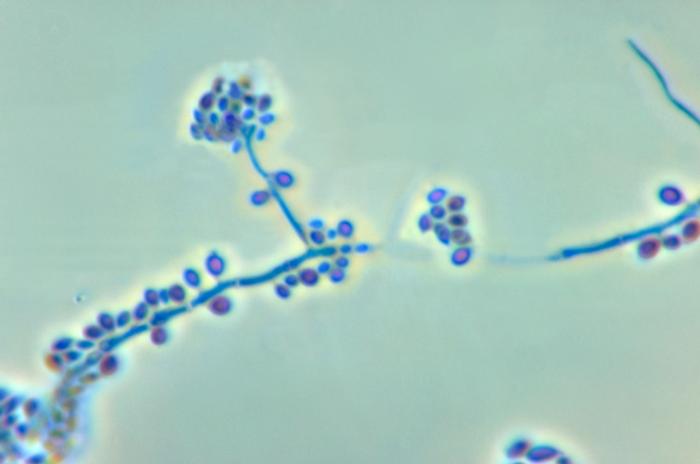
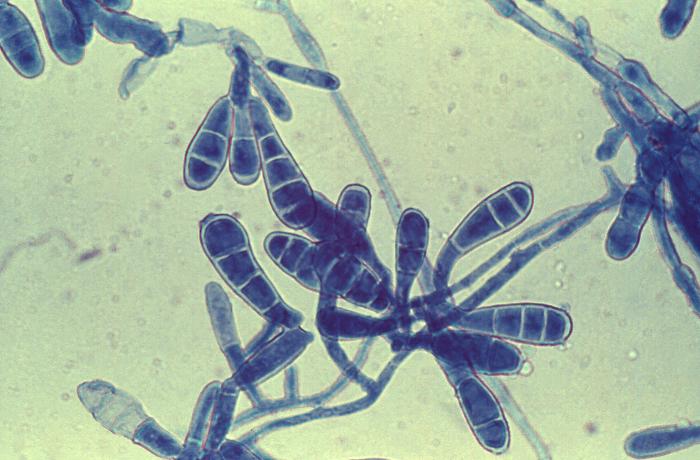
Actinomycetes is a family of bacteria that form long branching filaments that resemble the hyphae of fungus.
Actinomyces Israelii
Transmission:
1. Normal flora of oral cavity and female genital tract.
2. No person to person transmission.
Pathogenesis:
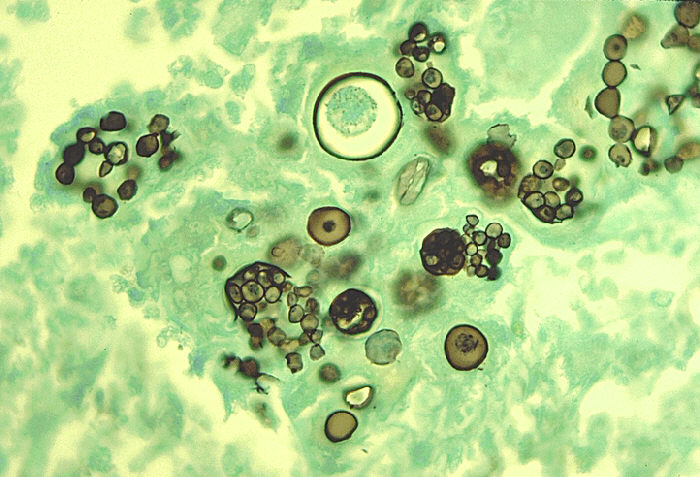
After local trauma or dental extractions, organism invades tissue and forms filaments surrounded by areas of inflammation. Sulphur granules are formed in pus. Pus discharges through the sinus tracts to the surface of the skin.
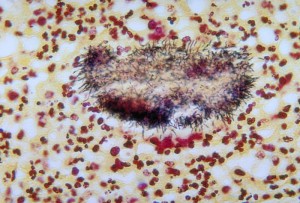
Clinical symptoms
1. Actinomycosis- hard, non tender swelling.
2. Initial lesions appear on face and neck
3. Later lesions involve chest or abdomen as well
4. Pelvis actini mycosis appear in women who have retained an intra-uterine device for a long period of time.
Lab diagnosis:
Specimen
1. Pus
2. Sputum
3. Infected tissue.
Microscopy
1 .Gram positive
2. Non motile
3. Non spore forming.
4. In Zn staining of crushed granules
a. branches are not acid fast.
b. club shaped forms that surround the colonies are acid fast.
5. In gram staining, clubs are gram negative.
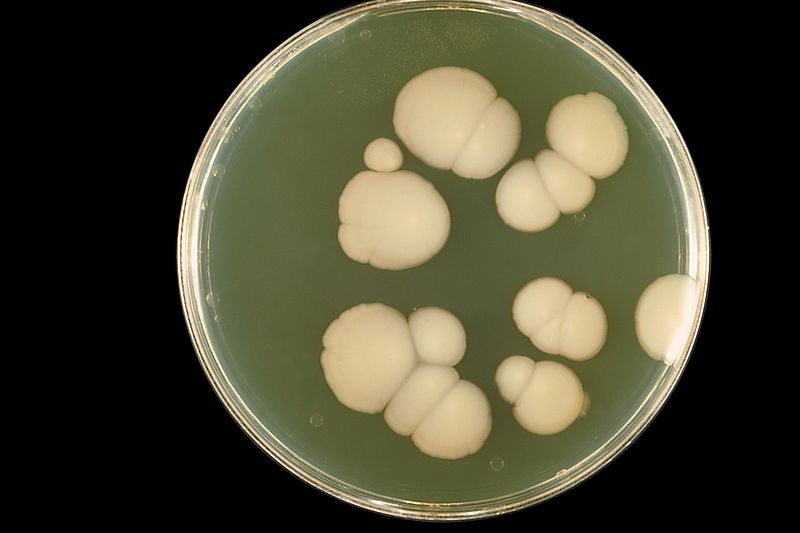
Culture
1. Anaerobic
2. Microaerophilic
3. Isolated crushed granules on blood agar.
a. smalll cream or white colonies.
b. rough nodular surfaces
c. 5 – 7 days of incubation.
d. colonies glisten and adhere to the medium.
Serological Tests
PCR
Treatment:
Penicillin G with surgical drainage. No vaccine is available.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself