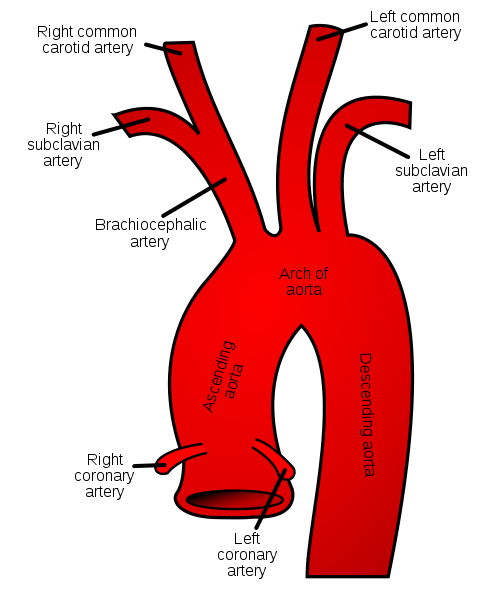
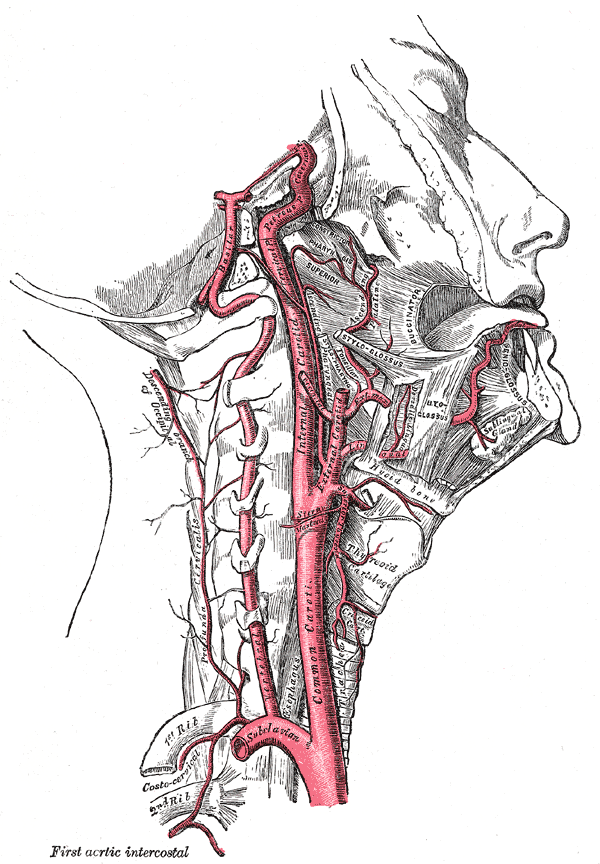
The common carotid artery has separate origins on the left and the right side, arising from the brachiocephalic artery behind the sternoclavicular joint on the right side, while that from the arch of aorta in the superior mediastinum on the left.
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
The artery passes upwards, running through the neck from the sternoclavicular joint to the upper border of the thyroid cartilage. At the level of the thyroid cartilage, the common carotid artery divides into its two terminal branches:
1. External carotid artery
2. Internal carotid artery
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
Carotid sinus:
A localized dilatation is present at the bifurcation of common carotid artery or the beginning of internal carotid artery, known as the carotid sinus. Here, the tunica adventitia is thick while the tunica media is thinner, as compared to other parts. A number of nerve endings of the glossopharyngeal nerve are also found in the tunica adventitia. Thus carotid sinus serves as a receptor, detecting changes in the blood pressure. A rise causes vasodilatation and reduced heart rate.
Carotid body:
Another structure located posterior to the point of division of the common carotid artery and supplied by the glossopharyngeal nerve, is the carotid body. The carotid body serves as a chemoreceptor, detecting reduced oxygen tension and increased carbon dioxide levels in blood. These two conditions cause an increase in the respiratory movements and lead to an increased blood pressure.
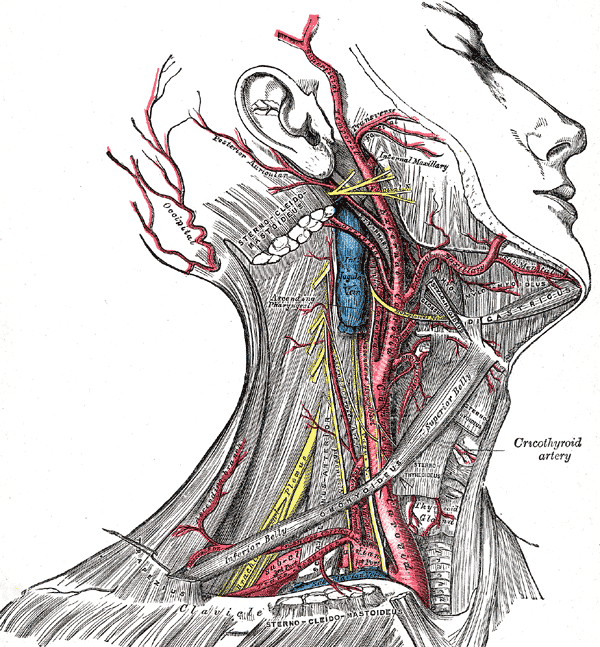
The common carotid artery is closely related to the internal jugular vein and the vagus nerve, as all these structures are present within the carotid sheath, a condensation of the deep cervical fascia.
Relations:
Anterolaterally:
Skin, fascia, sternothyroid, sternohyoid, sternocleidomastoid and the superior belly of omohyoid.
Posteriorly:
Sympathetic trunk, prevertebral muscles, transverse processes of the lower four cervical vertebra and the vertebral vessels (in lower part).
Laterally:
Internal jugular vein and vagus nerve (located posterolaterally).
Medially:
Pharynx, larynx and below them; the trachea and esophagus, also is the lobe of the thyroid gland.
Branches:
No branch arises from the common carotid artery, except the two terminal branches:
1. External carotid artery
2. Internal carotid artery
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself