Mycobacterium leprae is an acid fast bacillus, non motile, non spore forming, straight or slightly curved bacterium, responsible for causing leprosy.
Pathogenesis:
Transmission:
Transmission occurs by prolonged contact with patients discharging M. leprae in nasal secretions from skin lesions. Humans are the natural hosts.
Organisms replicate intracellularly typically in skin histiocytes, endothelial cells, Schwann cells of nerves.
In leprosy, nerves are damaged by two processes:
1. Direct contact with bacterium.
2. Cell mediated immune attack on the nerves.
Types of Leprosy
1. Tuberculoid form
2. Lepromatous form.
Tuberculoid leprosy:
Cell mediated immune response is strong and limited growth takes place. Very few acid fast bacilli are seen. Granulomas containing giant cells are formed. Neres are damaged by cell mediated immunity. Cell mediated immune response consists of :
- Cd 4 + cells
- IL 2
- IL12.
- GAMA interferon
Lepromine skin test is positive.
Lepromatous leprosy:
Cell mediated immune response is poor. Skin and mucous membrane lesions contain large number of acid host bacilli. Foamy histiocytes are formed rather than granulomas. Damage to nerves is caused by direct contact with bacteria. Lepromin skin test is negative. Organism prefers to grow in skin and superficial nerves.
Virulence factors:
- Mycolic acid
- Cd 4+ T-cells
- IL2
- IL12.
- Gama interferon
Predisposing factors:
1. Immunocompromised patients.
2. Prolonged exposure.
3. Malnutrition.
Clinical symptoms
Incubation time is of several years i.e. about 2 years.
Leprosy:
a. Tuberculoid:
• Hypopigmented macular skin lesions.
• Thickened superficial nerves.
• Anaesthesia
2. Lepromatous:
• Multiple nodular skin lesions.
• Leonine facies
ENL is characterized by:
1. Painful nodules especially on extensor surfaces of tibia and ulna.
2. Neuritis.
3. Uritis 4. Disfiguring appearance of disease results from
- The skin anaesthesia resulting in burns and other trauma which often become infected.
- Reabsorption of bone leads to loss of features.
- Infiltration of the skin and nerves lead to thickening and folding of skin.
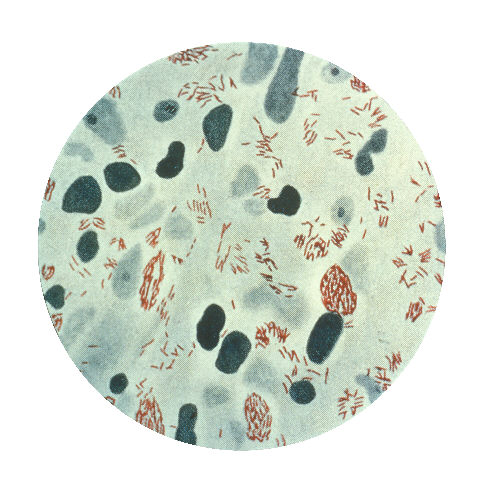
Lab diagnosis:
a.Specimen
1. Skin smear
2. Nasal scraping.
b. Microscopy
1. Modified ZN staining
a. Carbol fuchin
b. Heat
c. 5 percent H2SO4.
d. Methyene blue.
On microscopy we observe:
1. Acid fast bacilli
2. Non motile.
3. Non spore forming
4. Straight or slightly curved.
6. Foam cells containing many acid host bacilli.
Culture:
Culture is not performed because of slow growing bacteria.
Serological Test
PCR
Treatment:
Dapsone for 2 years. No vaccines are available.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself