Brucella is a genus of gram negative, small, non-encapsulated coccobacilli which are strict aerobes.
Route of entry
- Ingestion of contaminated milk products
- Through the skin by direct contact
- Inhaled in aerosols
Pathogenesis
- Majority are killed by macrophages, rest survive in macrophages
- Invade the body through mucous of upper intestinal and respiratory tracts or skin lesions.
- Enter sub serosa and are transported by macrophages to lymph nodes of liver, spleen and bone marrow
- Enter bloodstream
- Host response is granulomatous, which progresses to focal abscesses
- Produce endotoxin but no exotoxin
Virulence factors
• Endotoxin
Predisposing factors
• Inflected animals
• Unpasteurized milk
Clinical symptoms
• Incubation period is 01-03 weeks
• Fever is seen in minority of cases and it is undulating fever
• Chills
• Fatigue
• Malaise
• Anorexia
• Weight loss
• Enlarged spleen, liver, lymph nodes
• Pancytopenia
• Osteomyelitis –a complication
Lab Diagnosis
Specimen
• Blood
• Bone marrow
Microscopy
• Gram negative
• Small, coccobacilli
• Non-encapsulated
• Strict aerobes

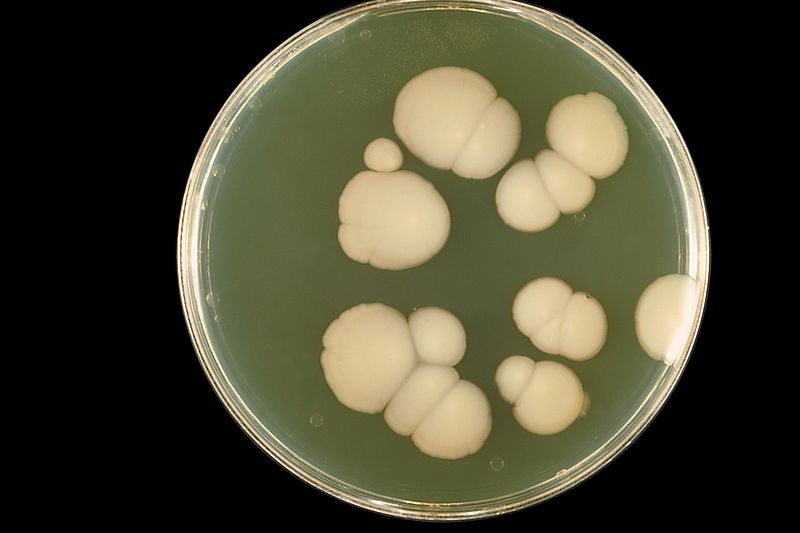
Culture
Strict aerobes, requiring 5-10% CO2
Tryptone soya diphase medium
Produce variety of colonies, e.g smooth, mucoid, colourless or grey, white colonies
TSI agar
No H2S is produced
Biochemical Tests
• Catalase +ve
• Oxidase +ve
• Indole -ve
• Hydrolyze urea
Serological tests
• Slide agglutination test with Brucella antiserum.
• Rapid IgM/IgG immunochromatographic assay
• PCR
Treatment
- Tetracycline
- No vaccine is available
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself