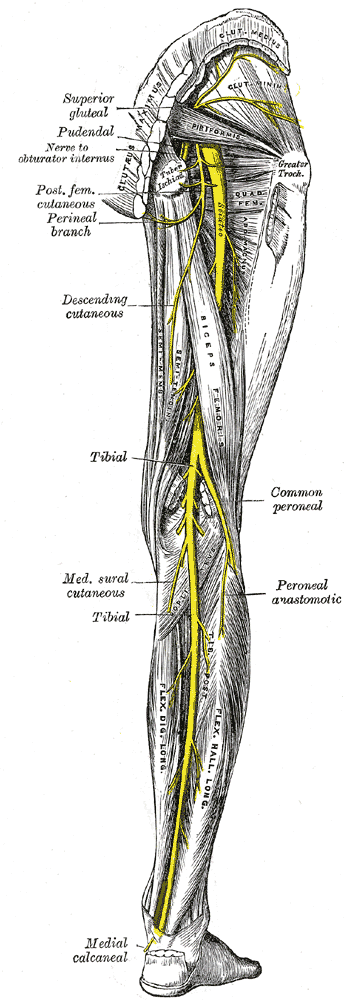
The common peroneal nerve is the smaller of the terminal branches of the sciatic nerve, the other being the tibial nerve. It runs downwards through the popliteal fossa and closely follows the medial border of the biceps muscle. It leaves the popliteal fossa by crossing the lateral head of the gastrecnemius superficially and passes behind the head of fibula. It winds laterally around the neck of the bone and pierces the peroneus longus muscle. Here, it divides into its two terminal branches; the superficial and the deep. As the nerve lies on the lateral aspect of the neck of fibula, it is subcutaneous and can be easily rolled against the bone.
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
Branches:
1. Cutaneous branches:
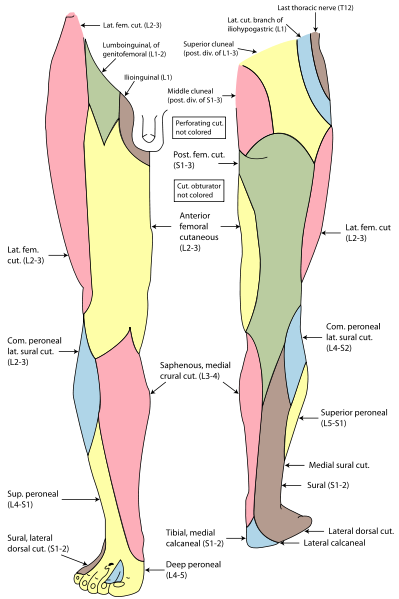
The sural communicating branch joins the sural nerve. The lateral cutaneous nerve of the calf supplies the lateral side of the back of skin of leg.
2. Muscular branches:
Muscular branches supply the short head of biceps femoris arising high up in the popliteal fossa.
Articular branches:
Articular branches supply the knee joint.
Terminal Braches:
1. Superficial Peroneal Nerve
2. Deep Peroneal Nerve
Superficial Peroneal Nerve:
Superficial peroneal nerve arises within the substance of peroneus longus on the lateral side of neck of fibula. It descends between the peroneus longus and peroneus brevis muscles. In the lower part of the leg, it is subcutaneous.
Branches:
1. Muscular branches:
Muscular branches supply the peroneus longus and brevis muscles.
2. Cutaneous branches:
The medial and lateral branches are distributed to the skin of the lower part of the front of leg and the dorsum of the foot. The branches supply the dorsal surfaces of the skin of all the toes except the adjacent sides of the first and second toes as well as the lateral side of the little toe.
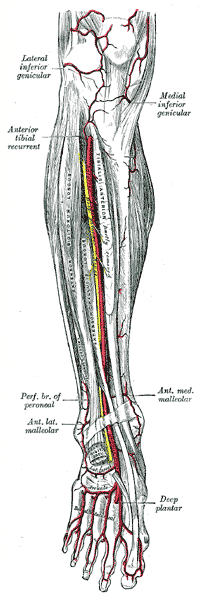
Deep Peroneal Nerve:
The deep peroneal nerve arises within the substance of peroneus longus lying on the lateral side of neck of fibula and enters the anterior compartment. After piercing the anterior fascial septum, it descends deep to extensor digitorum longus. Here, at first it lies lateral, then anterior and finally lateral to the anterior tibial artery. It passes behind the extensor retinaculum.
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
Branches:
1. Muscular branches:
Muscular branches supply the tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, peroneus tertius and the extensor hallucis longus.
2. Articular branches:
Articular branches supply the knee joint.
After passing deep to extensor retinaculum, the deep peroneal nerve lies on the lateral side of the dorsalis pedis artery. It, then, divides into:
1. Terminal branches: which are the articular branches to joints of the foot.
2. Medial branches: which supply the skin of adjacent sides of the big and second toe.
3. Lateral branches: which supply the extensor digitorum brevis muscle.
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself