Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a gram negative rod, which is non- spore forming, motile and a strict aerobe.
Route of Entry
Pseudomonas is present in the human colon. It is also found in soil and water. It is also an opportunistic bacteria and colonies upper respiratory tract.
Pathogenesis
• Endotoxin is released which produces symptoms of sepsis and septic shock. Endotoxin causes inhibition of protein synthesis by ADP ribosylation of elongation factor 2.
• Elastase and protease both are histotoxic and facilitate invasion of the organism in to blood stream
• Pyocyanin is a pigment which colors the pus in a wound blue, damages the cilia and cells of the respiratory tract.
• Some strains have “ type III secretion system” which
- Transfers exotoxins from the bacteria directly into adjacent human cell
- It is mediated by transport pump in the bacterium cell wall.
- 4 exoenzymes are transferred
- Exo- S is the most destructive exoenzyme, causes ADP- ribosylation of a Ras protein, damaging the cytoskeleton.
Virulence factors
- Endotoxin
- Extoxin
- Pyocanin
- Elastase
- Protease
- Type III secretion system
- Exo S
Predisposing Factors
- Extensive burns
- Damaged skin host defenses
- Chronic respiratory disease
- Normal clearance mechanisms are impaired
- Immunocompromised
Clinical symptoms
- UTI
- Pneumonia
- Wound inflections
- Sepsis
- Endocarditis
- External otitis
- Osteochondritis
Lab Diagnosis
Specimen
• Pus
• Urine
• Sputum
• Effusions
• Blood
Microscopy
• Gram- negative rods
• Non- spore forming
• Motile
• Some strains are capsular
• Strict aerobes
Culture
- Strict aerobes
- Non- fementers
- Produce two pigments
- Pyocyanin, a blue- green pigment
- Pyoverdin, a yellow- green fluorescent pigment
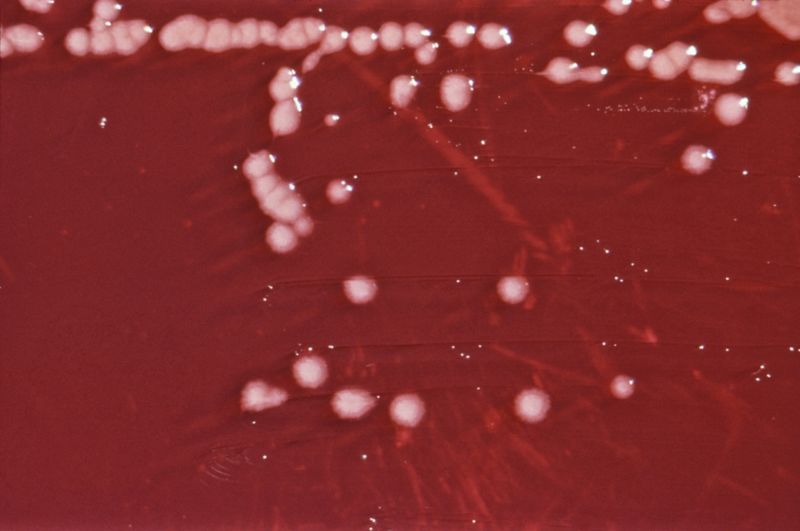
Blood agar
Large flat colonies are formed. Pigments diffuse in to the medium giving a dark greenish- blue color.
MacConkey agar
Pale colored colonies are produced.
CLED agar
Green colonies are formed.
Biochemical Tests
• Triple sugar Iron (TSI) Agar
- Alkaline Slant
- Alkaline Butt
- No gas
- No H2S
• Oxidase positive
• Non- glucose fermenters
Serological tests
• Pyocyanin typing
• PCR
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself