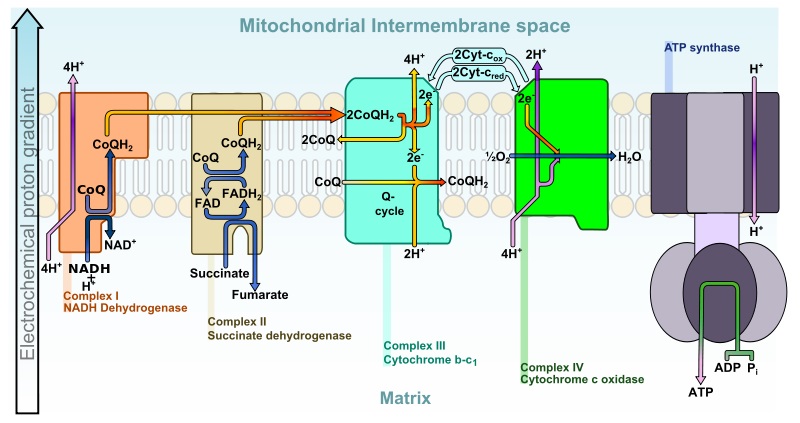
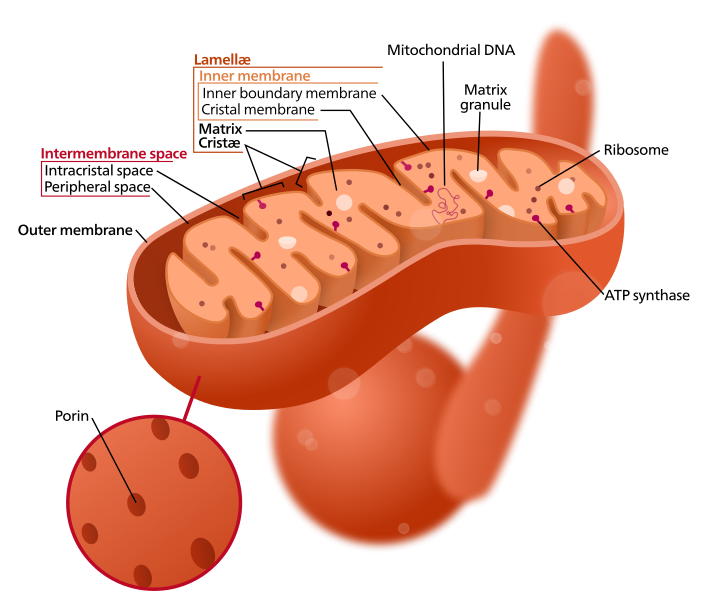
ATP is generated in the body by
- Oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria
- Anaerobic glycolytic pathway (liver)
ATP depletion by 5% -10% of normal affects:
a. Cell membrane Na pump
- Leading to increased c-AMP resulting in increased glycolysis
- Increased lactic acid & increased PO4 with decreased pH, results in decreased activity of enzymes.
b. Calcium pump fails resulting in Calcium influx.
c. Unfolded protein response.
Irreversible damage to mitochondria and lysosomal membrane results in cell necrosis.
Mitochondrial damage
Mitochondria is damaged by increased cytoplasmic calcium, free oxygen radicals, oxygen depletion and mitochondrial gene mutation. As a consequence, mitochondrial permeability transition pore stops oxidative phosphorylation. Squestered cytochrome c & caspases proteins enter cytoplasm & trigger apoptosis.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself