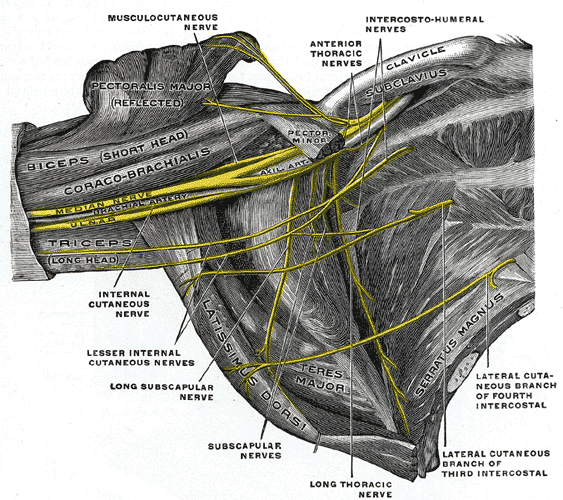
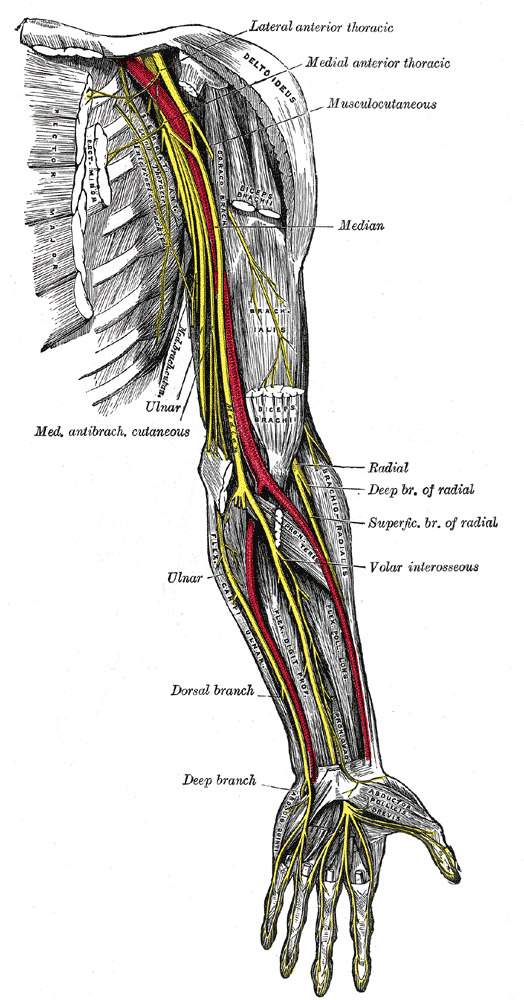
Ulnar nerve arises from the medial cord of the brachial plexus, lying on the medial side of the brachial artery. In the middle of the arm, at the insertion of coracobrachialis, the ulnar nerve pierces the medial fascial septum. It is accompanied by the superior ulnar collateral artery and enters the posterior compartment. It passes behind the medial epicondyle. No branches are given off in the anterior compartment of the upper arm.
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
On passing behind the septum, the ulnar nerve is covered posteriorly by the medial head of triceps and is accompanied by the superior ulnar collaterals.
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
At the elbow joint, the ulnar nerve lies behind the medial epicondyle on the medial ligament of the elbow joint. It continues downwards to enter the forearm between the two heads of the origin of flexor carpi ulnaris.
It gives off articular branches to the elbow joint.
The ulnar nerve runs in the forearm between the flexor carpi ulnaris and the flexor digitorum profundus. In the distal two thirds of the forearm, the ulnar artery lies on the lateral side of the ulnar nerve.
At the wrist, the ulnar nerve becomes superficial and lies between the tendons of flexor carpi ulnaris and the flexor digitorum superficialis. The ulnar nerve enters the palm by passing in front of the flexor retinaculum and lateral to the pisiform bone. Here, the ulnar artery lies lateral to it.
Branches:
1. Muscular branches:
Muscular branches are given off to the flexor carpi ulnaris and the medial half of the flexor digitorum profundus.
2. Articular branches:
Articular branches are given off to the elbow joint.
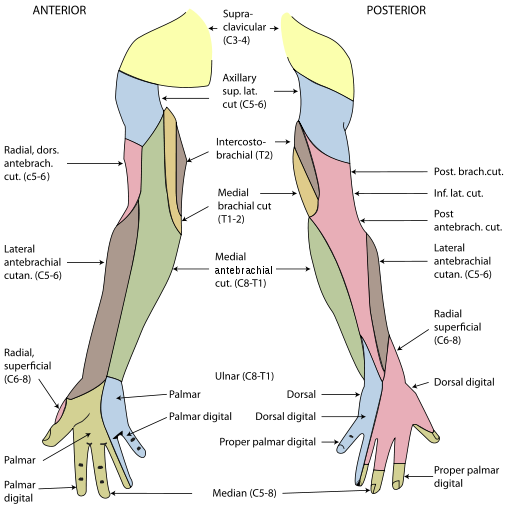
3. Palmar Cutaneous Branch:
A small branch in the middle of the forearm which supplies the skin of the hypothenar eminence.
4. Dorsal Posterior Cutaneous Branch:
A large branch which arises from the distal third of the forearm and passes medially between the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris and ulna. It is distributed to the posterior surface of the hand and fingers.
Cutaneous Supply of Arm, Forearm and Hand
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
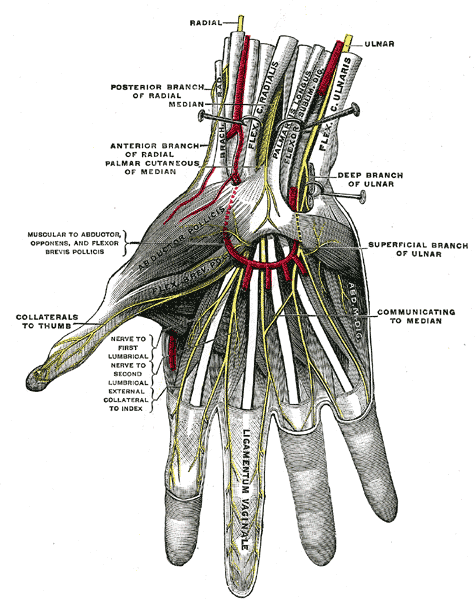
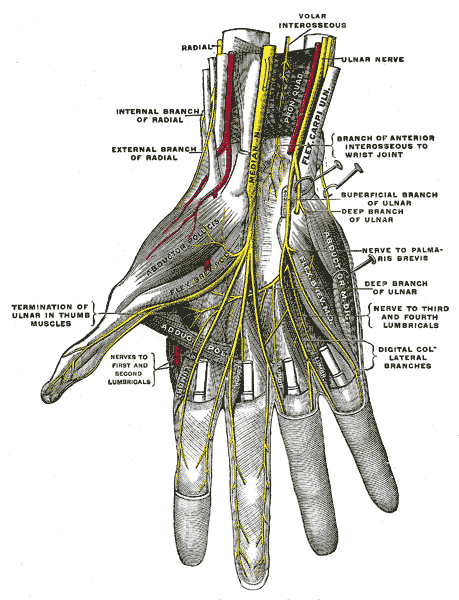
The ulnar nerve enters the palm anterior to the flexor retinaculum along the lateral border of the pisiform. As the nerve crosses the retinaculum, it divides into superficial and deep terminal branches.
Superficial Branch:
The superficial branch descends into the palm, lying in the subcutaneous tissue, between the pisiform and the hook of hamate. The ulnar artery is on its lateral side. This is the site where the nerve and the artery may lie in the fibro-osseous tunnel, the tunnel of Guyon, created by the fibrous tissue derived from the superficial part of the flexor retinaculum. The nerve may be compressed at this site, thus, is clinically important.The nerve gives:
a. Muscular branches:
Muscular branches supply the palmaris brevis.
b. Cutaneous branch:
The cutaneous branch supplies the palmar aspect of the medial side of the little finger and the adjacent sides of the little and ring fingers. It also supplies the distal half of the dorsal aspect of each finger.
Deep Branch:
The deep branch runs backwards between the abductor digiti minimi and the flexor digiti minimi. It pierces the opponens digiti minimi and winds around the lower border of the hook of hamate, passing laterally within the concavity of the deep palmar arch. The nerve lies behind the long flexor tendons and in front of the metacarpal bones and the interossei muscles. It gives off:
a. Muscular branches:
Muscular branches supply the three muscles of the hypothenar eminence as well as the palmar and dorsal interossei, the third and fourth lumbrical and both heads of the adductor pollicis.
b. Palmar Cutaneous Branch:
Palmar cutaneous branch is given off in front of the forearm and crosses anterior to the flexor retinaculum. It supplies the skin over the medial part of the palm.
Superficial Palmar Arch:
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
Deep Plantar Arch:
Grey’s Anatomy 20th edition
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself