Endocrine System uses chemical signals for cell to cell communication. It coordinates the function of cells.The response to an endocrine signal occurs within minutes to hours.
Photo by GreenFlames09
Hormones – cell to cell communication molecules
- Use chemical signals for cell to cell communication
- Coordinate the function of cells
- Response to an endocrine signal occur within minutes to hours
Endocrine Glands
- Ductless glands
- Clumps or cords of secretory cells surrounded by network of small blood vessels
- Hormones are poured directly into blood
The signal chemicals are
• Made in endocrine cells
• Transported via blood
• Receptors are on target cells
Neurotransmitters are chemicals secreted by neurons that diffuse across a small gap to the target cell. Neurons use electrical signals as well.
Hormones secreted by neurons are known as neurohormones. Thus they have a neural origin. e.g.
• Anti Diuretic Hormone (ADH)
Exocrine Glands- Pour secretion through duct system
Dual Glands- Endocrine/ Exocrine function – both present e.g., Pancreas
Paracrine Horomones
• Site of synthesis & site of action close together
• Act on adjacent cells
Autocrine Horomnes
Site of synthesis & effector (target) – same cell
Recurrent / Periodic Glands
• Appear & disappear according to physiological demand
• eg., Corpus Luteum & Placenta
Classification of Hormones
1. Proteins & Polypeptides
2. Steroids
3. Amino Acid – Tyrosine derivative
Proteins & Polypeptides
< 100 amino acids – peptide
> 100 amino acids – protein
Examples:
• Ant. & Post. Pituitary hormones
• Insulin / Glucagon
• Growth hormone
• Parathyroid hormone etc.
Steroids
Have Cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene nucleus
Example:
• Cortisol
• Aldosterone
• Testosterone
• Estrogen etc.
Amino Acid – Tyrosine Derivatives
• Thyroid Hormones
• Epinephrine / Norepinephrine
Transport
– Globulin
– Albumin
only 2 – 3% is in FREE FORM (biologically active)
Storage
• Not usually stored – except
1. THYROXINE –by combining with TYHYROGLOBULIN
2. INSULIN – can be stored in β – cells of pancreas
in complex form with Zinc
3. ADH – by combining with
– Neurophysin – I
– Neurophysin – II
Inactivation / Clearance from Plasma
i. Metabolic destruction by tissues
ii. Binding with tissues
iii. Excretion by LIVER into BILE
– By conjugation with glucoronide etc.
iv. Excretion by kidneys into urine
v. Skin
Modes of Hormonal Regulation
(A) Feed back system
(B) Neural Control
(C) Chronotropic Control
(A) Feed back system (Mainly)
– Negative Feed back (almost always)
– Positive Feed back
i. Hormone – Hormone level
ii. Substrate – Hormone level
iii.Mineral – Hormone level
(B) Neural Control
i. Adrenergic
ii. Cholinergic
iii.Dopaminergic
iv.Serotinergic
v. GABAergic
(C) Chronotropic Control
i. Diurnal Rhythm
ii. Sleep – Wake Rhythm
iii.Menstrual Rhythm
iv.Seasonal Rhythm
v. Developmental Rhythm
vi.Circhoral Rhythm
vii.Ultradian Rythm
Feedback System
i. Hormone – Hormone Negative Feed Back

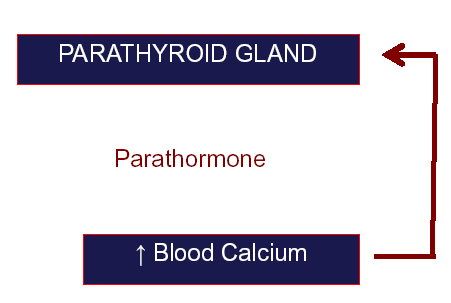
ii. Substrate – Hormone Negative Feed Back

iii. Mineral – Hormone Negative Feed Back
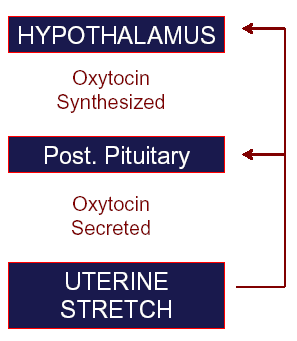
iv. Parturition – Oxytocin Positive Feed Back
v. Suckling – Oxytocin Positive Feed Back
Negative Feedback controls
Long & Short loop reflexes

(C) Chronotropic Control
1. Diurnal Rhythm
– ↑ Prolactin secretion during night
2. Sleep Wake Rhythm
– Infants / Children – ↑ GH during sleep
– ↑ ACTH & ↑ Cortisol during sleep
3. Menstrual Rhythm
– ♀ reproductive life (15 – 45 yrs)
– Ovarian steroids – Estrogen & Progesterone
4. Seasonal Rhythm
– Esp in lower animals (Frogs – Hibernate)
5. Developmental Rhythm
– eg., Growth Rythm
6. Circhorral Rhythm
– change on hourly basis eg., insulin after food intake
7. Ultradian Rhythm
– moment to moment change eg., epinephrine
Want a clearer concept, also see
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself