Examination of extraocular movements may be carried out in the steps given below:
- Introduction and permission
- Sit at the level of the patient
- Observe for:
- Abnormal head posture (head rotation, chin lift/depression, head tilt)
- Ptosis
- Lid retraction
- Proptosis
- Check gross visual acuity monocularly
- Give commands properly (keep eye on the target and follow without moving your head)
- Hirchburg with torch at one arm length
- Cover/uncover test (only if there is deviation, to see the primary and secondary deviation in paralytic squint and not to check phorias)
- Check versions (ask for presence of diplopia and painful movements) Check in all 9 diagnostic positions of the gaze. On the right left gaze check widening of palpebral aperture (Duanes). On up gaze, check fatiguabillity (Myasthenia). On down gaze, check lid lag (Myasthenia, aberrant 3rd nerve regeneration) and AV pattern. Check Cogan twitch sign from down to primary position.
- Check ductions only if version are abnormal (full ductions in concomitant and limited in inconcomitant squints)
- Check vergenc (convergence/divergence)
- NPC may also be seen to asses exact amplitude (with correction of refractive error and with a RAF rule or with a scale.
- Check saccades (vertical and horizontal)
- Check vestibulo-ocular reflex. Horizontal and vertical (dolls eye reflex)
- Thank the patient
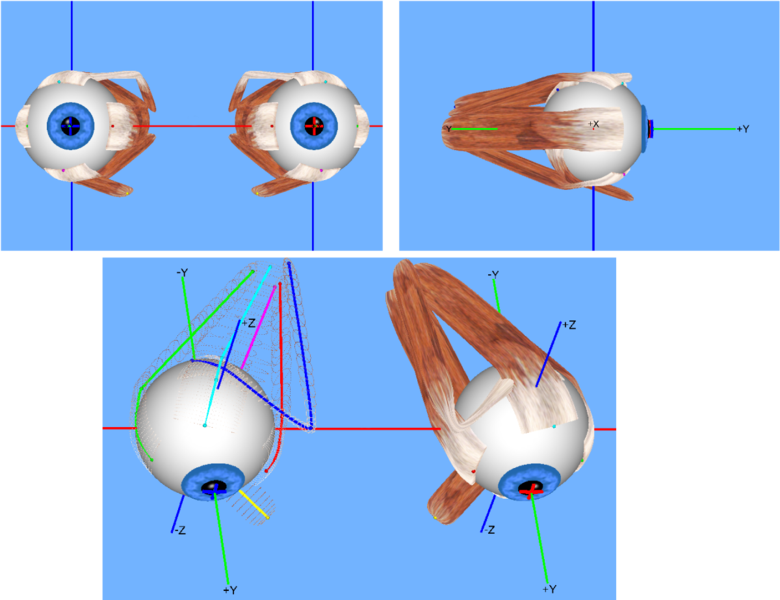
Image courtesy of Thomas.haslwanter
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself