Drugs which increase the efficiency of heart are called cardiotonic drugs.
Efficiency is the ratio of oxygen consumption to work done. These drugs cause decrease in oxygen consumption or work load on heart.
Catecholamines like adrenaline, although increase the force of contraction, but are not cardiotonic because they increase the work load and oxygen consumption.
Chemistry
All drugs contain glycone and aglycone portion. Structure includes:
- Steroid nucleus responsible for actions.
- Unsaturated lactones ring at C-17, responsible for pharmacological actions
- At C3 sugar is attached –pharmacokinetic actions -glycone
Plant Sources
a. Digitalis purpurea.
Digitoxin, gitoxin, gitalin
b. Digitalis lanata
Digoxin, digitoxin, gitoxin
c. Strophanthus kombe
Strophanthin
d. Strophanthus gratus
Ouabain
“An account of the foxglove and some of its medicinal uses: with practical remarks on dropsy and other diseases”
WILLIAM WITHERING, 1785
Mechanism of Action
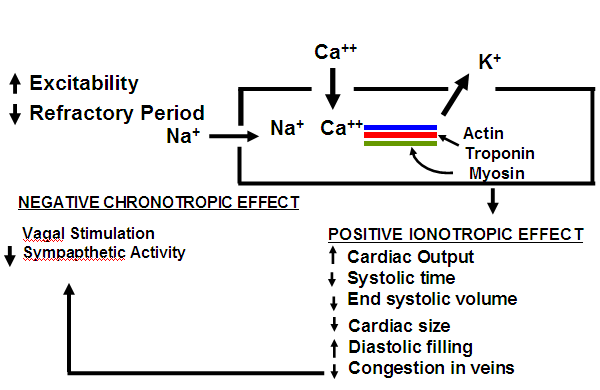
After phase 3 Na+ K+ ATPase pump is activated, when this pump is inhibited Na+ remains inside. No entry of K+ occurs from outside. Increased Na+ leads to increased Ca++ intracellulary because:
- Increased entry through Ca++ channels
- Increased release of Ca++ from sarcoplasmic reticulum
- Inhibition of Na+ Ca++ exchange occurs.
Increased intracellular Ca++ breaks troponin bridge causing increased sliding of actin and myosin filament. Increased contraction of cardiac muscles causes positive ionotropic effect by directly blocking (direct effect). This causes decrease in oxygen consumption and decreased work load (indirect effect) by:
- Vagal stimulation
- Decreased AV conduction
- Decreased sympathetic activity (contributing to decreased heart rate)
Pharmacological Actions
- Due to increase in force of contraction, cause a decrease in systolic time (duration of contraction).
- Increase in stroke volume
- Decrease in end diastolic volume
- Increase in automaticity of heart (decrease in transmembrane electrical potential and cardiac refractory period)
- All these effects lead to decrease in heart size.
ECG changes
- As increase in force of contraction and decrease in action potential occurs, a decrease in QT interval occurs.
- Due to decrease in AV conduction, prolongation of PR interval occurs (very important sign of digitalis toxicity)
- Increased force of contraction sometimes causes ischemia; size of T wave may be decreased or be inverted. In toxicity disappearance of T wave occurs.
- ST segment sags below the base line or the iso-electric line.
Refractory Period
Decrease in refractory period of atrial muscles occurs. There is increase in automaticity, which causes increase in refractory period of AV tissue (due to decreased conduction).
Other Effects
- Increase in renal blood flow due to increased circulation
- Cause alpha 1 mediated vasoconstriction, which may cause increase in peripheral vascular resistance.
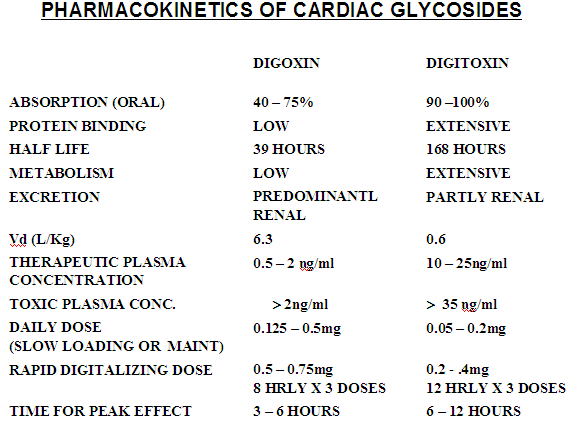
Pharmacokinetics
Therapeutic Uses
- Acute Congestive Cardiac Failure
- Treatment of paroxysmal supraventricular arrhythmias
In congestive cardiac failure with high cardiac output due to hyperthyroidism, cardiotonic drugs are not effective.
Adverse effects/toxicity of cardiac glycosides
Due to low TI, plasma levels are monitored.
1. GIT
Nausea and vomiting, due to stimulation of CTZ.
Anorexia
2. CVS
Bradycardia
AV block
Cardiac arrhythmias
3. CNS
Headache
Vertigo
Restlessness/ Agitation
Nightmares
Neuralgias
Paresthesias (abnormal sensations)
4. Endocrines
Gynecomastia (due to steroid nature)
5. Eye
Blurred vision
Photophobia
Optic neuritis
Scotomas (blind spots on retina)
Disturbance of colour vision (esp. yellow)
Xanthopsia
6. Serum Potassium
Acute digitalis over dosage causes hyperkalemia due to inhibition of Na+ K+ ATPase. K+ accumulates in blood.
Predisposing factors
Diseases
Especially heart diseases like Myocarditis
Renal diseases in case of Digoxin
Pulmonary disease
Hypoxia
Drugs
Electrolytes disturbances
Digitalization
* Loading dose 0.75-1.5 mg
* Maintenance dose 0.0625-0.5 mg
Drug Interactions
1. Diuretics, Adrenal steroids (cause hypokalemia)
2. Quinidine (anti-arrhythmic, causes displacement of digoxin from binding sites as has high protein binding, plasma conc. of digoxin increases)
3. Verapamil, Nifedipine, Amiodarone (used HTN and arrhythmias, cause increase in plasma levels of digoxin from plasma binding sites)
4. Beta blockers (causing increase in bradycardia and heart block)
5. Calcium channel blockers (causing bradycardia)
Treatment of toxicity
- For bradycardia atropine is given (physiological antagonism)
- Hypokalemia is treated by K+ infusion, given carefully.
- Phenytoin Na+, although antiepileptic, but has antiarrhythmic effects and least effects AV conduction, so used in arrhythmias
- Fab Fragment of antibody (cardiac glycosides bind more with this and less with Na+ K+ ATPase) and monoclonal antibodies are used in severe over dosage of cardiac glycosides.
Most of the cases are treated by withdrawal.
Continue Reading
Drug Treatment of Cardiac Failure
Bipyridine Derivatives -Milrinone and Inamrinone
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself