The word mycology is derived from the word ‘mykos’ meaning fungus. Mycoses is a disease caused by a fungus. Mycology can simply be defined as the study of fungi.
Fungi
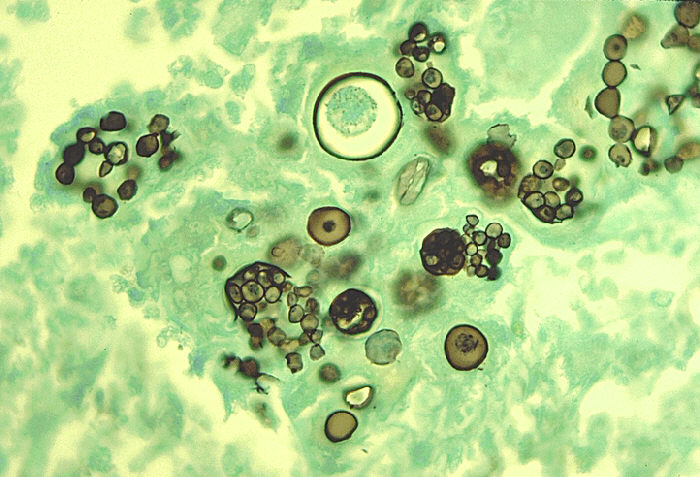
Fungi are widely distributed in nature (air, water, soil, decaying organic debris). There are approximately 400,000 types of fungi. They are eukaryotic, having highly developed cellular structure and are facultatively anaerobic or strict aerobic. Regarding nutrition, they are chemotropic, i.e. obtain nutrition by absorption. This is because they are non-photosynthetic.
Fungi- Morphological Classification
1. Yeast
2. Mould
3. Dimorphic
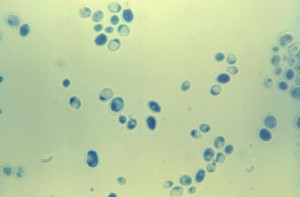
1. Yeast
Yeasts are unicellular organisms. Microscopically they are oval to round, with a diameter of around 3-15 µm. They reproduce by budding. Pseudohyphae are formed by them. Macroscopically pasty colonies are formed (resemble bacteria in this regard).
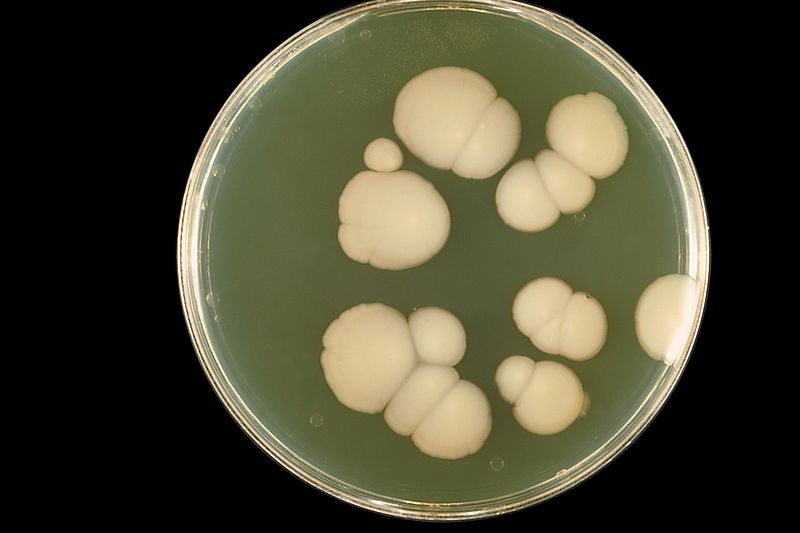
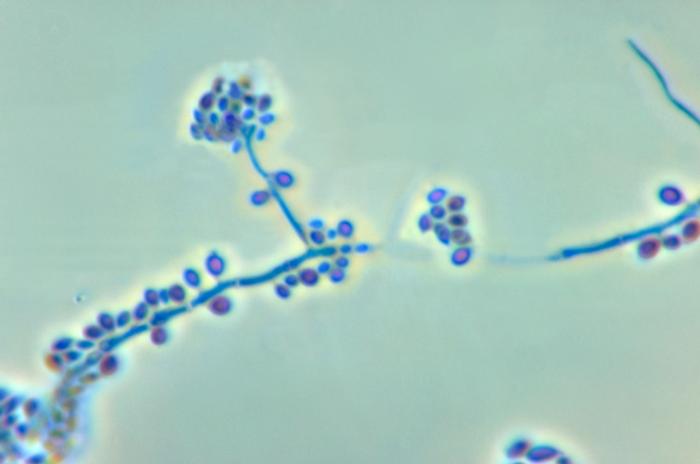
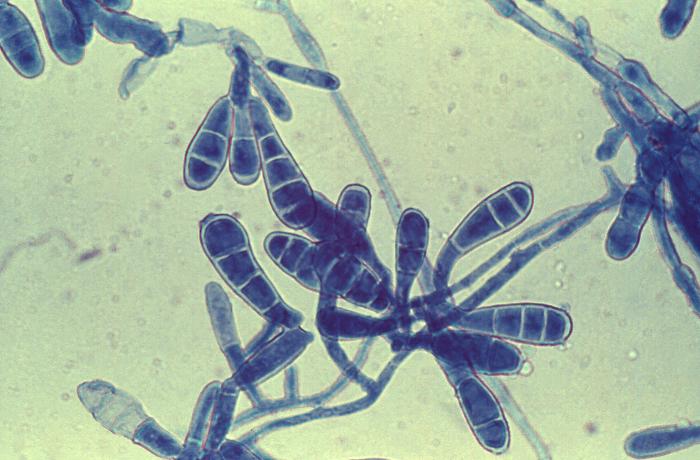
2. Mould
Moulds are multicellular. Microscopically hyphae are formed with a diameter of about 2-10 µm. They produce spores. Macroscopically, surface texture is cottony/wooly/velvety or granular.

Mycoses:
Mycoses are the diseases cause by fungi. Mycoses may be:
1. Superficial
2. Cutaneous
3. Subcutaneous
4. Systemic
5. Opportunistic
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself