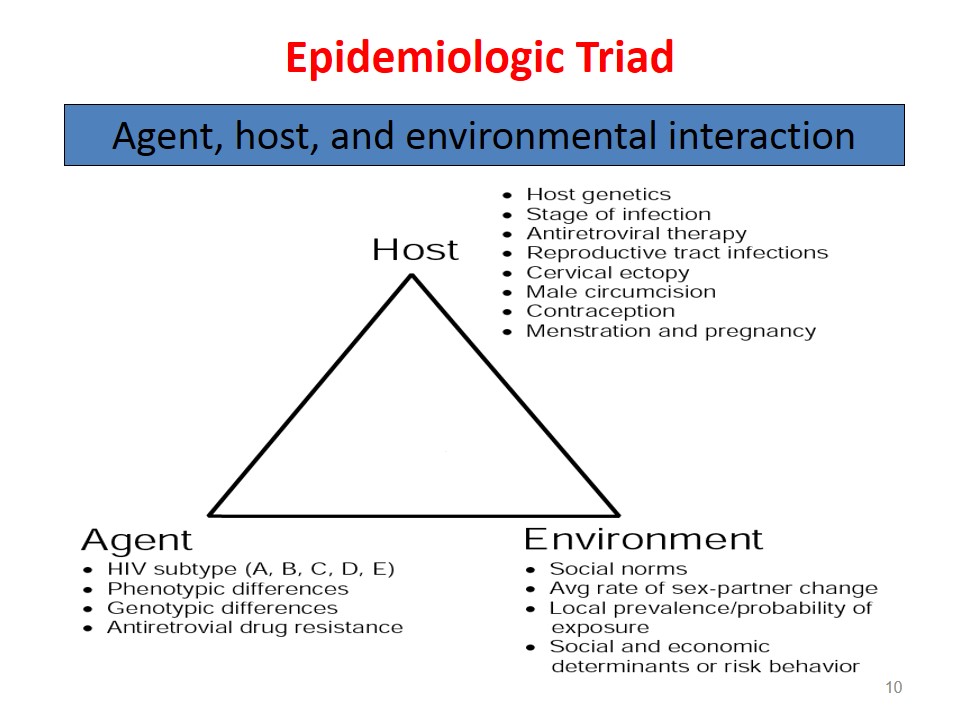
According to Rothman: Any event, act, or condition preceding disease or illness without which disease would not have occurred or … Read More »
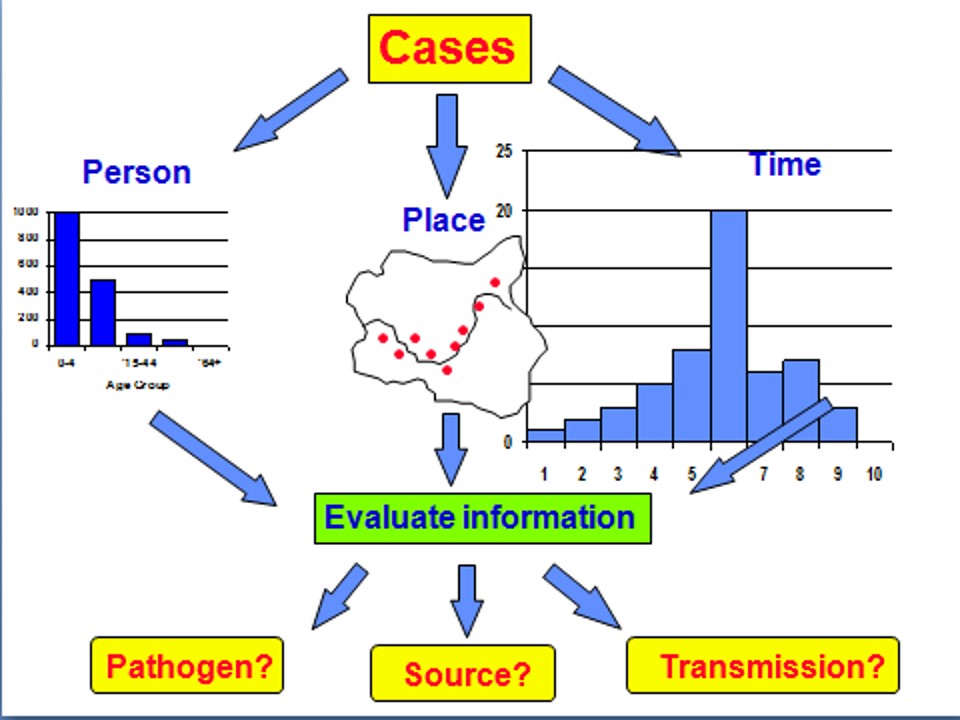
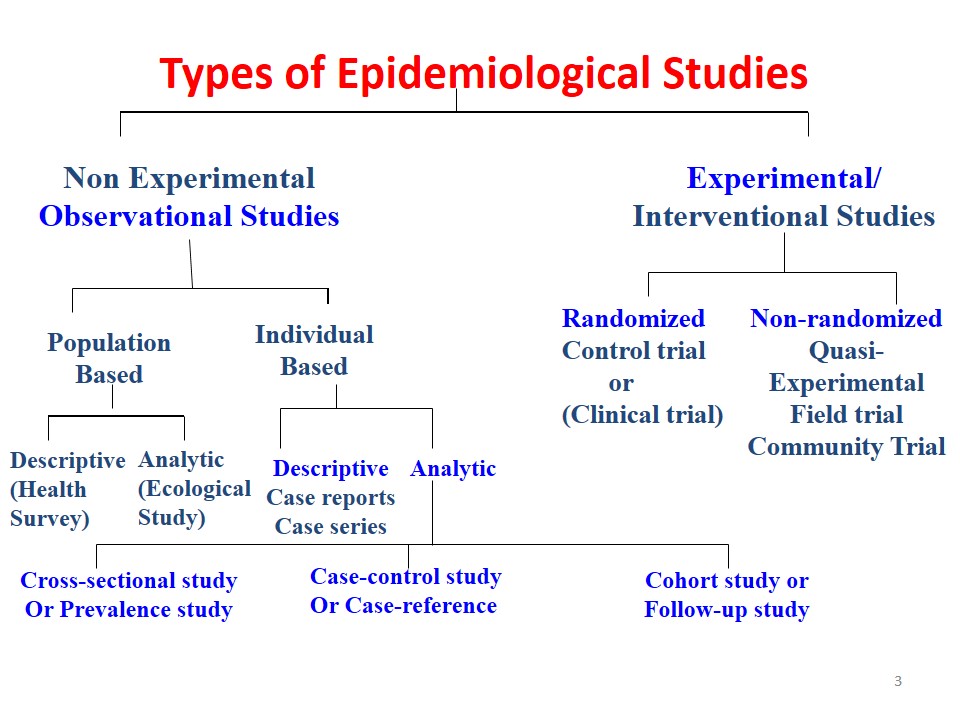
Investigation of Epidemic
Epidemic is the unusual occurrence in a community or region of disease, specific health-related behavior (e.g. smoking) or other health … Read More »
Bias in Research Studies
What is Bias? An error in sampling or testing that systematically under- or over-represents one outcome (answer) over the other. … Read More »
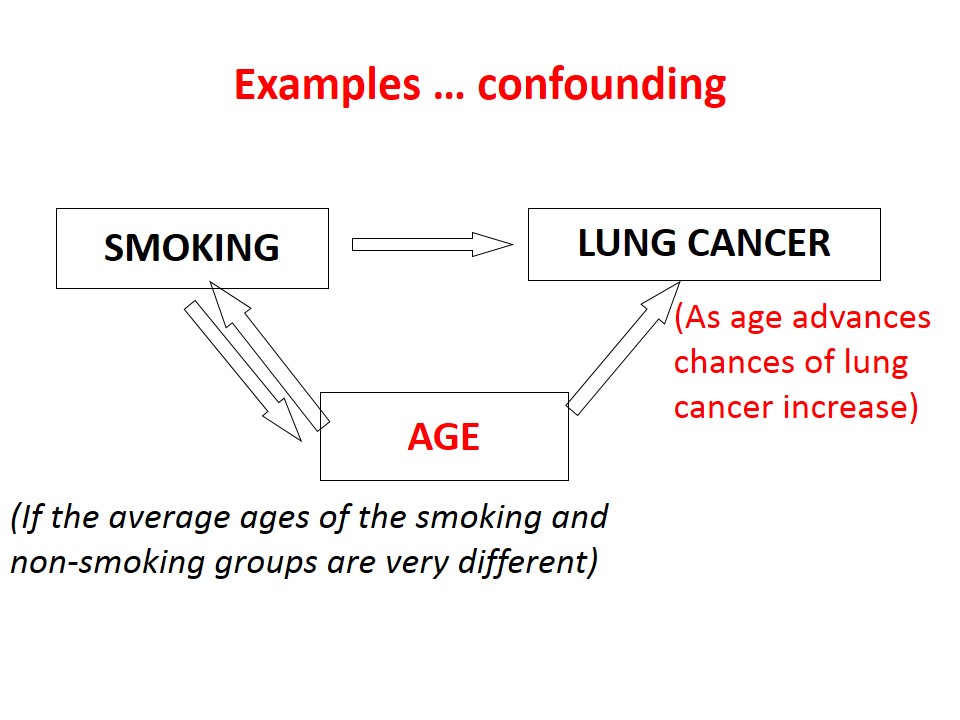
Spurious Association, Multifactorial Causation and Evidence of Causation
Spurious Association Sometimes an observed association between a disease and suspected factor may not be real. For example a study … Read More »
Quasi Experimental Studies
Quasi experimental designs are based on the same structure as experimental designs but lack the randomization, control, or both. These … Read More »
Non-Randomized Trials
Trial is from the French ‘trier’ (to try). Trial may be: • Clinical trial –in which we apply therapeutic interventions … Read More »
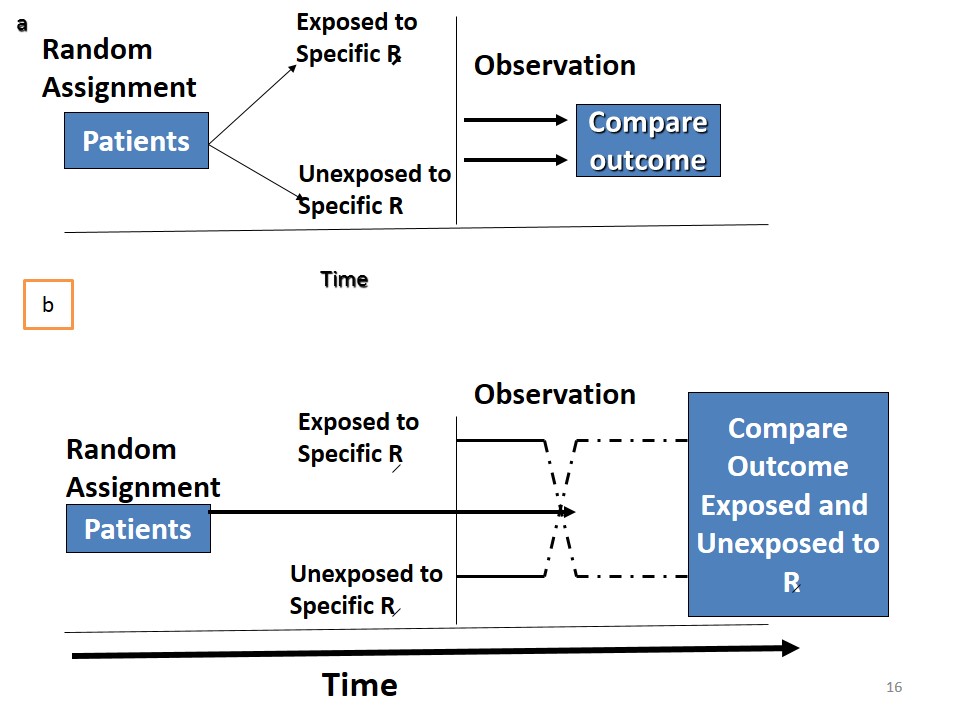
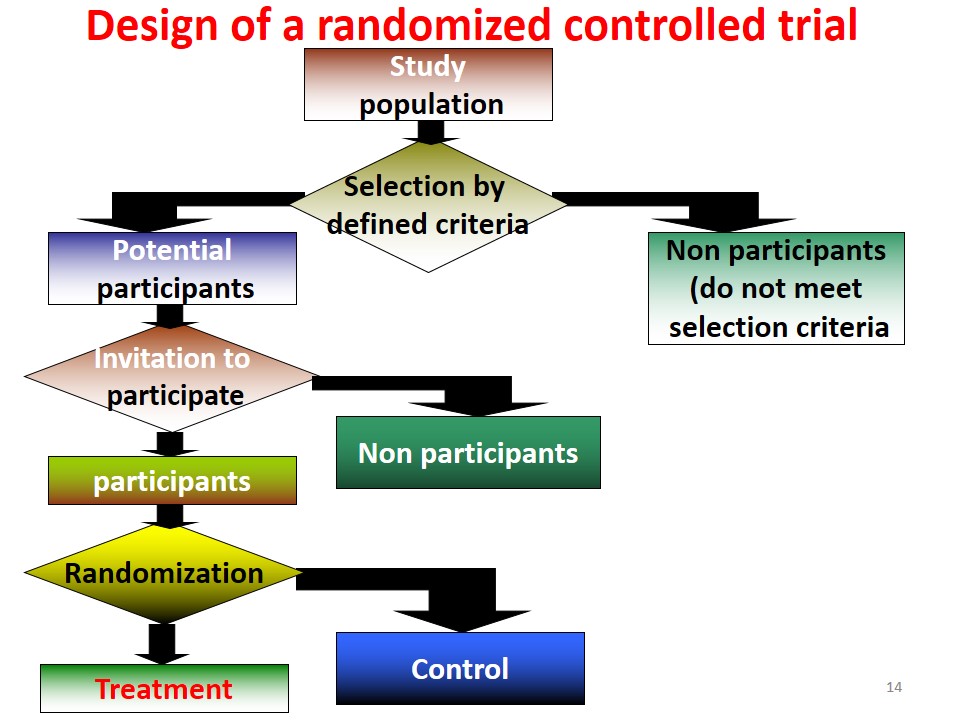
Randomized Controlled Trials
An epidemiological experiment in which subjects in a population are randomly allocated into groups, usually called study and control groups … Read More »
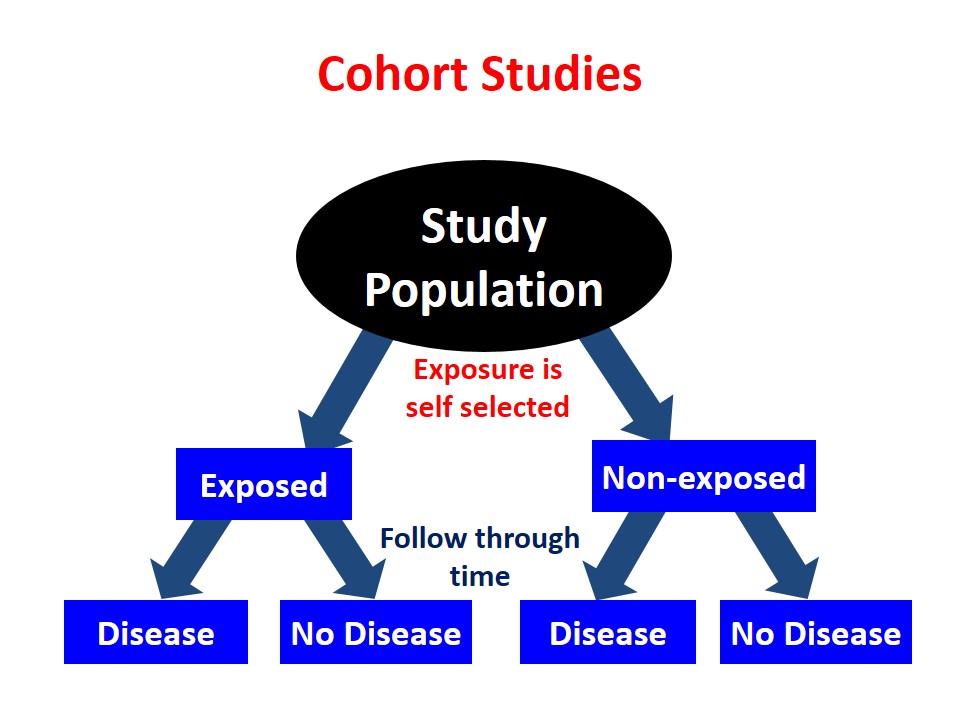
Cohort Studies
Cohort is an ancient Roman military unit of 300-600 men, a group of soldiers marching forward in battle. Cohort studies … Read More »
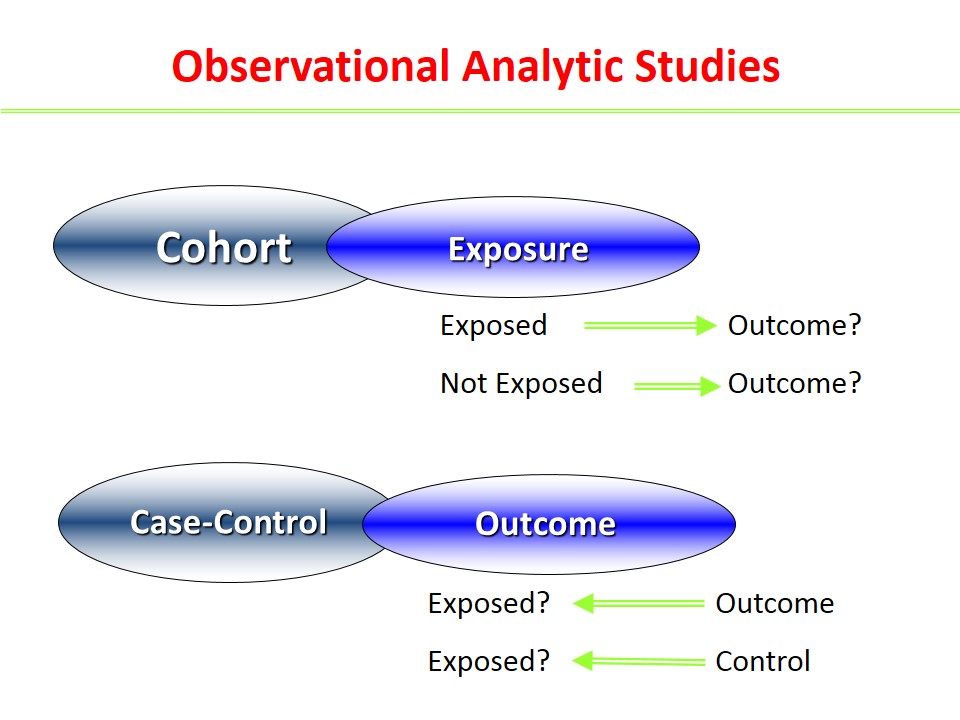
Differences between Case Control and Cohort Studies
The differences between case control and cohort studies may be summarized as follows: Case Control Study Cohort Study • Proceeds … Read More »
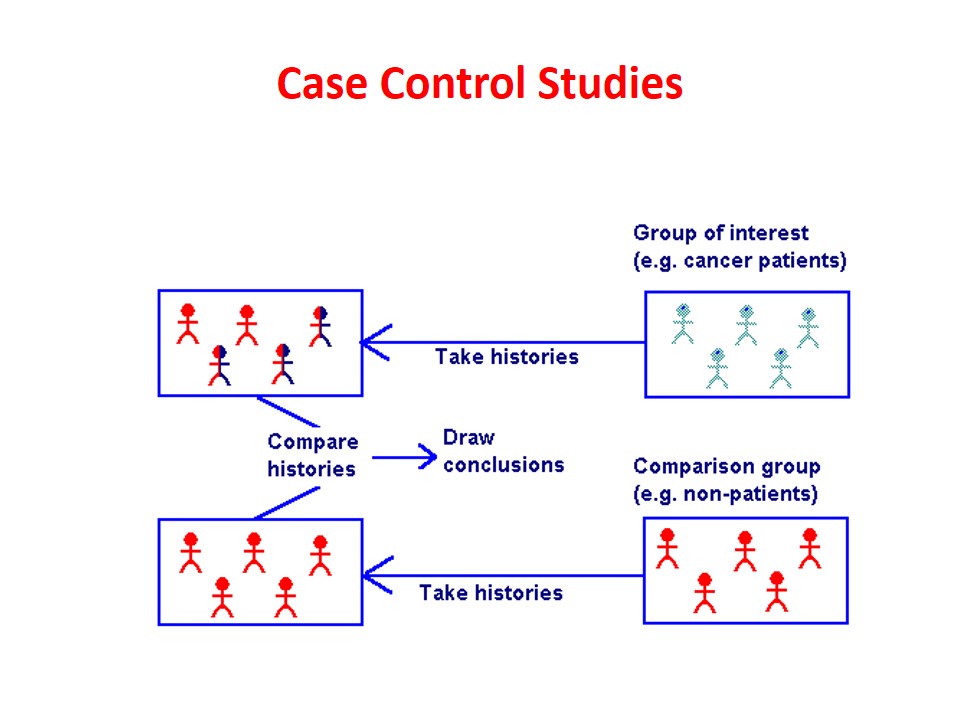
Case Control Studies
In case control study, we start with diseased group (“cases”); which we compare with non-diseased group (“controls”). We look back … Read More »
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself