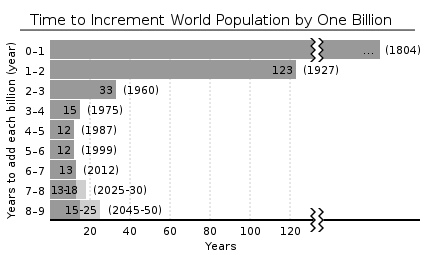
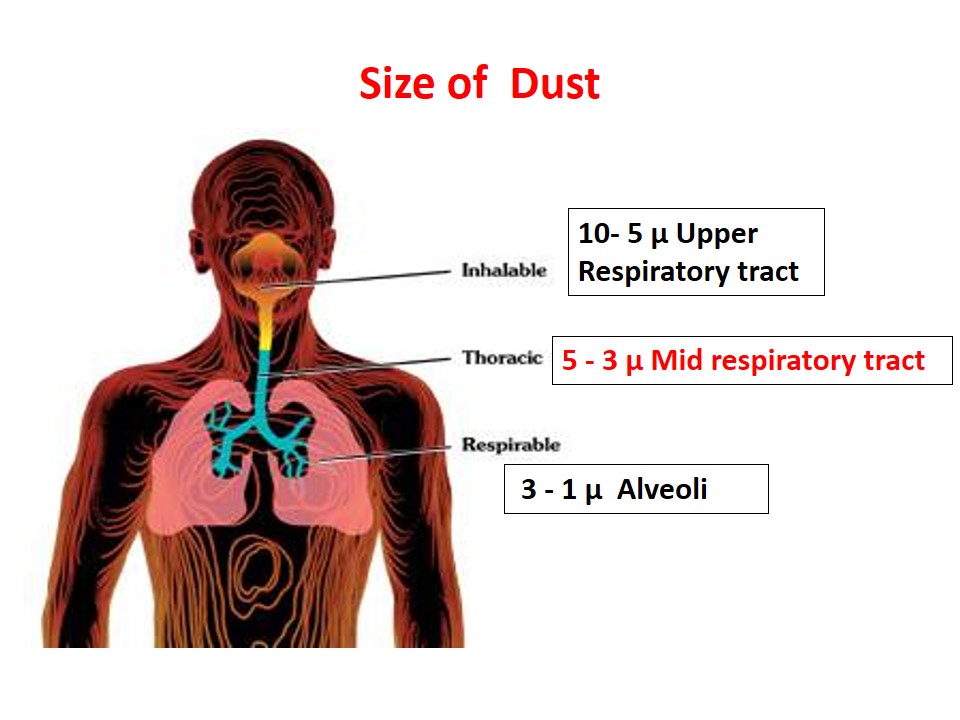
The word “research” has originated from the French word “recherche” which means to travel through or survey. Research may be defined as:
• Collection, analysis & interpretation of data so as to find solutions to a problem.
• Careful, systematic, patient study & investigation in some field of knowledge undertaken for the purpose of discovering or establishing facts or principles
• Process of investigation and examination of a subject from different points of view
• To search or investigate exhaustively
Research Types
1. Basic research:
Finding something new not known before necessary to generate new knowledge and technologies, e.g.
• How did the universe begin?
• How does a crystal melt?
2. Applied research:
Necessary to identify priority problems and to design and evaluate policies and programs for optimal health care and delivery, applying the findings of others e.g.
• What is the most efficient and effective vaccine against Influenza?
Research Types
Why do research?
• You prove your worth as a researcher
• Academia runs on Publish-or-perish
• Problem solving -Poverty, hunger, social and racial tension, natural disasters, health related issues, outbreaks
• Different communities may have unique problems
• Looking for fresh solutions
• An opportunity to connect with others
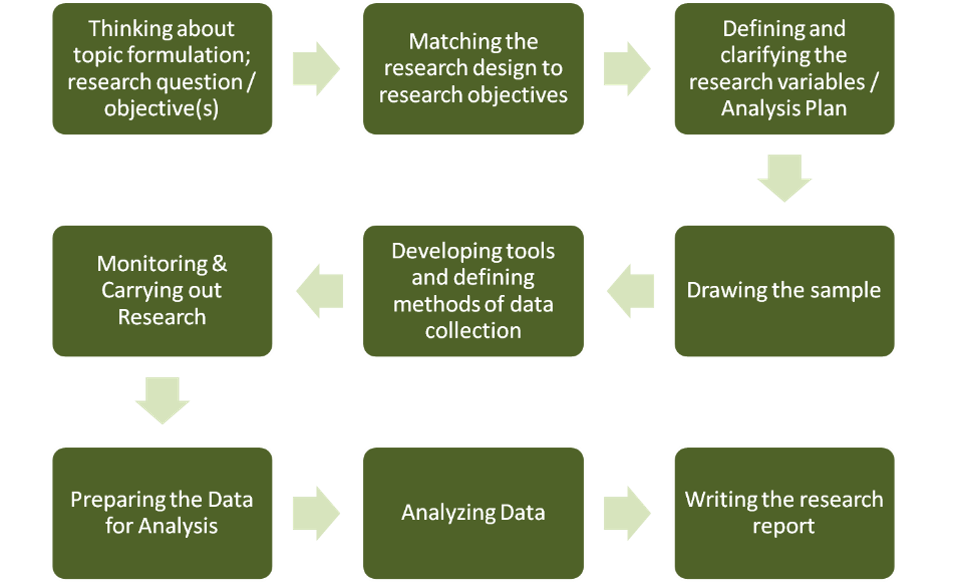
Steps in Designing & Conducting Research
Selecting a Research Topic
How to Choose a Research Topic
- Decide which subject interests you the most.
