Liver Points of Identification: 1. Hexagonal arrangement of hepatic lobules visible. 2. Portal triads present (bile duct, hepatic artery and … Read More »
Case based learning: Fracture dislocation of vertebrae
A 25 year old patient was admitted to the emergency department with suspected spinal cord injury[1]. On questioning she gave … Read More »
A Case of Epidural Hematoma
Case Scenario: A 15 year old[1] boy was hit on the temple[2a][2b] with a baseball and he became unconscious[3]. After … Read More »
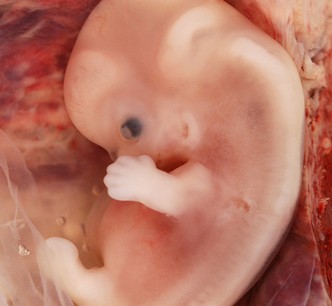
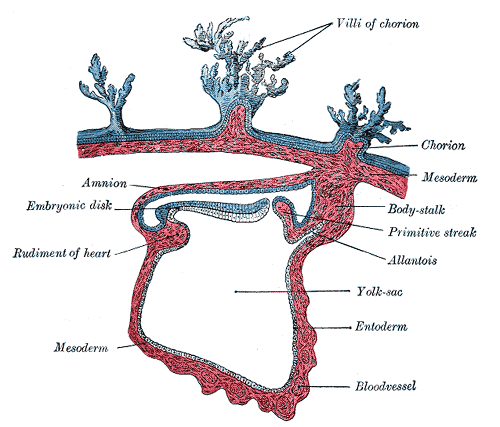
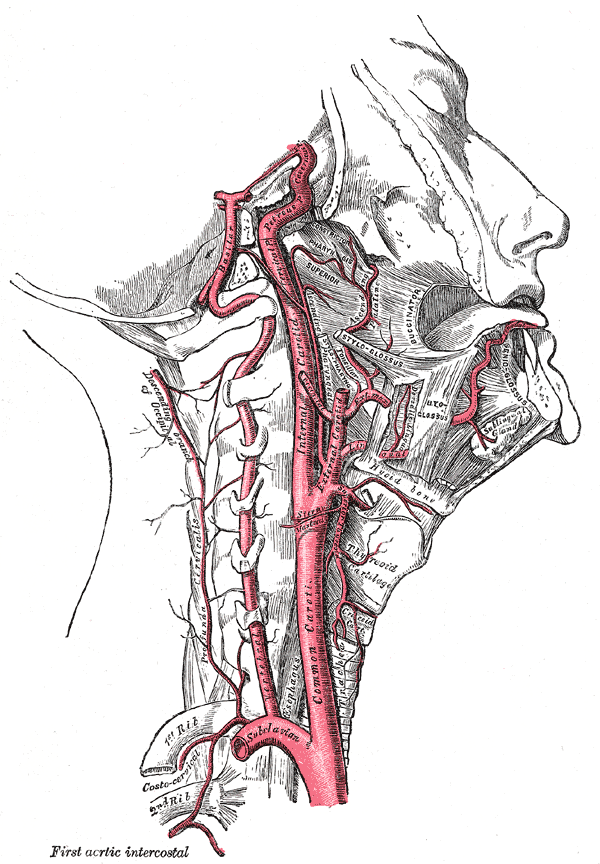
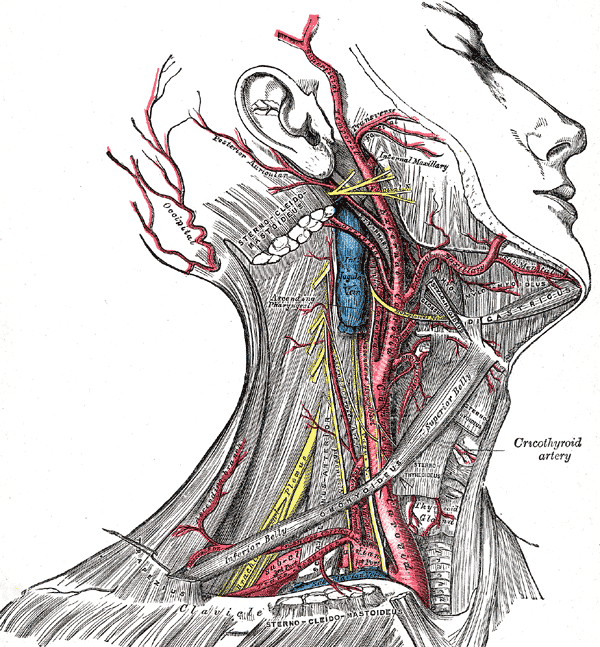
Development of Urogenital System
THE URINARY SYSTEM THE KIDNEYS, which excrete urine THE URETERS, which convey urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder … Read More »
Large Intestine
1) The primary function of the large intestine is the reabsorption of water and inorganic salts. The only secretion of … Read More »
Small Intestine
The small intestine is divided into a. duodenum b. jejunum c. ileum. The duodenum 1) The duodenum is the first … Read More »
Appendix
Points of Identification: 1) Large accumulations of lymphoid tissue in the lamina propria and submucosa. 2) Intestinal villi are usually … Read More »
Large Intestine
Unique Features: 1) Teniae coli – three bands of longitudinal smooth muscle in its muscularis 2) Haustrations – pocket like … Read More »
Small Intestine
Duodenum Points of Identification: The submucosa contains an abundant number of Brunner’s glands. Jejunum Points of Identification: Jejunum is identified … Read More »
Stomach
Points of Identification: 1) Mucosa is thrown into longitudinal folds called rugae. 2) Simple tall columnar epithelium 3) Lamina propria … Read More »
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself