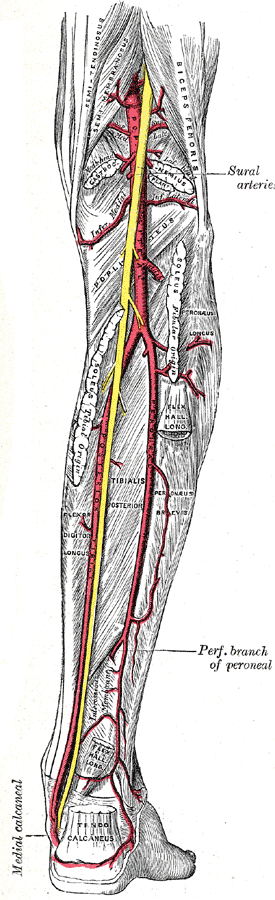
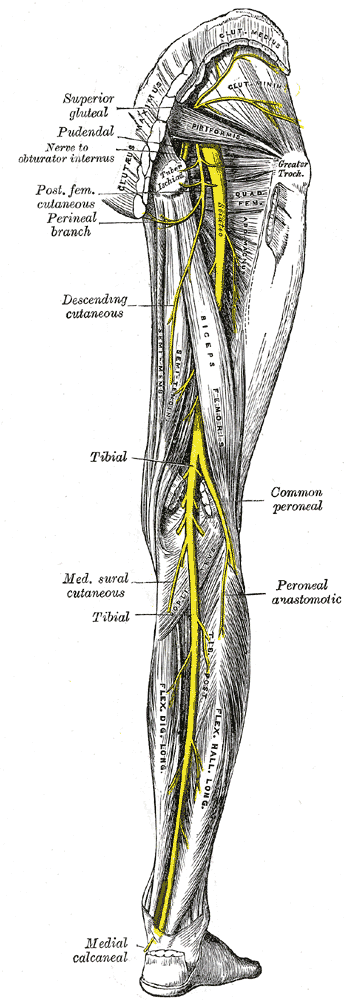
Tibial nerve is the larger of the terminal branches of sciatic nerve, the other being the common peroneal nerve. It arises in the lower third of thigh and runs downwards through the popliteal fossa, at first lying on the lateral side of the popliteal artery, then posteriorly and finally on the medial side. The popliteal vein lies between the artery and nerve throughout its course. The tibial nerve enters the posterior compartment of the leg by passing beneath the soleus muscle.
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
Branches in Popliteal Fossa:
1. Cutaneous branches:
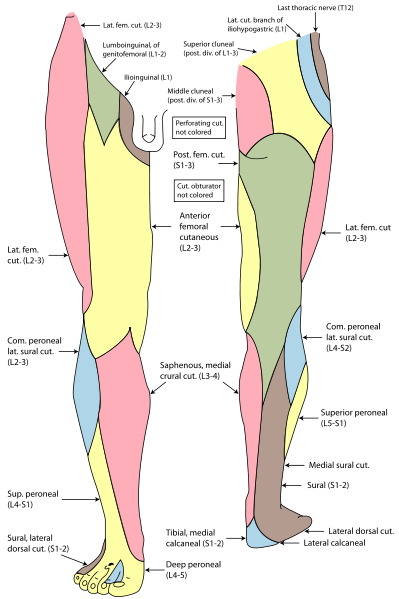
The sural nerve descends between the two heads of the gastrecnemius and is joined by the sural communicating branch of the common peroneal nerve. Numerous small branches arise from the sural nerve to supply the skin of calf and the back of leg. The sural nerve accompanies the small saphenous vein behind the lateral malleolus.
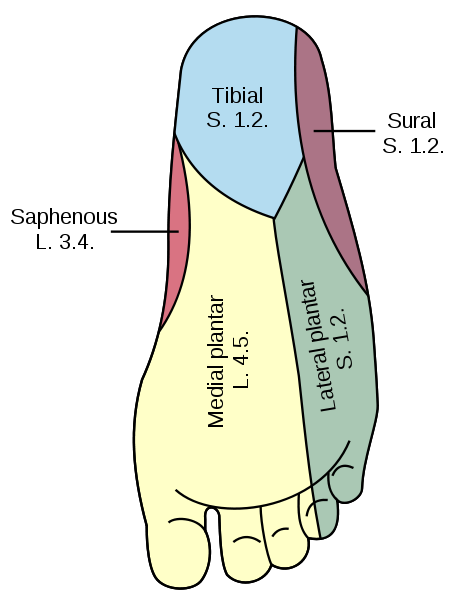
It is distributed to the skin along the lateral border of the foot and the lateral side of the little toe.
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
2. Muscular branches:
Muscular branches supply both heads of the gastrecnemius, plantaris, soleus and the popliteus muscles.
3. Articular branches:
Articular branches supply the knee joint.
Tibial nerve lies on the posterior surface of tibialis posterior muscle and further down the leg, on the posterior surface of tibia. The nerve accompanies the posterior tibial artery and lies at first on its medial side, then crosses posterior to it and finally lies on its lateral side. The nerve along with the artery passes behind the medial malleolus, between the tendons of the flexor digitorum longus and the flexor hallucis longus. It is covered here by the flexor retinaculum. It ends by dividing into medial and lateral plantar nerves.
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
Branches in the Leg:
1. Muscular branches:
Muscular branches supply the soleus, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus and tibialis posterior.
2. Cutaneous branches:
The medial calcaneal branch supplies the skin over the medial surface of the heel.
3. Articular branches:
Articular branches supply the ankle joint.
Terminal branches:
1. Medial Plantar Nerve:
The medial plantar nerve arises from beneath the flexor retinaculum and runs forward deep to the abductor hallucis muscle accompanied by the medial plantar artery. In comes to lie in the space between the abductor hallucis and the flexor digitorum brevis muscles.
Branches:
1. Muscular branches:
Muscular branches supply the abductor hallucis, flexor digitorum brevis, flexor hallucis brevis and the first lumbrical.
2. Cutaneous branches:
The plantar digital nerves run to sides of the medial three and a half toes. They extend onto the dorsum and supply the nail beds and the tips of the toes.
Lateral Plantar Nerve:
The lateral plantar nerve arises from beneath the flexor retinaculum and runs forward deep to the abductor hallucis and flexor digitorum brevis. It is accompanied by the lateral plantar artery. When reaches the base of the fifth metatarsal bone, it divides into superficial and deep branches.
Superficial terminal branch:
Superficial terminal branch supplies the flexor digiti minimi and interosseous muscles of the fourth inter metatarsal space. The plantar digital branches pass on to the side of the lateral one and a half toes. The superficial terminal branch extends onto the dorsum and supplies the nail beds and the tips of toes.
Deep terminal branch:
The deep terminal branch curves medially with the lateral plantar artery to supply the adductor hallucis, second, third and fourth lumbricals along with all interossei except the fourth inter metatarsal space.
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself