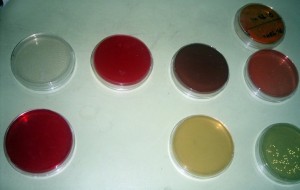
The main types of culture media are:
- Basic media
- Enriched and enrichment media
- Selective media
- Differential media
- Transport media
Basic Media
These are simple media such as nutrient agar and nutrient broth, that will support the growth of microorganisms, which do not have special nutrient requirements e.g. nutrient agar. They are often used in preparation of enriched media, to maintain the stock cultures of controlled strains of bacteria and for subcultering pathogens from differential or selective media prior to performing biochemical and serological identification tests.
Enriched and Enrichment Media
Enriched media are the artificial culture media that are enriched with whole blood, lyze blood, serum, extra peptones, special extracts or vitamins to support the growth of pathogens which require additional nutrients or growth stimulants e.g. blood agar, chocolate agar, trypton soya agar.
Enrichment media are liquid media that increase the number of pathogens due to the presence of certain substances that discourage the multiplication of unwanted bacteria e.g. selenide F broth. This is used for enrichment of Salmonella in faeces or urine. Brain heart infusion is used for blood culture specimens.
Selective Media
These are the media which contain substances that prevent or slow down the growth of microorganisms other than the pathogens for which the media are intended e.g. xylene lysine deoxy cholate
Differential Media
These are the media to which indicators, dyes or other substances are added to differentiate microorganisms. E.g. thiosulphate citrate bile salt sucrose (TCBS), Mac Conkey’s agar, cysteine lactose electrolyte deficient (CLED). The indicator in Mac Conkey’s medium is phenol red and that in CLED is bromothymol blue.
Transport Media
These are mostly semi-solid media that contain ingredients to prevent the overgrowth of commensals and ensure the survival of aerobic and anaerobic pathogens when specimens cannot be cultured soon after collection. Their use is particularly important when transporting microbiological specimens from health centers to district microbiology lab e.g. Cary Blair medium for preserving enteric pathogens.
Nutrient Agar
It is a basic culture medium. Its ingredients are:
- Peptones
- Sodium chloride
- Agar
It does not support growth of certain Streptococci like group A and group B Streptococci, Pneumococci, Neisseria, Haemophilus, etc.
Blood Agar
It is an enriched medium. On this medium, Staphylococci give golden color or whitish colonies, which may be hemolytic. Group A and group B Streptococci give beta hemolytic colonies while pneumococci give alpha hemolytic colonies. In this medium 7% whole blood is added to nutrient agar, after sterilization.
Chocolate Agar
When the blood agar is heated, RBCs are broken down and media becomes chocolate in color. This medium facilitates growth of Neisseria, haemophilus and pneumococci.
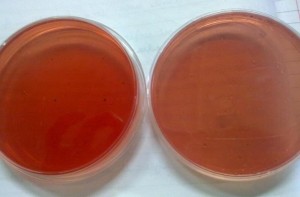
Mac Conkey’s Agar
It is differential medium used to differentiate lactose fermenting bacteria from non-lactose fermenters. Lactose fermenters form pink colonies while non-lactose fermenters give pale yellow colonies.
Phenol red is the indicator present in this medium.
Mac Conkey’s agar (left) and Crystal Mac Conkey’s agar (right)
CLED
It is used for isolation of urinary pathogens. Lactose fermenters give yellow orange colonies and non-lactose fermenters form blue colored colonies. It is a selective as well as differential medium. Bromo thymol blue is the indicator.
TCBS
It is a selective and differential medium for growth of Vibrio cholera which give yellow colored colonies and other Vibrio species, e.g. Vibrio parahemolyticus, which gives green colored colonies.
It is an alkaline medium (pH >8.4)
Sabouraud Agar
It is a selective medium used for isolation of various fungi.
Robertson cooked meat Medium
It is a nutritious fluid broth used in enrichment, rapid growth and maintenance of microorganisms, especially anaerobes.
Lowenstein Jensen Medium
It is a selective medium for growth of mycobacterium tuberculosis, which takes about 6-8 weeks for growth and the colonies are rough and pale yellow. Ingredients include malachite green which acts as an indicator and also inhibits the growth of other microorganisms.
Alkaline Peptone Water
It is an enrichment medium used for Vibrio cholera. It can also be used for transportation if time of transportation is less than 10 hours.
Brain Heart Infusion
It is used for enrichment of blood specimen.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself