothiazines, Anticholinergics, Diuretics, Amphetamines, Cocaine, MAOIs
b. Chemical Hazards
Routes of entry of chemical hazards include inhalation (main route of entry), ingestion and skin absorption.
Chemical agents may be:
1. Metals – Lead, As, Hg, Cd, Ni , Co
2. Aromatic Hydrocarbons – Benzene, Toluene, Phenol
3. Aliphatic Hydrocarbons – Methyl alcohol
4. Gases
a. Simple asphyxiants : N2, CH4, CO2;
b. Chemical asphyxiants : CO, H2S, HCN
c. Irritant gases: Ammonia, SO2, Cl2
TLV (Threshold Limit Value)
“Time-weighted average concentration for a normal 8-hour working day and a 40-hour working week, to which nearly all workers may be repeatedly exposed day after day, without adverse effect”
c. Biological Hazards
Biological hazards include:
• Bacteria – Tetanus, Tuberculosis, Anthrax, Brucellosis (Milkmen), Gonorrhea
• Virus – Hepatitis, HIV
• Protozoal & Parasitic – Malaria, Hookworms, Hydatid (Dog-handlers), tapeworms
• Fungi (Agri-workers) – Tinea-infections, Psittacosis, Coccidiomycosis, Ornithosis
d. Mechanical Hazards
Mechanical hazards include:
• Injuries – Falls, cuts, abrasions, concussions, contusions
• Ergonomic Disorders – Musculo-skeletal disorders(MSDs), Cumulative-trauma-Disorders (CTDs)
• Ergonomics – Adjustment of Man & Machine
• Ergo-friendly tools – Tools which reduce the stresses or problems resulting in CTD’s / MSD’s.)
e. Psychosocial Hazards
Psychosocial hazards include lack of job satisfaction, insecurity, poor interpersonal relations, work pressure, ambiguity.
Psychological & behavioral changes including hostility, aggressiveness, anxiety, depression, alcoholism, drug addiction, sickness absenteeism
Psychosomatic disorders like hypertension, headache, body-ache, peptic ulcers, asthma, diabetes, heart disorders.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself