Insulin is a hormone secreted by beta cells within the pancreas. It is essential in regulating the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats in the body.
The hormone insulin is a peptide hormone consisting of 2 polypeptide chains.
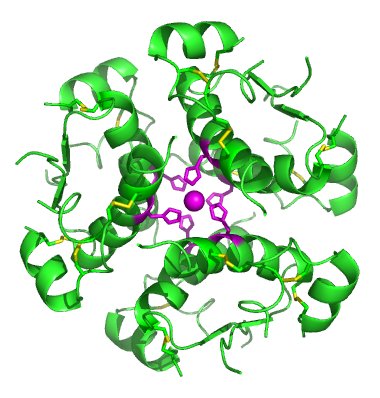 Image courtesy of Takometer at en.wikipedia
Image courtesy of Takometer at en.wikipedia
Primary structure (amino acid sequence) :
In the beta cells within islets of Langerhans of the pancreas, insulin is originally produced as a single molecule preproinsulin (composed of 110 amino acids).
Secondary structure:
After preproinsulin has passed through the endoplasmic reticulum, 24 amino acids (“the signal peptide”) are removed by enzyme action from one end of the chain, leaving another form Pro-insulin, which folds and bonds to give the molecule much of the final structure
Tertiary structure:
It is composed of two peptide chains referred to as the A chain and B chain. A and B chains are linked together by two disulfide bonds, and an additional disulfide is formed within the A chain. In most species, the A chain consists of 21 amino acids and the B chain of 30 amino acids.
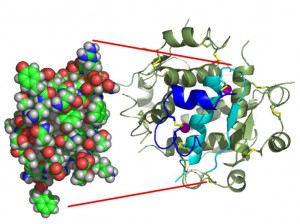 Image courtesy of Isaac Yonemoto at wikipedia.org
Image courtesy of Isaac Yonemoto at wikipedia.org
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself




