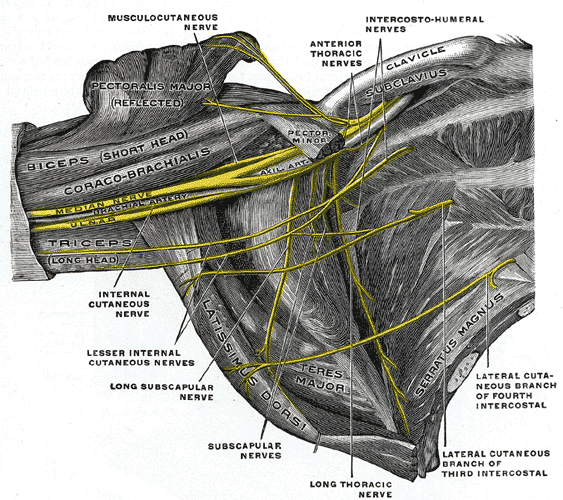
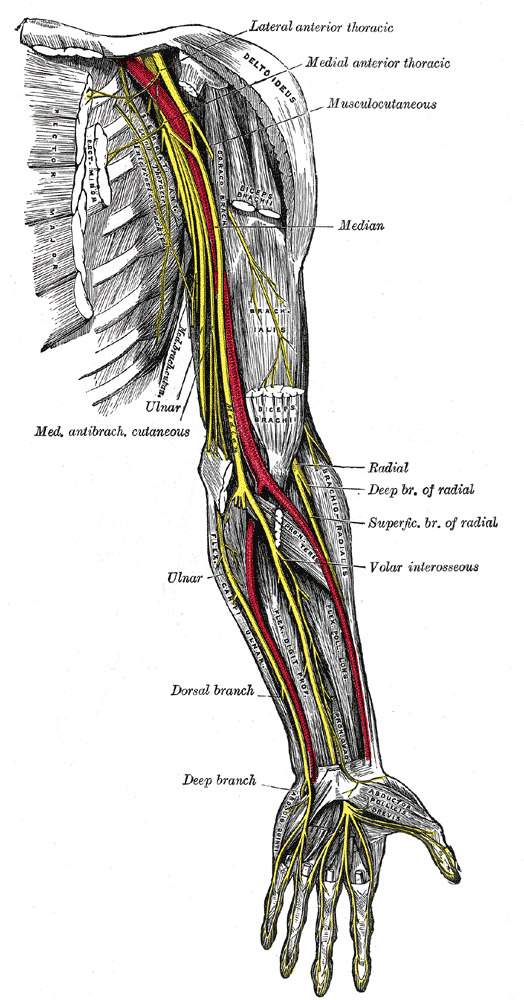
Median nerve, originating from the medial and lateral cords, lies on the lateral side of the brachial artery.
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
Halfway down its course, it crosses the brachial artery and continues on its medial side. It gives no branches in the upper arm, except the vasomotor nerve to the brachial artery.
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
The median nerve leaves the cubital fossa by passing between the two heads of the pronator teres. It continues down, lying behind the flexor digitorum superficialis and rests posteriorly on the flexor digitorum profundus.
At the wrist, the median nerve emerges from the lateral border of the flexor digitorum superficialis lying behind the tendon of palmaris longus.
It enters the palm behind the flexor retinaculum.
Branches:
1. Muscular branches:
Muscular branches supply the pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus and the flexor digitorum superficialis.
2. Articular branches:
Articular branches supply the elbow joint.
3. Anterior Interosseous nerve:
Anterior interosseous nerve arises as the median nerve emerges between the two heads of the pronator teres. It passes down the anterior surface of the interosseous membrane between the flexor pollicis longus and the flexor digitorum profundus. It ends on the anterior surface of the carpus.
a. Muscular branches:
Muscular branches supply the flexor pollicis longus, pronator quadratus and the lateral half of flexor digitorum profundus.
b. Articular branches:
Articular branches supply the wrist, the distal radioulnar joint and the joints of hand.
4. Palmar cutaneous branch:
The palmar cutaneous branch given off in front of the forearm crosses anterior to the flexor retinaculum and supplies the skin over the lateral aspect of the palm.
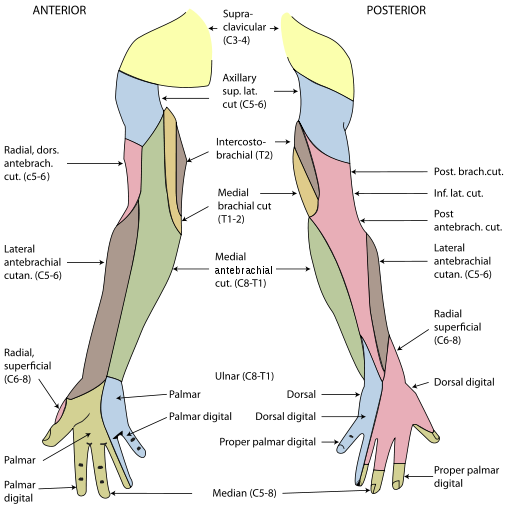
Cutaneous nerve supply of arm, forearm and hand
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
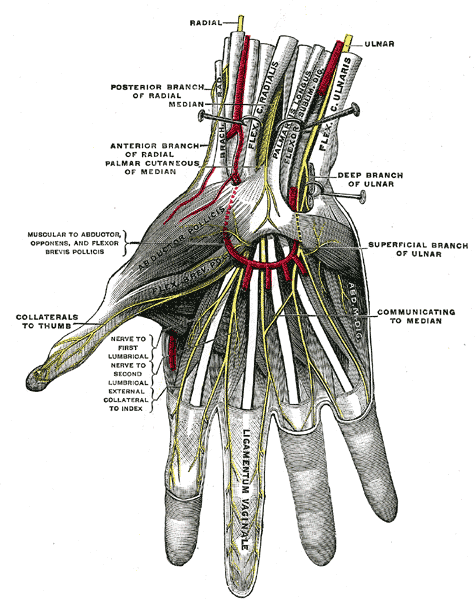
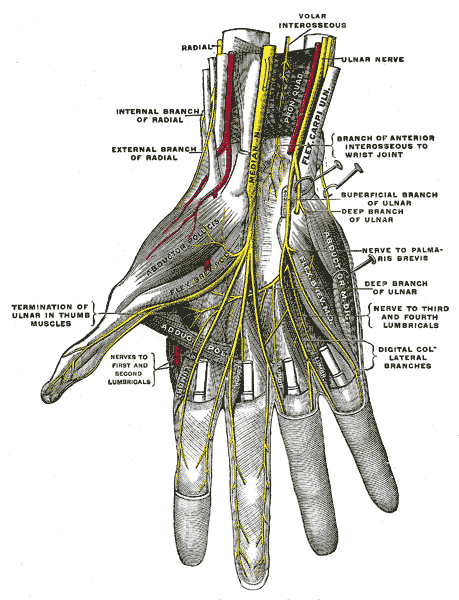
The median nerve enters the palm by passing behind the flexor retinaculum and through the carpal tunnel. It immediately divides into two terminal branches; the medial and lateral branches.
1. Muscular branch:
Muscular branch takes a recurrent course around the lower border of the flexor retinaculum and lies about one finger breadth distal to the tubercle of scaphoid. It supplies the muscles of the thenar eminence and the first lumbrical.
2. Cutaneous branches:
Cutaneous branches supply the palmar aspect of the lateral three and a half fingers and the distal half of the dorsal aspect of each finger. One branch also supplies the second lumbrical muscle.
Superficial palmar arch
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
Deep Palmar Arch
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself