Leishmaniasis is a group of diseases caused by Leishmania species, which are obligate intracellular parasites, belonging to phylum protozoa.
Classification
Phylum: Protozoa
Subphylum: Sarcomastigophore
Class: Zoomastigophore
Genus: Leishmania
Specie: L. donovani
L. tropica
Different species of Leishmania cause different diseases. L. donovani causes visceral leishmaniasis, while L. tropica causes cutaneous leishmaniasis.
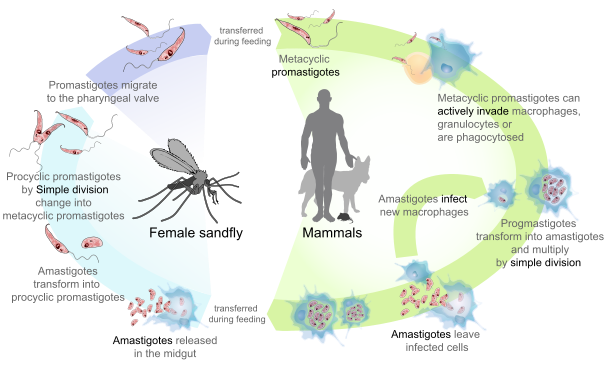
Life Cycle
Source
Animals are natural reservoirs of this disease
Distribution
World wide distribution, found in Africa, sub-continent, Middle East and South America.
Habitat
Resides in reticuloendothelial system of human beings. Organisms occur in two forms:
a. Promastigote form –flagellated
b. Amastigote form
Vector of disease is sandfly, when sandfly bites infected individual, it picks up amastigote form. This then converts into promastigote form in gut of sandfly by binary fission. The promastigote form then multiplies and travels to pharynx of sandfly. Sandfly transmits this form when it bites another host. In dermis of host, i.e. humans, the promastigote enters macrophages, loses its flagellum and becomes amastigote form. This lives and multiplies within reticuloendothelial system. The disease remains localized to skin or mucous membranes in case of infection with L. tropica, and involves different organs in cases of L. donovani.
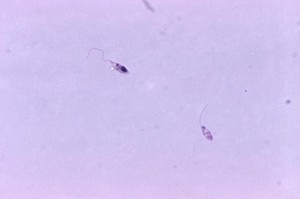
Morphology
Amastigote
These are small, round and oval bodies 25 µm in diameter. They contain a nucleus and an elongated body called kinetoplast.
Promastigote
This developing form is found in sandfly. These are elongated flagellated bodies having a nucleus and a kinetoplast.
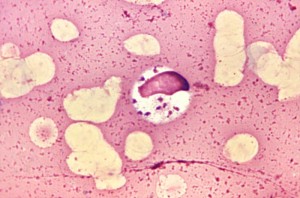
Lab Diagnosis
Visceral Leishmaniasis
LD bodies are seen in smear prepared from blood, bone marrow or splenic puncture. Organisms can be cultured in lab as well, but they develop in culture media after several weeks. Animal inoculation and molecular methods can also be applied.
Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
LT bodies can be seen in specimen prepared from skin and mucous membrane. Promastigote form in smears provide direct evidence of disease. Intradermal skin test can provide indirect evidence of this form of disease.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself