Also known as Cholinergic drugs or Cholinomimetic drugs or Cholinoceptor activating drugs.
Definition
These are the group of drugs which produce effects resembling those produced by the stimulation of parasympathetic autonomic nervous system on the target organs
Neurotransmitter involved is acetylcholine. Most of the peripheral autonomic nervous system fibers cause synthesis and release of acetylcholine. They activate the parasympathomimetic system, thus called cholinergic fibers.
All preganglionic and most of parasympathomimetic postganglionic and some postganglionic sympathetic fibers, adrenal medulla and skeletal somatic muscle fibers constitute the cholinergic fibers.
Parasympathomimetics were discovered form muscarine alkaloid obtained from natural source, which produces effects by affecting organs similar to parasympathetic system, thus receptors were termed muscarinic receptors.
Nicotine was discovered to act on skeletal muscle NMJ and autonomic ganglia, such receptors were termed nicotinic. They were further discovered by Dale.
Synthesis, storage, Release & inactivation
Mechanism of Action
a. G –protein linked (Muscarinic), through transmembrane 2nd messenger signaling
b. Ligand gated Ion channels (Nicotinic)
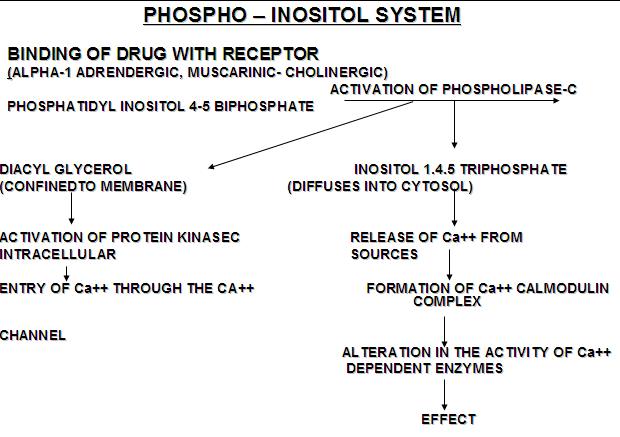
Muscarinic receptors act through DAG/IP3 second messenger system.
Cholinergic Receptors
1. Muscarinic
M1 = Nerves, Stomach, Brain
Antagonist: Pirenzepine
M2 = Heart, Nerves, Smooth Muscle.
Antagonist: Gallamine
M3 = Glands, Endothelium, Smooth Muscle.
M4 and M5 newly discovered, role not yet known
Muscarinic receptors act through the IP3/DAG cascade. They also cause activation of guanylcyclase activity by increasing cGMP (decrease cAMP in heart and smooth muscles). Calcium is released from sarcoplasmic and endoplasmic reticulum.
M1, M3 and M5 act through IP3/DAG cascade
M2 and M4 act by decreasing the levels of cAMP activating the K+ channels.
2. Nicotinic
a. Present in neuromuscular junction, NM
Agonist: Phenyl Trimethyl Ammonium
Antagonist: Tubocurarine
b. Present in autonomic ganglia, adrenal medulla, NN
Agonist: Dimethyl phenyl piperazinium
Antagonist: Hexamethonium
Classification
A. Directly Acting –act by causing release of acetyl choline
B. Indirectly Acting –inactivate enzymes involved like pseudocholine esterase, thus hydrolysis of acetylcholine does not occur
A. Directly Acting Cholinergic Drugs:
I. Choline Esters
II. Cholinomimetic Alkaloids
a. Mainly Muscarinic Agonists
Natural Alkaloids:
Arecholine
Synthetic Alkaloid:
Oxotramorine
Selective M3 agonists
Cevimeline
b. Mainly Nicotinic Agonists
Natural Alkaloids:
Synthetic Alkaloids:
Dimethyl phenyl piperazinium (DMPP)
Varenicline
Tertiary alkaloids
Quaternary amines
B. Indirectly Acting Cholinergic Drugs (Anticholinesterases)
I- Reversible
a. Carbamates
b. Alcohols
II- Irreversible
I- Reversible
a. Carbamates
Tertiary amines
Physostigmine
Quaternary Ammonium compounds
Neostigmine
Pyridostigmine
Distigmine
Ambenonium
Demecarium
b. Alcohols
Edrophonium
c. Miscellaneous
Tacrine
Donepezil
Galantamine
Rivastigmine
II. Irreversible Anticholinesterases (Organophosphorus Compounds)
1. Therapeutically useful:
Ecothiophate
2. War Gases:
Sarin
Tuban,
Soman
3. Insecticides:-
Parathion
Malathion
DiisopropylFlurophosphate (DFP)
Tetramethyl Pyrophosphate (TMPP)
Octamethyl Pyrophosphotetraamide (OMPA)
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself