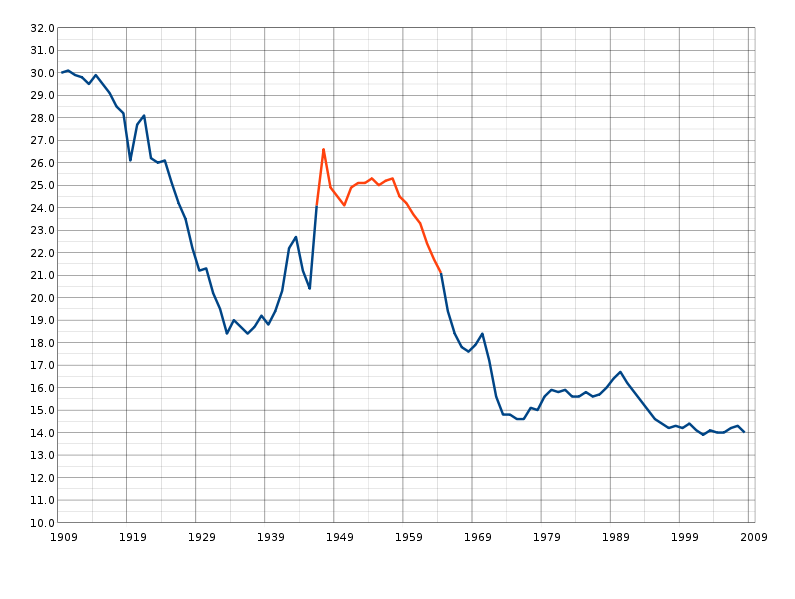
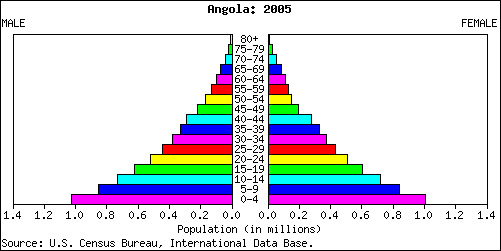
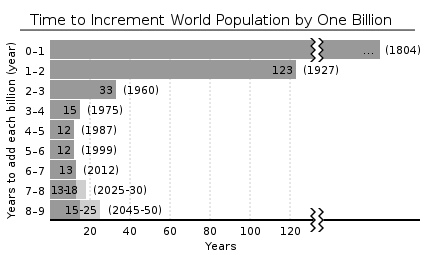
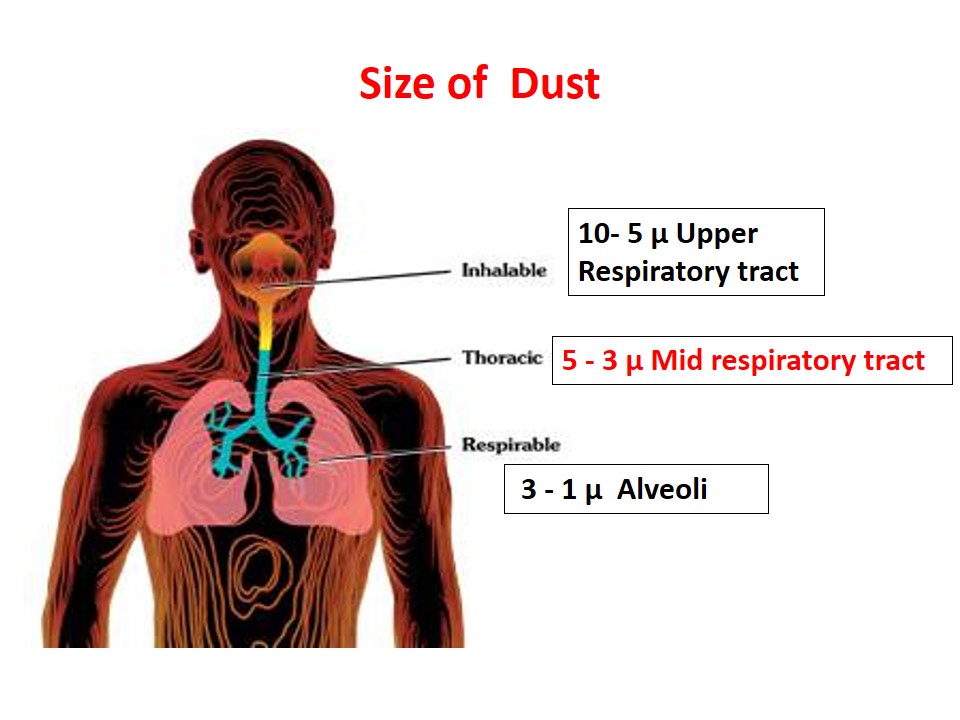
Investigator may collect data by direct interview, mail of questionnaire, review of previously collected data, histories and other similar methods.
By comparing the two groups, investigator can explain why the cases developed the outcome and controls did not.
Control group can also be some other group in a hospital having some other treatment than case group.
Selection of Cases and Controls
Specific diagnostic and clinical criteria is used to identify them as a case. Criteria should be:
a. Comprehensive
b. Specific
c. Homogenous samples
Population based study
General population is taken.
Advantages: generalizability
Disadvantages: Too expensive
Hospital based study
Patients are obtained from the hospital.
Advantages: Easy
Disadvantages: Generalizability is less. Cases are used within a specific period.
Cases and controls are matched on a variety of relevant factors:
1. Age
2. Sex
3. Race
4. Occupation
Any other variable that influences the disease status.
Sources
a. Hospital available controls
b. Population based controls having that disorder
c. Special groups
i. Family members
ii. Friends of those with disease
Hospital available controls are different from healthy subjects who might be exposed to the same risk factors, as they are ill so the effects would be minimized.
Analysis Issues:
a. Selection bias
b. Misclassified
c. Observation bias
d. Interviewer bias
e. Recall bias
f. Confounding effect of extraneous variables
Case Definition
It is the diagnostic and clinical criteria that identifies a person as a case.
Read more about research methodology…
- Introduction to Research Methodology
- The Basics of Research Methodology
- A Concept of Research Process
- Choosing Research Topics
- Review of Literature for Research Purpose
- Formulating a Research Question
- Formulation of Objectives in Research
- Variables in Research
- Developing a Questionnaire in Research
- Sample Selection and Sampling Techniques
- Introduction to Study Designs
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself