Pancreas is both an exocrine and an endocrine organ. Pancreatic acini secrete digestive juices while Islets of Langerhans are involved in endocrine functions. Islets of Langerhans are 1 to 2 million in number and produce insulin, glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide.
Islet of Langerhans
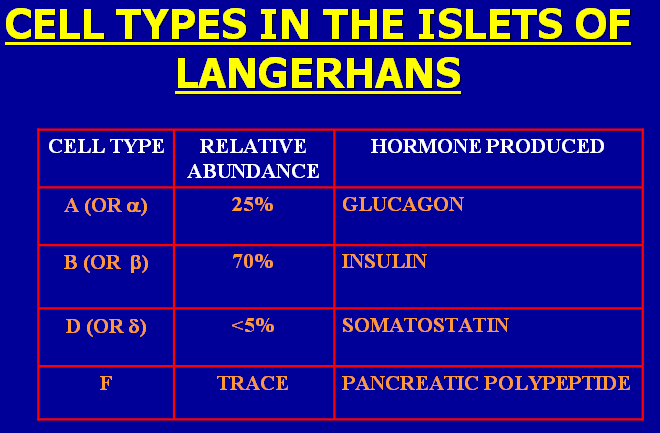
4 types of cells are present. These include
1.Alpha cells:
constitute about 25 % and produce glucagon
2. Beta cells:
constitute about 60 % and produce insulin & amylin
3. Delta cells:
constitute about 10 % and produce somatostatin
4. PP cells:
constitute about 5 % and produce pancreatic polypeptide
Photo by Rafael Mondini Bueno
Insulin Structure
•Hetero Dimer, A & b chain
•A & b chain have 21 and 30 amino acids respectively
•Two intra chain disulfide bridge connnect a7 to b7 and a20 to b19 and third intra chain disulfide bridge in a chain connnects residue 6 and 11
•Insulin formes isologous dimer through h-bonding between peptide groups of b24 and b26 of two monomers and at high concentration these are organized as hexamers each with two atoms of zinc
•At physiologic concentrations insulin is in monomeric form
•Synthesized as prepro hormone (11, 500) 100 amino acid
•23 amino acid leading sequence directes entry in to endoplasmic reticulum and than is removed (9000)
• Converted to insulin and c-peptide by enzymatic change
Metabolism Of Insulin
•Half life < 3-5 minutes
•Metabolized in liver, kidneys and placenta
•About 50% of insulin is removed in a single pass through the liver
•Insulin specific protease
•Glutathione Insulin Transhydrogenase wich reduces the disulfide bonds and then A and B chains are rapidly degraded
Regulation Of Insulin Secretion
40-50 units/day which is 15-20% of hormone stored in gland. Factors regulating insulin secretion are:
A. Glucose
– treshold lelvel 80-100 mg/dl
maximum response at 300-500 mg/dl.
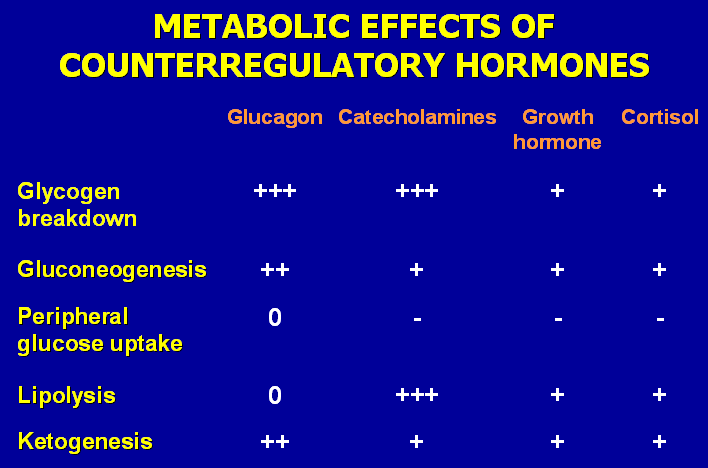
Hormones
– epinephrine
– Somatostatin
– B-adrenergic agonists
– Growth hormone
– Cortisol
– Placental lactogen
– Estrogens
– Progestins
– Glucagon like peptide
– GIP
C. Pharmacologic agent
– sulfonyluria (tabutamide)
Glucagon
•29 amino acids
•Precursor of much larger molecules
•30-40% is glucagon and other is inactive larger molecule
•Half life is 5 minutes
•Liver is main site of glucagon degradation
•Level of glucagon in portal blood is much higher than in peripheral blood
Pancreatic Polypeptide
•Function unknown
•Produced by F. Cells, as 36 amino acid peptide
•Its secretion is increaesd due to
– Increased Protein content in meal
–Fasting
–Decreased Somatostatin secretion
–Exercise
–Acut hypoglycemia
•Suggested function is on hepatic glycogen level and GIT secretion
Somatostatin
•Origin – hypothalamus
•Pancreas d – cell of islets
•Cyclic peptide and produced as prohormone
Actions
1. Inhibits release of other pancreatic hormones and act a paracrine hormone for their regulation
2. Reduces delivery of nutrients from GIT
3. Reduces Gastric emptying & acid formation
4. Reduces G.I.T secretion
5. Reduces Pancreatic exocrine secretion
6. Reduces Splanchic blood flow
7. Slows sugar absorption
Want a clearer concept, also see
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself