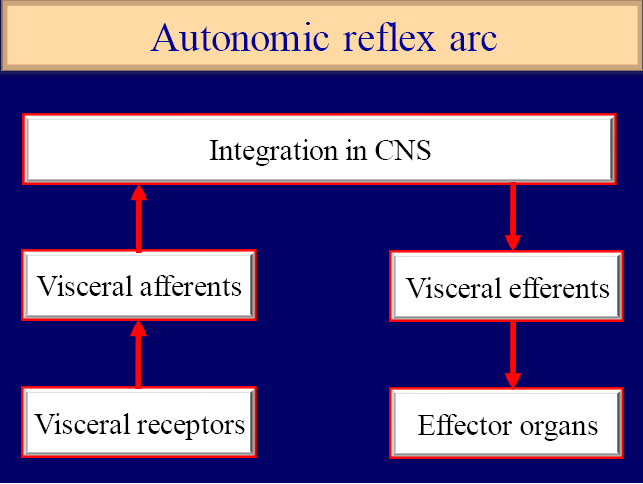
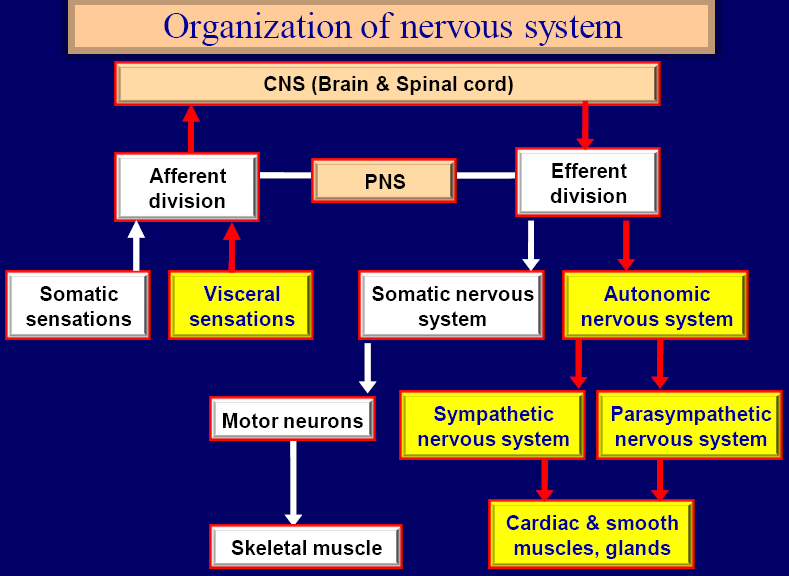
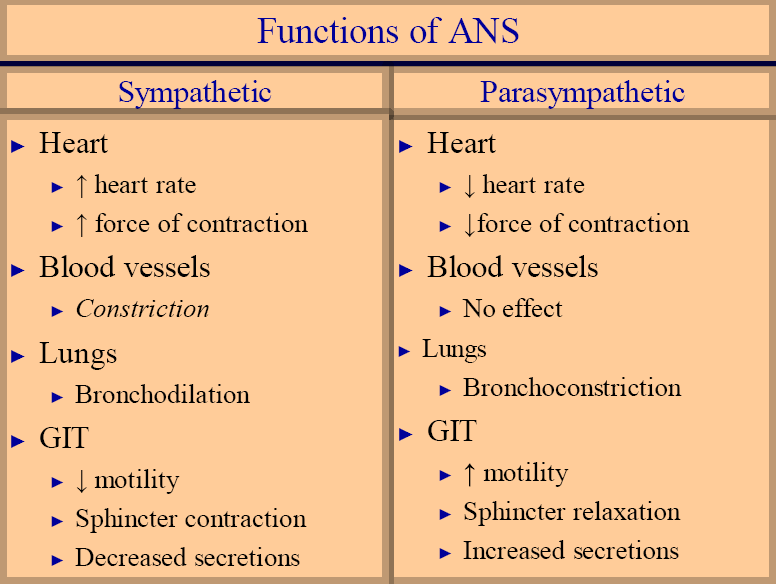
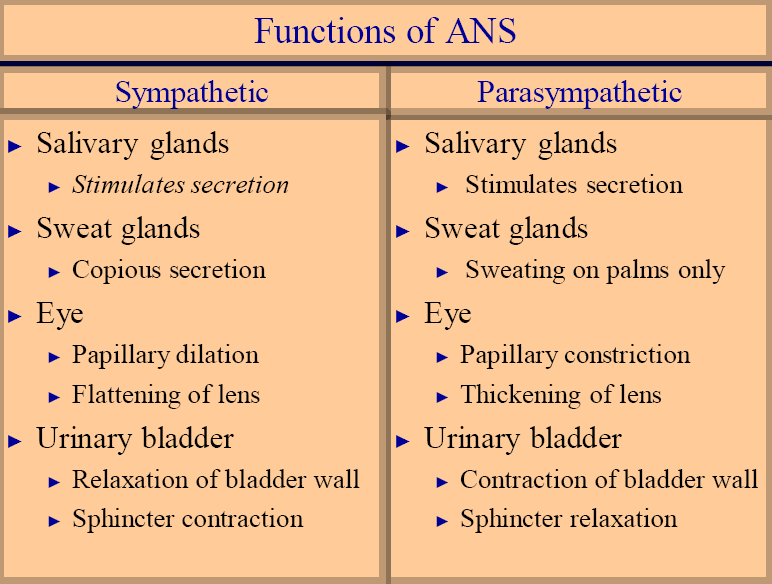
Part of nervous system that controls visceral functions including:
- Cardiac muscle,
- smooth muscle (blood vessels, GIT, urinary bladder etc)
- glands (secretions)
This system is not under voluntary control
Sympathetic division
►Thoracolumbar (T1to L2)
Parasympathetic division
►Craniosacral (III, VII, IX, X cranial nerves & S1to S4)
Dual supply
►All the viscera supplied by both the divisions of ANS
►Sympathovagal balance determines the ultimate function of the viscera
In autonomic nervous system:
►Two neuron chain from CNS to effector organ
►Pre and postganglionic neurons
Somatic nervous system
►Single neuron connects CNS with effector organ
Ganglion
►Cluster of neurons outside CNS
Autonomic ganglion
►Site of synapse between autonomic pre & post ganglionic fibers
►Paravertebral ganglionic chain
►Prevertebral (collateral) ganglia
Cell body of preganlionic neuron
►Lies in CNS
►Spinal cord (sympathetic division)
►Brain and spinal cord (parasympathetic division)
Cell body of postganglionic neuron
►Lies in autonomic ganglia
Sympathetic nervous system
►Short preganlionic fibers
►Long postganglionic fibers
Parasympathetic nervous system
►Long preganlionic fibers
►Short postganglionic fibers
Neurotransmitter released:
Cholinergic fibers
►Fibers releasing acetylcholine
Adrenergic fibers
►Fibers releasing noradrenalin
►All preganlionic fibers are cholinergic
►All postganglionic parasympathetic fibers are cholinergic
►Almost all postganglionic sympathetic fibers are adrenergic
►postganglionic sympathetic fibers to sweat glands and piloerector muscles are cholinergic
Receptors
►Nicotinic receptors -in autonomic ganglia
►Muscarinic receptors -in effector organs stimulated by postganglionic cholinergic fibers
►Adrenergic receptors -in effector organs stimulated by postganglionic adrenergic fibers
►α adrenergic receptors (α1 and α2)
►βadrenergic receptors (β1 and β2)
Functions of Autonomic Nervous System
Sympathetic and parasympathetic components of ANS function to maintain homeostasis at subconscious level -maintain stable internal environment
Sympathetic nervous system
►Prepares and mobilizes the body in emergency (fright, fear, pain, rage etc)
►Fight or flight reaction
Parasympathetic nervous system
►Conserves and stores energy -puts the body in cool and calm state
In Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
Mass discharge of sympathetic system
►Simultaneous discharge of all portions of sympathetic nervous system as a unit
►Due to activation of hypothalamus as a result of fright, fear or pain
►Also called alarm or stress response of the body
►Prepares the body for ‘emergency’
►Mass discharge of sympathetic system
►Increased BP
►Increased blood flow to active muscles
►Less blood flow to skin and GIT
►Increased rate of cellular metabolism
►Increased glycogenolysis and lipolysis
►Increased muscle strength
►Increased mental activity
►Papillary dilation
►Increased respiratory rate
Sympathetic and parasympathetic tone
►Basal rate of discharge
►Allows single division to adjust stimulation level of an organ
►Sympathetic tone to blood vessels
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself