Motility test is useful for identification of bacteria which possess similar biochemical reactions. Following methods are used for doing the motility test: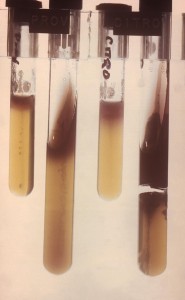
- Hanging drop method
- By using motility medium like motility indole urea, motility indole ornithine.
Hanging Drop Method
Materials
Glass slide, cover slip, distilled water, normal saline, glass pipette, soft paraffin
Procedure
Place a drop of bacterial suspension on the center of cover slip, apply wax or soft paraffin over the corners of the cover slip. Put a glass slide gently over the cover slip and hold it upside down. It should be in such a manner that bacterial suspension should be hanging between the cover slip and glass slide. Examine under the microscope, first under 10x, then under 40x.
We should minimize the light to be giving a contrast in the background. Margins of drop are specially seen. True bacterial motility must be differentiated from non-motile particles, which may show Brownian movement.
Motility Detection by Motility Medium
Materials
Tube motility medium and a wire loop which is used to stab the medium
Non-motile organisms which lack flagella, are usually going to form a single line of growth that does not spread into the surrounding area. While a motile bacterium will grow and make a hazy zone around the stab line.
Some Important Motile and Non-motile Bacteria
- All enterobacteriaceae are motile, except Shigella species
- Klebsiella species are non-motile
- Pseudomonas species are motile with the help of a unipolar flagellum
- Vibrio colony has a shooting star motility
- Campylobacter has a darting motility
- Giardia lamblia has a falling leaf motility
- Listeria monocytogenes has a tumbling motility
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself