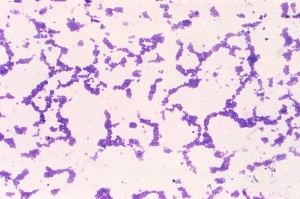
It is a basic test to differentiate between Staphylococci and Streptococci. Both are gram positive cocci.
 Principle
Principle
Catalase is produced by certain bacteria, which acts as a catalyst in breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.
Requirements
Glass rod, test tubes, hydrogen peroxide, test organisms, control organisms
Procedure
- Take 2-3 ml of hydrogen peroxide in a test tube
- Take a colony of test organism with sterile wooden or glass rod and immerse it into hydrogen peroxide solution.
- Observe for generation of bubbles. This indicates oxygen production.
Interpretation
- If bubbles are produced, the organism is catalase positive (Staphylococci)
- If bubbles are not produced, the organism is catalase negative (Streptococci)
Quality Control
Always have positive and negative control of known organisms, along with the test organisms. Staphylococcus aureus may be used as positive control and Staphylococcus pneumoniae as negative control.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself

Point of correction: In quality control, the negative control its not Staphylococcus pneumoniae but I think you wanted to say Streptococcus pneumoniae since all staphs are catalase positive.
Thank you for nice explanation.