- Where do we get our ideas from?
- Advisor/ Committee members/ colleagues
- Reading literature/publications
- Library/internet
- Conferences/seminars
- Draw inspiration from anywhere you can
- Do not undermine your library
- Consult the librarian for help with tracking down research papers or writings, and read the abstracts.
- Consult your supervisor at each stage, and in case of difficulty.
KEEP A RESEARCH DIARY
Save Everything in your research diary. That crumpled note in the wastebasket might be just the insight you need. Write down your thoughts as you proceed, not just those of others. Key each bit of information, quotation, etc. to its source, cell # or website, author/title, p. #
Label and date all notes, in each draft.
Stealing from one source is plagiarism, while stealing from many is research: Jacob Kraicer, U Toronto
Ask the Right Questions
All data are equal unless you discriminate among these with questions. You cannot expect to find an answer without a question. Asking the right question is critical to doing good research. There is a need to refine the relevant questions and focus on the most important one(s). The question is the focus of research.
Example of a Bad Research Question
- Does globalization affect Pakistan?
- What causes cancer?
Example of a Good Research Question
- Is there a connection between international cosmetics prices and living standards in Pakistan?
- Has oral contraceptive use any link with Breast Cancer?
Literature Search Strategy on Internet
Summarize your topic in one or two sentences. Identify the unique ideas or concept associated with your topic. Choose appropriate keywords for each concept. Establish the relationship between each keyword and concept.
For General Info: www.google.com.pk/:
For Research Articles Only: http://scholar.google.com.pk/
For translating text from any language: http://translate.google.com.pk/
For Google Images: http://www.google.com.pk/imghp?hl=en&tab=ii
To get answers for your questions: www.ask.com/
Example of Pub Med Resource
PubMed is derived from two words, Publications, and Medical. It is a project of the National Institute of Health, National Library of Medicine. It is available on the internet, there are thousands of med journals on this list. It searches for you from about 21 million citations.
For more details of PubMed, you may visit.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/PubMed/
Free Medical Journals: websites
- http://www.lau.edu.lb/libraries/research-tools/free-journals-list.php.
- www.freemedicaljournals.com/
- http://highwire.stanford.edu/lists/freeart.dtl
- DOAJ(Directory of open access journals): http://www.doaj.org/
- MedIND (http://medind.nic.in/)
Medical Search Engines
- MedHunt (www.medhunt.com)
- MedNets (www.mednets.com)
- HealthAtoZ (www.healthatoz.com)
- DoctorNet (www.doctornet.com)
- MedConnect (www.medconnect.com)
- OMNI (www.omni.ac.uk)
- and many more…. Get a complete list by typing “medical search engines” in any good browser.
Some Good Medical Websites:
- www.medscape.com : an excellent site for medical professionals. Free registration, access to specialty and subspecialty pages, full-text articles and the latest medical news and events. Includes CME content.
- www.who.int : the website of the WHO. Provides the latest activity of the WHO, annual reports, bulletins,monographs, research funding reports and forms, global vital statistics and trends.
- www.cdc.gov : the official website of the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) in Atlanta, Georgia, USA. It provides global information on a variety of diseases, chiefly infectious diseases, epidemiology and disease control. The statistical software Epi Info is available for download from this site.
Structure of a printed scientific paper
- Title
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Materials & Methods
- Results
- Tables
- Figures
- Discussion
- Acknowledgements
- References
Read more about research methodology…
- The Basics of Research Methodology
- A Concept of Research Process
- Choosing Research Topics
- Review of Literature for Research Purpose
- Formulating a Research Question
- Formulation of Objectives in Research
- Variables in Research
- Developing a Questionnaire in Research
- Sample Selection and Sampling Techniques
- Data Collection in Research
- Introduction to Study Designs
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself