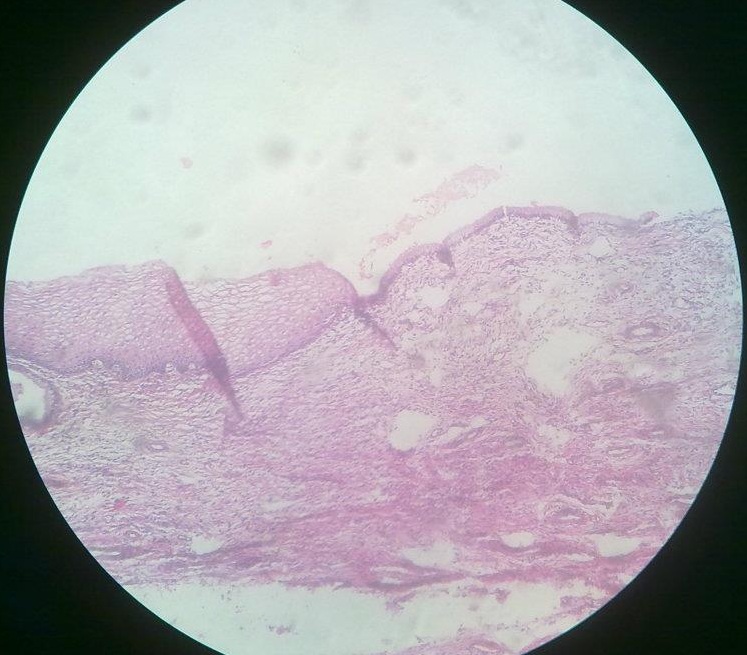
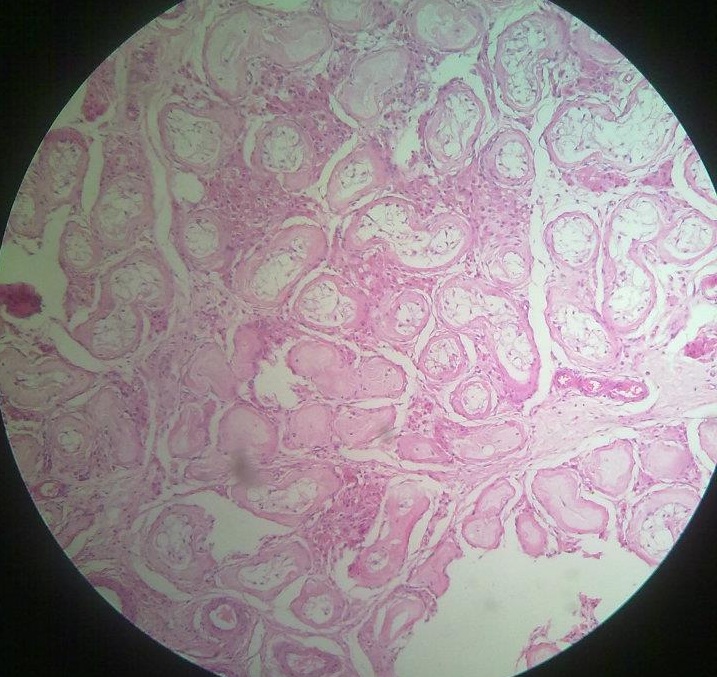
Amyloidosis is a medical condition resulting from aggregation of extracellularly deposited abnormal proteins called amyloid fibrils that cause damage to … Read More »
Intracellular Accumulations
Intracellular accumulations include the following: 1. Water (hydropic change) 2. Fatty change: fats may accumulate in the liver as fatty … Read More »
Cellular Aging
Cellular death due to aging is caused by accumulation of injurious events and genetically controlled developmental programme. Mechanism of Aging … Read More »
Types of Necrosis
Necrosis may be coagulative, liquifactive, caseous, fat necrosis, gummatous necrosis or fibrinoid necrosis. Coagulative Necrosis Coagulative necrosis is the commonest … Read More »
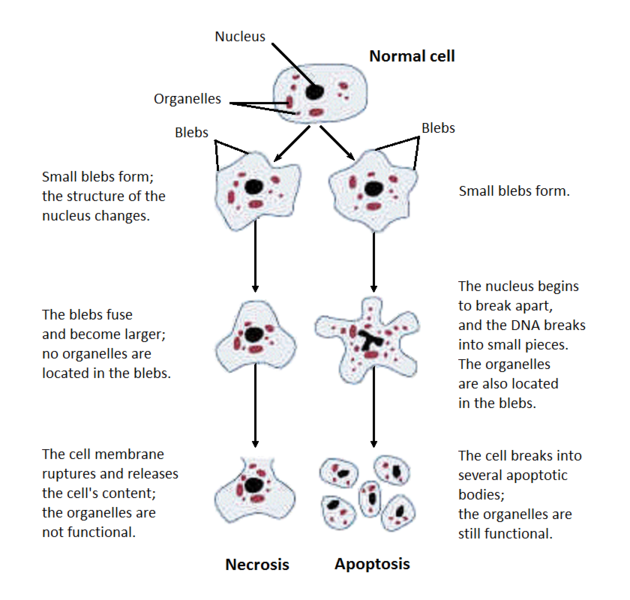
Necrosis
Necrosis is the denaturation of proteins & enzymatic digestion. It is irreversible local cell death and cellular dissolution in living … Read More »
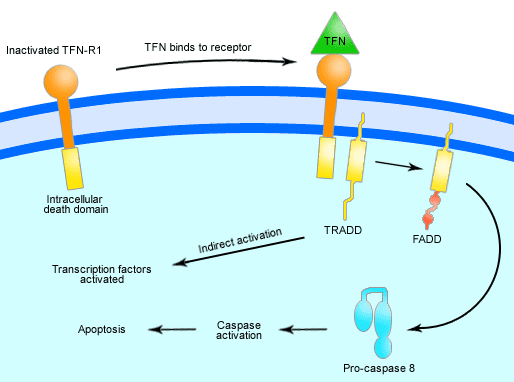
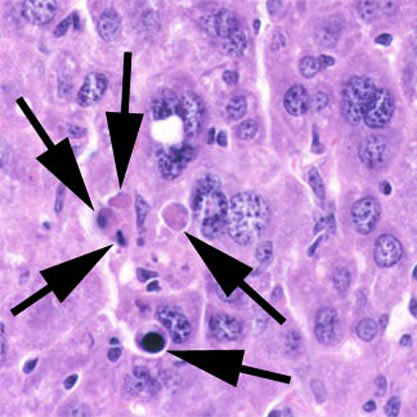
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is the programmed cell death or suicide in which the cell membrane remains intact. No inflammatory reaction takes place. … Read More »
Cell Death
Cell death is the ultimate result of irreversible injury. It may be: a. Physiological –e.g. during embryogenesis b. Therapeutic –e.g. … Read More »
Cell Injury
Stress beyond the adaptive limit of the cell results in cell injury. Cell injury may be: a. Reversible injury: stimulus … Read More »
Cervical Metaplasia
Uterine cervix protrudes in upper vagina and contains endocervical canal, linking uterine cavity to vagina. Endocervical canal is lined by … Read More »
Atrophy of Testes
Testes may undergo atrophy, i.e. shrinkage in size of cells by loss of cell substance. Causes: Progressive atherosclerotic narrowing of … Read More »
 howMed Know Yourself
howMed Know Yourself