Vomiting
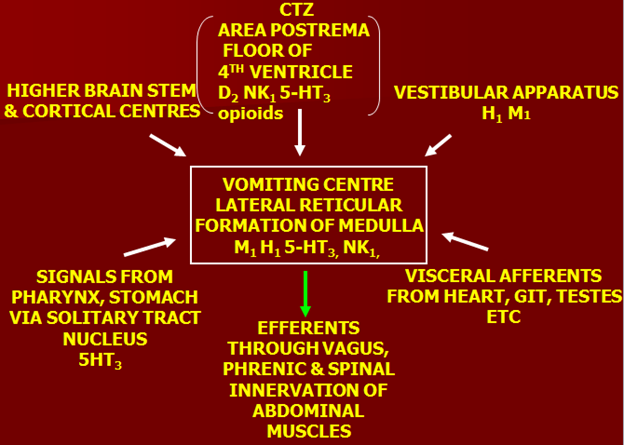
Vomiting center is located in the lateral reticular formation of medulla (M1, H1, 5HT3, NK1 and others are involved). Stimulus comes from different areas. Efferents move through vagus nerve.
Important afferents include:
- CTZ also known as area postrema located in the floor of 4th ventricle (D2, NK1 and 5HT3 are involved)
- Vestibular apparatus –motion sickness is associated (H1, M1, vestibular nerve)
- Higher brain stem and cortical centers
- Signals from pharynx, stomach via solitary tract nucleus, 5HT3
- Visceral afferents from heart, GIT, testes, etc.
Once stimulated, efferents move through the vagus, phrenic and spinal innervation of abdominal muscles.
Events in the process of emesis
- Nausea
- Decrease of gastric tone
- Decrease or absence of peristalsis
- Tone of upper small intestine increases
- Upper portion of stomach & lower esophageal sphincter relax
- Coordinated contraction of diaphragm and abdominal muscles leads to vomiting
Classification of anti- emetics
1. Subtituted benzamides
- Metoclopramide –commonly used having multiple effects, D2, 5HT3, 5HT4, other effects)
- Trimethobenzamide
2. Phenothiazines
- Prochlorperazine
- Chlorpromazine
- Thiethyl perazine
3. Butyrophenones
- Domperidone (mortilium)
- Droperidol
- Haloperidol
4. Serotonin receptor blockers
- Ondansetron
- Granisetron
- Dolasetron
- Palonosetron -40 hrs, highest affinity for 5HT3 receptors
5. Anti-histamines
- Dimenhydrinate
- Diphenhydramine
- Promethazine
- Cyclizine
- Meclizine –least cholinergic effects
6. Anti-muscranic agents
- Hyoscine (scopolamine) important for motion sickness
7. Marijuana derivatives / cannabinoids
- Dronabinol
- Nabilone
8. Neurokinin receptor antagonist
- Aprepitant
- Fosaprepitant (rapidly converted into aprepitant, once given)
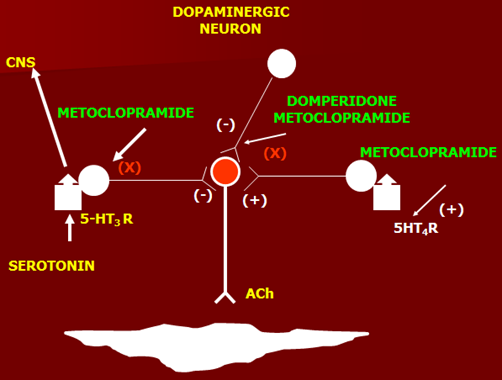
Metoclopramide
Mechanism of Action (central & peripheral)
A. Anti emetic effect
1. Central effect
Block D2 receptors in CTZ, main action at CNS
Also block 5HT3 receptors in vomiting center and CTZ, weaker action (afferent vagus nerve signals blocked)
2. Peripheral effect
Antiemetic effect by blocking 5HT3, blocking affects of vagus nerve going to CTZ
B. Prokinetic effect
5HT4 agonist effect in periphery
Enterochromaffin cells of GIT secrete 5HT in response to chemical and mechanical stimuli, serotonin has two effects:
- Stimulate 5HT receptors, vagus and spinal nerves stimulate
- Nor adrenergic and non cholinergic effect, inhibit acetylcholine release
Increasing inhibitory effect decreases acetylcholine while decreasing inhibitory effect increases acetylcholine, which is the prokinetic effect.
5HT4 in myenteric plexus releases acetylcholine, increasing gastric emptying.
Clinical Uses
1. Anti emetic effect
2. Gastro esophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Used because of prokinetic effect, given 30 minutes before meal. Also used adjunct to proton pump inhibitors and H2 blockers.
3. Long standing DM
Used in long standing diabetes mellitus, where diabetic gastroparesis occurs (delayed stomach emptying)
4. Post op conditions
Vagotomy, enterotomy. Decreased gastric emptying
5. Delayed type chemotherapy
Used in combination in delayed type chemotherapy induced nausea, vomiting along with other drugs
6. Post partum lactation
Since D2 blocker, increases post partum lactation
7. Non peptic non ulcer dysphagia
Also used effectively in non peptic non ulcer dysphagia
8. Hiccups
Uses in persistent type of hiccups
Adverse effects
As crosses blood brain barrier:
- Somnolence
- Nervousness
- Extra pyramidal symptoms -tremors
- Galactorrhea & ammenorrhea
Domperidone
Market name is Mortilium
Mechanism of Action
Having both central and peripheral effects, only D2 blocking effects in CTZ and produces anti-emetic effects.
In periphery block D2 receptors like metoclopramide. Disinhibit dopaminergic nerves, producing weak prokinetic effect.
As only D2 blockers, have no 5HT4 effects.
Comparison with metocloperamide
| Domeperidone | Metoclopramide |
| Butyrophenone | Substituted Benzamide |
| Does not cross BBB | Cross BBB |
| Only D2 blocking effect | D2, 5HT3, 5HT4 |
| Weak prokinetic | Stronger prokinetic |
| No sedative, CNS effects | Produce CNS symptoms |
| No EPS | EPS |
| Only act CTZ | Has effects on vomiting center (5HT3) |
Uses -same
Cannabinoids
Block CB1 receptor in and around vomiting center. Use is decreasing because of better options.
Also increase appetite
Previously used in cancer chemotherapy induced vomiting.
Currently only used when other agents fail.
Adverse effects
- Euphoria,
- Dysphoria,
- Ataxia,
- Drowsiness,
- Dry mouth,
- Appetite stimulation
- Withdrawal symptoms when discontinued.
5HT3 Antagonists
Mechanism of Action (central & peripheral)
Dual effects.
- CNS –block 5HT3 receptors in CTZ and vomiting center
- Periphery –block 5HT3 receptors blocking extrinsic stimuli
Serotonin is released from enterochromaffin like cells producing emetic effects
Uses
5HT3 blockers are primary agents in prevention of cancer chemotherapy induced nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, given 30 minutes before chemotherapy.
Slow I/V over 15 minutes time.
- In acute phase single drug,
- For delayed used in combination with:
- Drugs like steroids (dexamethasone)
- Neurokinin 1 receptor blockers
- 5HT3 receptor blockers
- Post radiation nausea, vomiting
- Hyper emesis of pregnancy (in 1st trimester no anti emetic is used)
- Blocks emesis by vagal stimulation
- Post op vomiting
Adverse effects
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- QT prolongation –Dolasetron has highest effect, not given with other drugs with QT prolongation.
NK1 antagonist
Aprepitant –oral preparation, crosses BBB
Fosaprepitant –I/V rapidly excreted
Used in combination for preventing delayed type vomiting in cancer chemotherapy.
Extensively metabolized by liver.
CYPA4 enzyme inhibitory effects. Important drug interactions as vincristine, vinblastine are also metabolized by CYPA4, thus dose correction is required.
Adverse effects
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- diarrhea
Steroids and Benzodiazepines
Benzodiazepines have direct anti-emetic effect used in anticipatory vomiting.
Effects include antianxiety, amnesic and sedative effects.
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself