The examination of squint may be summarized in the steps mentioned below:
1. Introduction
2. Visual acuity, best corrected visual acuity, (if less than 8 yrs cycloplegic refraction)
3. Torch Examination:
- Hirschbergs test
- Pseudostrabismus
- AHP
- Pupil (direct, consensual, RAPD)
- Epicanthus, telecanthus
- Ocular torticollis
4. Extraocular Movements:
- Versions
- Vergence
- Belchosky
- Diplopia
- Ductions if any obstruction in versions
- Saccades
- Duane’s retraction
- Nystagmus
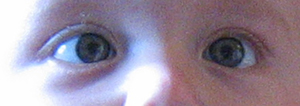
5. Cover Tests:
Cover, uncover, alternate cover and uncover test
i. Distant with glasses
ii. Near without glasses
6. Amount of Deviation:
a. Prism cover test (Manifest squint)
b. Maddox rod/wing (Ptosis)
| Non Paralytic Squint Binocular functions | Paralytic Squint |
| BSVTitmus/TNO/ synoptophore | Examination of Cranial Nerves:CN V : Sensation of face and muscles of mastication |
| Suppresion/ suppression scotoma | CN VII Frowning, close eyes, show teeth, blow air in mouth |
| 4 prism diopter base out test | CN VIII Click on both ears |
| Worth four dot | CN III Tremor, hemiparesis, gait |
| Bagolini Striated glasses | |
| Fixation David star |
7. Slit Lamp examination:
Anterior segment for sensory deprivation EXO/ESO
8. Fundoscopy:
9. Thank the patient
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself