Types:
Ø ABO system
Ø Rh System
Ø ABO system
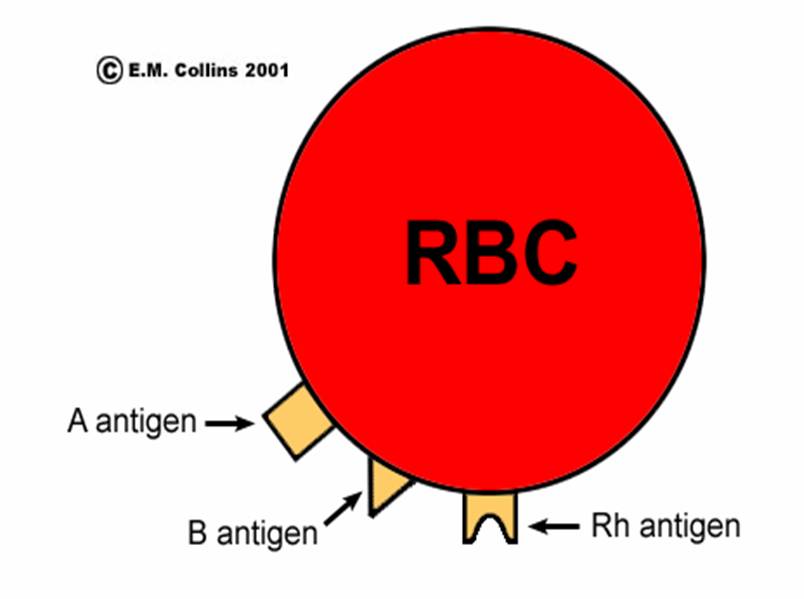
Ø Based upon A and B antigens (agglutinogens) present on cell membrane of RBCs
Ø Agglutinins are antibodies against A and B antigens present in plasma
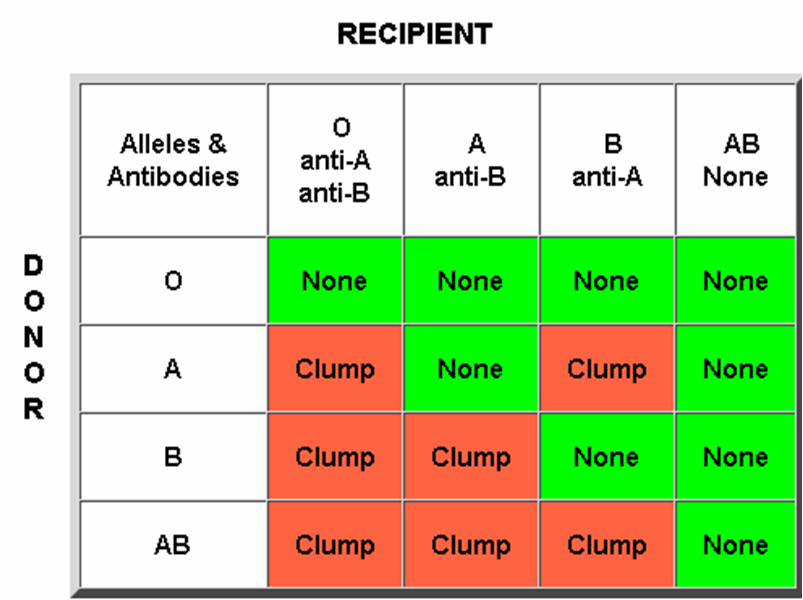
Ø Land steiner law – If an agglutinogen is present then its respective agglutinin will be absent
Ø Titer of agglutinins at various ages
► At birth zero
► Start producing at 2-8 months of life
► Maximum by age 8-10 years
► Start decreasing thereafter
Ø Prevalence of various blood types (ABO)
► O 47%
► A 41%
► B 9%
► AB 3%
Ø Rh system
► Based upon ‘D’ antigen (Rh factor)
► Rh positive means presence of D antigen
► Rh negative means absence of D antigen
► Anti Rh agglutinins are not present in plasma normally
► Upon first transfusion of Rh +ve blood to Rh –ve person, anti Rh agglutinins are formed and cause sensitization
ERYTHROBLASTOSIS FETALIS
Ø A haemolysing disorder of fetus and newborn due to blood group incompatibility with mother
Ø Rh incompatibility
Ø ABO incompatibility
Rh incompatibility
Ø Father Rh positive, mother Rh negative ® baby Rh positive
Ø Haemolysis leads to blast forms of RBCs in fetal blood hence the name erythroblastosis fetalis
Ø Sensitization of mother during first delivery
Ø First baby spared
Ø Increased incidence of disease with subsequent pregnancies with Rh +ve fetus
Ø Effect of anti Rh antibody on fetal RBCs
Ø Agglutination of fetal RBCs
Ø Haemolysis of agglutinated RBCs and release of bilirubin
Ø Bilirubin
Ø Jaundice
Ø Kernicterus
Ø Clinical picture
Ø Jaundice, anemia
Ø Enlargement of liver and spleen
Ø Presence in blood of nucleated blastic forms of RBCs
Ø Mental impairment
Ø Prevention
Ø Inj of anti Rh antibody to mother during postpartum period (within 48 hours)
Ø Treatment
Ø Replacement of neonate’s blood with Rh negative blood
TRANSFUSION REACTIONS
Ø Transfusing same blood type
► Pyrogenic reactions
► Allergic reactions
► Circulatory overload (anemic patients, infants)
► Tetany (citrate intoxication; massive transfusions)
► Hyperkalaemia (massive transfusions of stored blood)
► Iron overload (repeated transfusions)
► Thrombophlebitis
► Infections (AIDS, hepatitis B,C)
► Bleeding tendency (dilutional thrombocytopenia with stored blood)
Ø Transfusing mismatched blood
► Haemolytic reactions
Ø Immediate
Ø With ABO incompatibility
Ø Without agglutination
Ø Role of IgM antibodies (haemolysins)
Ø Activation of compliment system
Ø Delayed
Ø With Rh incompatibility
Ø Haemolysis followed by agglutination
► Haemolytic reactions
Ø Clinical Features
Ø Rigors, fever, Pain in loin, facial flushing
Ø Jaundice
Ø Hypotension
Ø Circulatory chock
Ø Haemoglobinaemia, heamoglobinurea
Ø Acute renal shut down, oligurea
Ø Death
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself

Me English no well, but had to say me like what you say. Thank you from Panama.
The layout for your blog is a bit off in Galeon. All The Same I like your site. I may have to install a “normal” browser just to enjoy it. 🙂