Temporal Region
TEMPORAL & INFRATEMPORAL FOSSA
n Situated on the side of head
n Bounded above by superior temporal line & below by zygomatic arch
n Infratemporal fossa is situated beneath base of skull, between pharynx & ramus of mandible
n Both communicate deep to zyg arch
CONTENTS OF TEMPORAL FOSSA
q Temporalis muscle and its covering fascia
q Deep temporal nerves and vessels
q Auriculotemporal nerve
q Superficial temporal artery
TEMPORALIS
n Origin: from bony floor of temporal fossa and deep surface of temp fascia
n Insertion: converge to tendon,which passes deep to zyg arch n inserted on coronoid process n ant border of ramus
n N.S: deep temporal n (br of ant div of mandibular div of trigem N)
n Action: ant n sup fibers elevate mandible. Post fibers retract mandible
TEMPORAL FASCIA
n Covers temporal muscle above zyg arch
n Attached above to sup temporal line & below to upper border of zygomatic
n Its deep surface gives origin to temporal muscles
DEEP TEMPORAL NERVES
n Two in no.
n Arise from anterior div of mandibular nerve
n Emerge from upper border of lateral pterygoid muscle and enter deep surface of temporal muscle
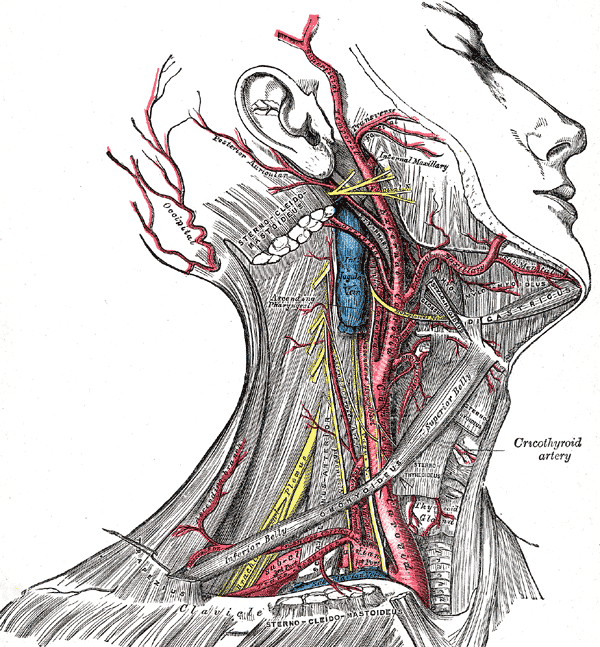
AURICULOTEMPORAL NERVE
n Branch of posterior division of mandibular nerve
n Emerges from upper border of parotid gland behind TMJ
n Crosses root of zygoma, behind superficial temporal artery and in front of the auricle
n Dictributed to skin of auricle, ext auditory meatus, scalp over temporal region
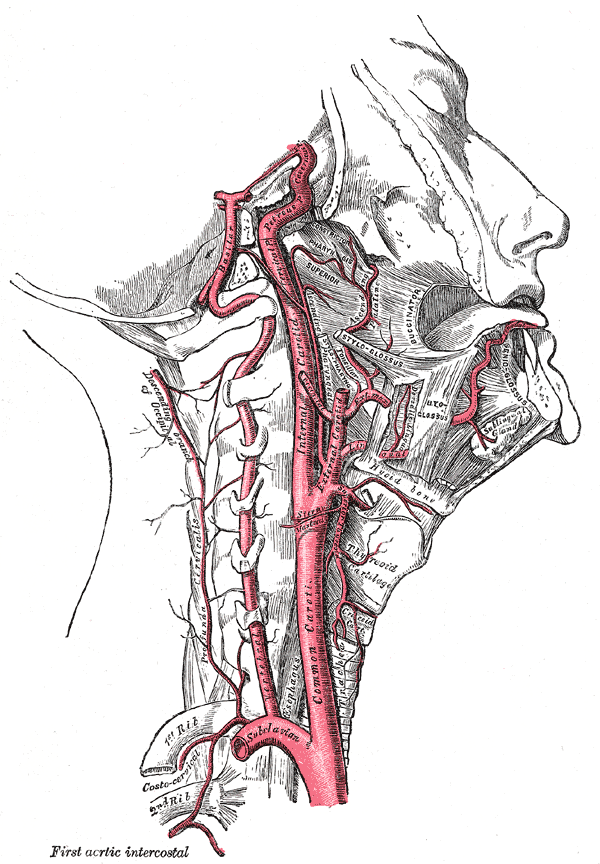
SUPERFICIAL TEMPORAL ARTERY
n A terminal branch of ECA
n Emerges from upper border of parotid, behind TMJ
n Crosses root of zygoma, in front of auriculotemporal N & auricle
n Here its pulsations felt
n Ascends onto the scalp and divide into anterior and posterior divisions
Infratemporal Region
q It is an irregular space, deep and inferior to the
zygomatic arch, deep to ramus of mandible, and posterior to the maxilla.
CONTENTS
q Lateral and medial pterygoid, tendon of
temporalis muscles
q Maxillary artery
q Pterygoid venous plexus
q Mandibular nerve and chorda tympani
nerve
q Otic ganglion
LATERAL PTERYGOID
n Origin: upper head arises from infratemporal surface of greater wing of sphenoid; lower head arises from the lateral surface lateral pterygoid
n Insertion: two heads converge as they pass backward and are inserted into front of neck of mandible and articular disc of TMJ
n N.S.: Anterior division of mandibular division of trigeminal nerve
n Action: pulls neck of mandible forward with articular disc during process of opening of mouth; acting with medial pterygoid of same side, it pulls neck of mandible forward with articular disc, causing jaw to rotate around opposite condyle, as in chewing
MANDIBULAR DIVISION OF TRIGEMINAL NERVE
n Sensory & motor roots of mandibular nerve emerge from skull through foramen ovale
n Immediately below the foramen,small motor root of mandibular nerve unites with large sensory root
n Mandibular nerve now descends and divides into a small anterior and a large posterior division
n Branches from main trunk:
q Meningeal branch
q Nerve to medial pterygoid– 2 bràotic ganglionàto tensor tympani n tensor veli palatini
q Branches from anterior division:
q masseteric & 2 deep temporal n and nerve to lateral pterygoid and one sensory (buccal)
Branches from posterior division:
n Auriculotemporal N (sensory)
n Lingual N (sensory)
n Inferior alveolar N (motor)
OTIC GANGLION
n Small parasympathetic ganglion – functionally assoc with CN 9
n Situated just below foramen ovale n medial to mandibular nerve
n Adheres to nerve to medial pterygoid, but functionally completely separate
n Preganglionic parasympathetic fibers originate in inf salivary nucleus of CN9
n Leave CN 9 by its tympanic br n then pass via tympanic plexus n lesser petrosal nerve to otic ganglion. Post ganglionic join auriculotemporal N. conveyed by this neve to parotid
Chorda tympani
n Branch of facial nerve in temporal nerve
n Enters infratemporal fossa thru petrotympanic fissure and runs downward and forward to join lingual nerve
n Carries preganglionic parasym fibers to submandibular & sublingual glands
n Also carries taste fibers from ant 2/3 of tongue n floor of mouth; cell bodies of taste fibers in sensory geniculate ganglion of facial Nerve n end by synapsing with cells of nucleus solitarius in Pons.
Maxillary artery
n Larger terminal br of ECA in parotid gland
n Arises behind neck of mandible.
n Leaves infratemporal fossa ,entering pterygopalatine fossa
n Branches in infratemporal fossa:
q Inferior alveolar artery
q Middle meningeal A– enters thru foramen spinosum– to meninges
q Small br– lining of ext auditory meatus, tympanic membr
q Muscular br– muscles of mastication
Branches of 1st (mandibular) part
q Deep auricular artery
q Anterior tympanic artery
q Middle meningeal artery
q Accessory meningeal artery
q Inferior alveolar artery
Branches of 2nd (Pterygoid) part
q Deep temporal artery
q Pterygoid artery
q Masseteric artery
q Buccal artery
Branches of 3rd (Pterygopalatine) part
q Posterior superior alveolar artery
q Infraorbital artery
q Descending palatine artery
q Artery of pterygoid canal
q Pharyngeal artery
q Sphenopalatine artery
Pterygoid venous plexus
n Receives veins, corresponding to branches of maxillary artery
n Its posterior end drained by maxillary vein.
n Communicates with facial vein thru deep facial vein
Maxillary vein
n Drains post end of pterygoid venous plexus
n Runs backward with max artery, on medial side of neck of mandible
n Joins superficial temporal vein within parotid to form retromandibular vein
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself

A very helpful site,good job…