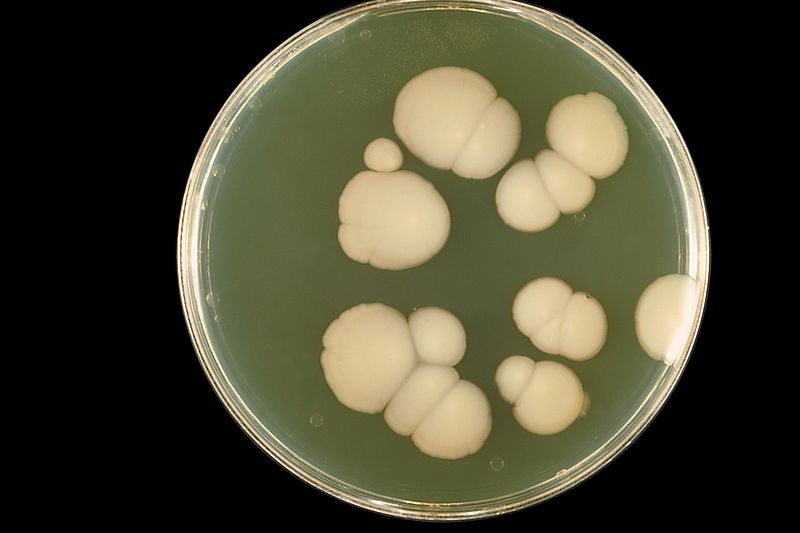
Proteus mirabilis is a gram negative rod with swarming motility. It is facultative anaerobic bacterium having urease activity.
Pathogenesis
Route of entry
Proteus is responsible for community and hospitalized acquired urinary tract infection. It is present in colon and colonies urethra.
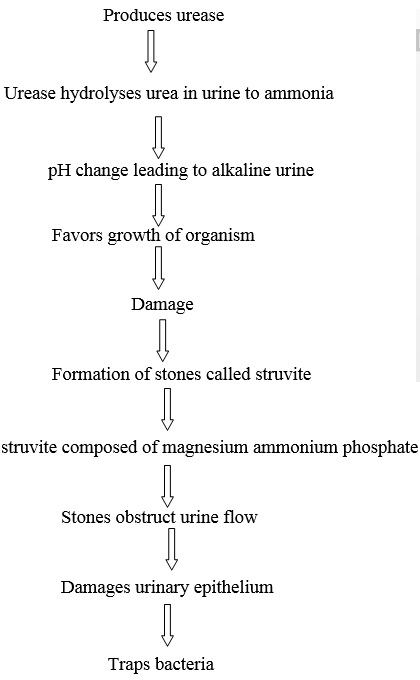
Virulence Factors
- Phenylalanine deaminase
- Urease
- O- antigen
- Pili
- Fimbriae for adherence
- Endotoxin
Predisposing factors
• I/V injections
• Urinary catheters
• Poor hygiene
• Malnutrition
• Young and elderly
Clinical symptoms
• UTI
• Pneumonia
• Wound infections
• Septicemia
Lab-Diagnosis
Specimen
• Urine
• Pus
• Sputum
Microscopy
• Gram- negative rods
• Facultative anaerobes
• Motile – swarming motility
• Non- encasulated
• Fimbriae
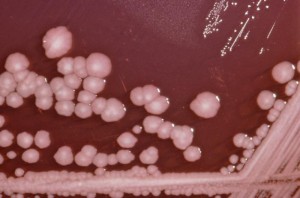
Culture
Blood agar
Swarming motility on blood agar
MacConkey agar
Non-lactose fermenting colonies, non-swarming because of bile salts
CLED
Non-lactose fermenting colonies, non-swarming because electrolyte deficient
Biochemical Tests
TSI Agar
- Slant Alkaline
- Butt Acidic
- Produces Gas
- Produces H2S
Catalase positive
Oxidase negative
Only ferments glucose, and sucrose
Reduces nitrate to nitrite
Urease positive
Phenylalanine deaminase positive
B- galactosidose negative
Indole negative
Serological Test
• PCR
Treatment
• Aminoglycosides
• Trimethoprim- sulfamethoxazole
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself